
The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws and/or nails.

Toes are the digits of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being digitigrade. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being plantigrade; unguligrade animals are those that walk on hooves at the tips of their toes.
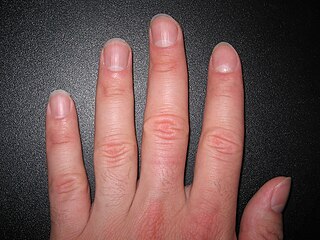
A nail is a protective plate characteristically found at the tip of the digits of all primates, corresponding to the claws in other tetrapod animals. Fingernails and toenails are made of a tough rigid protein called alpha-keratin, a polymer also found in the claws, hooves, and horns of vertebrates.

A nail disease or onychosis is a disease or deformity of the nail. Although the nail is a structure produced by the skin and is a skin appendage, nail diseases have a distinct classification as they have their own signs and symptoms which may relate to other medical conditions. Some nail conditions that show signs of infection or inflammation may require medical assistance.

A hematoma, also spelled haematoma, or blood suffusion is a localized bleeding outside of blood vessels, due to either disease or trauma including injury or surgery and may involve blood continuing to seep from broken capillaries. A hematoma is benign and is initially in liquid form spread among the tissues including in sacs between tissues where it may coagulate and solidify before blood is reabsorbed into blood vessels. An ecchymosis is a hematoma of the skin larger than 10 mm.

Pointe technique is part of classical ballet involving a technique that concerns pointe work, in which a ballet dancer supports all body weight on the tips of fully extended feet when wearing pointe shoes. A dancer is said to be en pointe when the body is supported in this manner, and a fully extended vertical foot is said to be en pointe when touching the floor, even when not bearing weight.

Athlete's foot, known medically as tinea pedis, is a common skin infection of the feet caused by a fungus. Signs and symptoms often include itching, scaling, cracking and redness. In rare cases the skin may blister. Athlete's foot fungus may infect any part of the foot, but most often grows between the toes. The next most common area is the bottom of the foot. The same fungus may also affect the nails or the hands. It is a member of the group of diseases known as tinea.

Diseases of the foot generally are not limited, that is they are related to or manifest elsewhere in the body. However, the foot is often the first place some of these diseases or a sign or symptom of others appear. This is because of the foot's distance from the central circulation, the heart and its constant exposure to pressures from the ground and the weight of the body.

An ingrown nail, also known as onychocryptosis is a common form of nail disease. It is an often painful condition in which the nail grows so that it cuts into one or both sides of the paronychium or nail bed. While ingrown nails can occur in the nails of both the hands and the feet, they occur most commonly with the toenails.

Paronychia is an inflammation of the skin around the nail, often due to bacteria or fungi.

Onychomycosis, also known as tinea unguium, is a fungal infection of the nail. Symptoms may include white or yellow nail discoloration, thickening of the nail, and separation of the nail from the nail bed. Fingernails may be affected, but it is more common for toenails. Complications may include cellulitis of the lower leg. A number of different types of fungus can cause onychomycosis, including dermatophytes and Fusarium. Risk factors include athlete's foot, other nail diseases, exposure to someone with the condition, peripheral vascular disease, and poor immune function. The diagnosis is generally suspected based on the appearance and confirmed by laboratory testing.
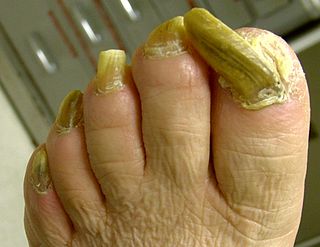
Onychogryphosis is a hypertrophy that may produce nails resembling claws or a ram's horn.

Subungual exostosis is a type of non-cancerous bone tumor of the chondrogenic type, and consists of bone and cartilage. It usually projects from the upper surface of the big toe underlying the nailbed, giving rise to a painful swelling that destroys the nail. Subsequent ulceration and infection may occur.
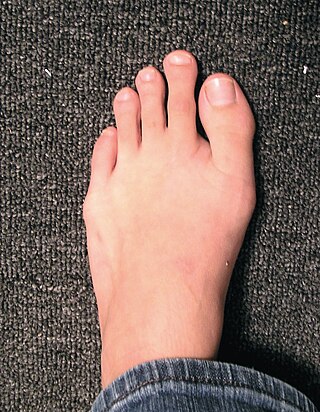
Morton's toe is the condition of having a first metatarsal bone that is shorter than the second metatarsal. It is a type of brachymetatarsia. This condition is the result of a premature closing of the first metatarsal's growth plate, resulting in a short big toe, giving the second toe the appearance of being long compared to the first toe.

Barefoot running, also called "natural running", is the act of running without footwear. With the advent of modern footwear, running barefoot has become less common in most parts of the world but is still practiced in parts of Africa and Latin America. In some Western countries, barefoot running has grown in popularity due to perceived health benefits.
Malalignment of the nail plate, also known as congenital malalignment of the great toenails or congenital malalignment syndrome, is a congenital malalignment of the nail of the great toe, and is often misdiagnosed although it is a common condition. It most commonly affects the halluces. The nail might be discolored and develop infections. If the misaligned nail becomes embedded in the lateral nail fold it can cause pain, inflammation and erythema.

A corn or clavus is an often painful, cone-shaped, inwardly directed callus of dead skin that forms at a pressure point near a bone, or on a weight-bearing part of the body. When on the feet, corns can be so painful as to interfere with walking. The visible portion of the corn tends to be more or less round, but corns are defined by having a hard tapering root that is directed inward, and pressure on the corn pushes this root deeper into the flesh. Pressure corns usually occur on thin or glabrous skin surfaces, especially on the dorsal surface of toes or fingers, but corns triggered by an acute injury may occur on the thicker skin of the palms or bottom of the feet.

The Vibram FiveFingers are a type of minimalist shoe manufactured by Vibram, originally marketed as a more natural alternative for outdoor activities. The footwear is meant to replicate being barefoot and has thin, flexible soles that are contoured to the shape of the human foot, including visible individual sections for the toes. The company settled a lawsuit in 2014 alleging false health claims and set aside $3.75 million to pay refunds of up to $94 to anyone who had purchased the product since March 21, 2009.

The toe box is the section of footwear that surrounds the toes on closed-toe shoes. Toe boxes that are too tight can cause injuries and foot deformities, whereas wider toe boxes may be used to treat or prevent common foot conditions such as broken toes, bunions, and Morton's neuroma. Toe boxes come in a variety of shapes and styles of construction, some of which are a matter of fashion, and some of which are designed for specialized functions.

A broken toe is a type of bone fracture. Symptoms include pain when the toe is touched near the break point, or compressed along its length. There may be bruising, swelling, stiffness, or displacement of the broken bone ends from their normal position.
























