Related Research Articles
Bromoderma is a skin condition characterized by an eruption of papules and pustules on the skin. It is caused by hypersensitivity to bromides, such as those found in certain drugs. There is at least one reported case of bromoderma caused by excessive consumption of a soft drink containing brominated vegetable oil.
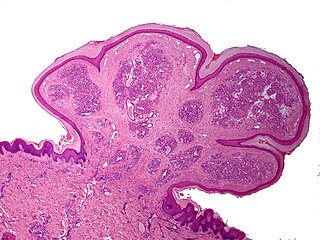
A pyogenic granuloma or lobular capillary hemangioma is a vascular tumor that occurs on both mucosa and skin, and appears as an overgrowth of tissue due to irritation, physical trauma, or hormonal factors. It is often found to involve the gums, skin, or nasal septum, and has also been found far from the head, such as in the thigh.

Granuloma annulare (GA) is a common, sometimes chronic skin condition which presents as reddish bumps on the skin arranged in a circle or ring. It can initially occur at any age, though two-thirds of patients are under 30 years old, and it is seen most often in children and young adults. Females are two times as likely to have it as males.
Atrophia Maculosa Varioliformis Cutis (AMVC) is an idiopathic noninflammatory macular atrophy subtype that affects young people. Clinically, it is distinguished by a variety of shaped, shallow, sharply demaracated depressions.

Angiofibroma (AGF) is a descriptive term for a wide range of benign skin or mucous membrane lesions in which individuals have:
- benign papules, i.e. pinhead-sized elevations that lack visible evidence of containing fluid;
- nodules, i.e. small firm lumps usually >0.1 cm in diameter; and/or
- tumors, i.e. masses often regarded as ~0.8 cm or larger.
Gianotti–Crosti syndrome, also known as infantile papular acrodermatitis, papular acrodermatitis of childhood, and papulovesicular acrolocated syndrome, is a reaction of the skin to a viral infection. Hepatitis B virus and Epstein–Barr virus are the most frequently reported pathogens. Other viruses implicated are hepatitis A virus, hepatitis C virus, cytomegalovirus, coxsackievirus, adenovirus, enterovirus, rotavirus, rubella virus, HIV, and parainfluenza virus.

Elejalde syndrome or neuroectodermal melanolysosomal disease is an extremely rare autosomal recessive syndrome consisting of moderate pigment dilution, profound central nervous system dysfunction, no immune defects, and hair with a metallic silvery sheen. The changes to hair and skin pigmentation are associated with altered melanosome trafficking.
Lupus erythematosus panniculitis presents with subcutaneous nodules that are commonly firm, sharply defined and nontender.
Anetoderma is a benign but uncommon disorder that causes localized areas of flaccid or herniated sac-like skin due to a focal reduction of dermal elastic tissue. Anetoderma is subclassified as primary anetoderma, secondary anetoderma, iatrogenic anetoderma of prematurity, congenital anetoderma, familial anetoderma, and drug-induced anetoderma.
Eccrine angiomatous hamartoma (EAH), first described by Lotzbeck in 1859, is a rare benign vascular hamartoma characterized histologically by a proliferation of eccrine and vascular components. EAH exists on a spectrum of cutaneous tumors that include eccrine nevus, mucinous eccrine nevus and EAH. Each diagnostic subtype is characterized by an increase in the number as well as size of mature eccrine glands or ducts, with EAH being distinguished by the added vascular component.

Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia usually presents with pink to red-brown, dome-shaped, dermal papules or nodules of the head or neck, especially about the ears and on the scalp.

Annular erythema of infancy(AEI) consists of self-limited eruptions of erythematous, annular to polycyclic patches and plaques. It is an idiopathic figurate erythema. Over several days, a single lesion disappears without leaving behind any scale or hyperpigmentation. Mostly affecting the trunk, face, and extremities, this rash has no symptoms. The diagnosis of AEI is made through a combination of histopathologic and clinical examinations. The disease first manifests in infancy, and if treatment is not received, the periodic eruptions usually stop after the first year of life.
Actinic granuloma (AG) was first described by O'Brien in 1975 as a rare granulomatous disease. Lesions appear on sun-exposed areas, usually on the face, neck, and scalp, with a slight preference for middle-aged women. They are typically asymptomatic, single or multiple, annular or polycyclic lesions measuring up to 6 cm in diameter, with slow centrifugal expansion, an erythematous elevated edge, and a hypopigmented, atrophic center.
Benign cephalic histiocytosis(BCH) is a non-Langerhan's histiocytosis that is uncommon and self-limiting, usually beginning towards the end of the first year of life. Gianotti et al. originally described it in 1971. Initially affecting the head and neck, this condition is characterized by several small eruptions of yellow to reddish-brow papules that heal on their own. Histological investigations have demonstrated that this disorder is associated with dermal proliferation of histiocytes, characterized by intracytoplasmic comma-shaped bodies, covered vesicles, and desmosome-like structure.
Generalized eruptive histiocytoma is a rare cutaneous condition characterized by widespread, erythematous, essentially symmetrical papules, particularly involving the trunk and proximal extremities.

Balloon cell nevus is a benign nevus. It appears like a melanocytic nevus.
Umbilical granuloma is the most common umbilical abnormality in newborn children or neonates, causing inflammation and drainage. It may appear in the first few weeks of newborn infants during the healing process of the umbilical cord due to an umbilical mass. It is the overgrowth of the umbilical tissue. It develops in about 1 out of 500 newborns. With appropriate treatment, it is expected to heal in 1~2 weeks.
Symmetrical drug-related intertriginous and flexural exanthema (SDRIFE), popularly known as baboon syndrome because of its resemblance to the distinctive red buttocks displayed by female baboons, is a systemic dermatitis characterized by well-demarcated patches of erythema distributed symmetrically on the buttocks. The cause of the syndrome may be drug-related: i.e., induced by systemic administration of hydroxyzine, penicillin, iodinated radio contrast media, and others.
Granuloma gluteale infantum is a cutaneous condition that appears in the anogenital region of infants as a complication of diaper dermatitis. According to some, no granulomas are found.
SACRAL syndrome is a congenital condition characterized by spinal dysraphism, anogenital, cutaneous, renal and urologic anomalies, associated with an angioma of lumbosacral localization.
References
- ↑ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- 1 2 Boralevi, F.; Léauté-Labrèze, C.; Lepreux, S.; Barbarot, S.; Mazereeuw-Hautier, J.; Eschard, C.; Taïeb, A. (April 2007). "Idiopathic facial aseptic granuloma: a multicentre prospective study of 30 cases". British Journal of Dermatology. 156 (4): 705–708. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2006.07741.x. PMID 17493068. S2CID 42050326.
- ↑ Orion, Camille; Sfecci, Alicia; Tisseau, Laurent; Darrieux, Laure; Safa, Gilles (July 19, 2016). "Idiopathic Facial Aseptic Granuloma in a 13-Year-Old Boy Dramatically Improved with Oral Doxycycline and Topical Metronidazole: Evidence for a Link with Childhood Rosacea". Case Reports in Dermatology. S. Karger AG. 8 (2): 197–201. doi:10.1159/000447624. ISSN 1662-6567. PMID 27920676.
- ↑ Baroni, Adone; Russo, Teresa; Faccenda, Franco; Piccolo, Vincenzo (September 28, 2012). "Idiopathic Facial Aseptic Granuloma in a Child: A Possible Expression of Childhood Rosacea". Pediatric Dermatology. Wiley. 30 (3): 394–395. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2012.01805.x. ISSN 0736-8046. PMID 23016512. S2CID 42012198.
- ↑ Prey, Sorilla; Ezzedine, Khaled; Mazereeuw-Hautier, Juliette; Eschard, Catherine; Barbarot, Sébastien; Boralevi, Franck; Taïeb, Alain; Léaute-Labrèze, Christine (April 8, 2013). "<scp>IFAG</scp> and Childhood Rosacea: A Possible Link?". Pediatric Dermatology. Wiley. 30 (4): 429–432. doi:10.1111/pde.12137. ISSN 0736-8046. PMID 23560522. S2CID 5188504.
- ↑ Hasbún Z, C.; Ogueta C, I.; Dossi C, T.; Wortsman, X. (2019). "Idiopathic Facial Aseptic Granuloma: Updated Review of Diagnostic and Therapeutic Difficulties". Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas (English Edition). Elsevier BV. 110 (8): 637–641. doi:10.1016/j.adengl.2019.07.009. ISSN 1578-2190.
- ↑ Lobato-Berezo, Alejandro; Montoro-Romero, Soledad; Pujol, Ramón M.; Segura, Sonia (2018). "Dermoscopic features of idiopathic facial aseptic granuloma". Pediatric Dermatology. 35 (5). doi:10.1111/pde.13582. ISSN 0736-8046. PMID 29962067. S2CID 49644725.