| Graham-Little syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Graham-Little syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by lichen planus-like skin lesions. [1] :648 It is named after Ernest Graham-Little. [2]
| Graham-Little syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Graham-Little syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by lichen planus-like skin lesions. [1] :648 It is named after Ernest Graham-Little. [2]
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment.

Lichen planus (LP) is a chronic inflammatory and immune-mediated disease that affects the skin, nails, hair, and mucous membranes. It is characterized by polygonal, flat-topped, violaceous papules and plaques with overlying, reticulated, fine white scale, commonly affecting dorsal hands, flexural wrists and forearms, trunk, anterior lower legs and oral mucosa. Although there is a broad clinical range of LP manifestations, the skin and oral cavity remain as the major sites of involvement. The cause is unknown, but it is thought to be the result of an autoimmune process with an unknown initial trigger. There is no cure, but many different medications and procedures have been used in efforts to control the symptoms.
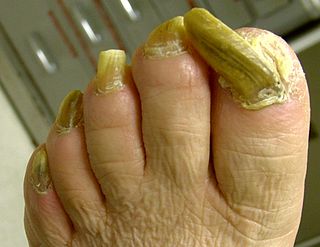
Onychogryphosis is a hypertrophy that may produce nails resembling claws or a ram's horn.

The Bulbous corpuscle or Ruffini ending or Ruffini corpuscle is a slowly adapting mechanoreceptor located in the cutaneous tissue between the dermal papillae and the hypodermis. It is named after Angelo Ruffini.
Chondrodysplasia punctata is a clinically and genetically diverse group of rare diseases, first described by Erich Conradi (1882–1968), that share the features of stippled epiphyses and skeletal changes.

Hidrocystoma is an adenoma of the sweat glands.
Gram-negative rosacea is a cutaneous condition that clinically looks like stage II or III rosacea.
Ichthyosis linearis circumflexa is a distinctive skin condition of generalized hyperkeratosis and polycyclic and serpiginous erythematous plaques with a characteristic, migratory, double-edged scale at the margins, and is the typical cutaneous manifestation of Netherton's syndrome.
Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus is a clinically distinct subset of cases of lupus erythematosus that is most often present in white women aged 15 to 40, consisting of skin lesions that are scaly and evolve as poly-cyclic annular lesions or plaques similar to those of plaque psoriasis.
Cutaneous perforating disorders include the following:
Perforating folliculitis is a skin condition in humans characterized by discrete follicular keratotic eruptions involving mainly the hairy parts of the extremities.
Erythema gyratum repens is a figurate erythema that is rapidly moving and usually a marker of underlying cancer, usually from the lung.
Multiple cutaneous leiomyomas, also known as Pilar leiomyomas, arise from the arrectores pilorum muscles, and are made up of a poorly circumscribed proliferation of haphazardly arranged smooth muscle fibers located in the dermis that appear to infiltrate the surrounding tissue and may extend into the subcutis.
Tufted folliculitis presents with doll's hair-like bundling of follicular units, and is seen in a wide range of scarring conditions including chronic staphylococcal infection, chronic lupus erythematosus, lichen planopilaris, Graham-Little syndrome, folliculitis decalvans, acne keloidalis nuchae, immunobullous disorders, and dissecting cellulitis.

Syringocystadenoma papilliferum is a benign apocrine tumor.

Cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis (CSVV), also known as hypersensitivity vasculitis, cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis, hypersensitivity angiitis, cutaneous leukocytoclastic angiitis, cutaneous necrotizing vasculitis and cutaneous necrotizing venulitis, is inflammation of small blood vessels, characterized by palpable purpura. It is the most common vasculitis seen in clinical practice.
Plummer's nail is a clinical sign in which there is onycholysis, or separation of the nail from the nail bed, particularly affecting the ring and little fingers. It occurs in patients with thyrotoxicosis. About 5% of hyperthyroid patients display abnormal nail changes. Plummer's nail is also associated with psoriasis, traumatic injury, and allergic contact dermatitis.
Parakeratosis pustulosa is a cutaneous condition which is exclusively seen in children, usually involving one finger, most commonly the thumb or index finger, with the affected nail showing subungual hyperkeratosis and onycholysis.
Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis, or Bazex syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by psoriasiform changes of hands, feet, ears, and nose, with involvement of the nails and periungual tissues being characteristic and indistinguishable from psoriatic nails. The condition is associated with carcinomas of the upper aerodigestive tract.

Koenen's tumor is a cutaneous condition that results in fifty percent of tuberous sclerosis cases.It can be subungual too.
| Classification |
|---|
| This condition of the skin appendages article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |