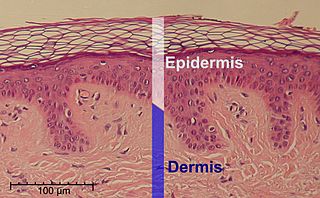
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that make up the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss. The epidermis is composed of multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a base layer composed of columnar cells arranged perpendicularly.

A nail disease or onychosis is a disease or deformity of the nail. Although the nail is a structure produced by the skin and is a skin appendage, nail diseases have a distinct classification as they have their own signs and symptoms which may relate to other medical conditions. Some nail conditions that show signs of infection or inflammation may require medical assistance.

Acanthosis nigricans is a medical sign characterised by brown-to-black, poorly defined, velvety hyperpigmentation of the skin. It is usually found in body folds, such as the posterior and lateral folds of the neck, the armpits, groin, navel, forehead and other areas.
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment.

Telogen effluvium is a scalp disorder characterized by the thinning or shedding of hair resulting from the early entry of hair in the telogen phase. It is in this phase that telogen hairs begin to shed at an increased rate, where normally the approximate rate of hair loss is 125 hairs per day.

Palmoplantar keratodermas are a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by abnormal thickening of the palms and soles.

Trichorrhexis nodosa is a defect in the hair shaft characterized by thickening or weak points (nodes) that cause the hair to break off easily. This group of conditions contributes to the appearance of hair loss, lack of growth, and damaged-looking hair.

Hyperkeratosis is thickening of the stratum corneum, often associated with the presence of an abnormal quantity of keratin, and also usually accompanied by an increase in the granular layer. As the corneum layer normally varies greatly in thickness in different sites, some experience is needed to assess minor degrees of hyperkeratosis.

Meleda disease (MDM) or "mal de Meleda", also called Mljet disease, keratosis palmoplantaris and transgradiens of Siemens, is an extremely rare autosomal recessive congenital skin disorder in which dry, thick patches of skin develop on the soles of the hands and feet, a condition known as palmoplantar hyperkeratosis. Meleda Disease is a skin condition which usually can be identified not long after birth. This is a genetic condition but it is very rare. The hands and feet usually are the first to show signs of the disease but the disease can advance to other parts of the body. Signs of the disease include thickening of the skin, on hands and soles of feet, which can turn red in color. There currently is no cure and treatment is limited, but Acitretin can be used in severe cases.

Pityriasis rubra pilaris refers to a group of chronic disorders characterized by reddish orange, scaling plaques and keratotic follicular papules. Symptoms may include reddish-orange patches on the skin, severe flaking, uncomfortable itching, thickening of the skin on the feet and hands, and thickened bumps around hair follicles. For some, early symptoms may also include generalized swelling of the legs, feet and other parts of the body. PRP has a varied clinical progression and a varied rate of improvement. There is currently no known cause or cure for PRP.

Morphea, is a form of scleroderma that involves isolated patches of hardened skin on the face, hands, and feet, or anywhere else on the body, with no internal organ involvement.

Cutis laxa or pachydermatocele is a group of rare connective tissue disorders in which the skin becomes inelastic and hangs loosely in folds.

Pachyonychia congenita is a rare group of autosomal dominant skin disorders that are caused by a mutation in one of five different keratin genes. Pachyonychia congenita is often associated with thickened toenails, plantar keratoderma, and plantar pain.

Cutis verticis gyrata is a medical condition usually associated with thickening of the scalp. People show visible folds, ridges or creases on the surface of the top of the scalp. The number of folds can vary from two to roughly ten and are typically soft and spongy. These folds cannot be corrected with pressure. The condition typically affects the central and rear regions of the scalp, but sometimes can involve the entire scalp.

Urbach–Wiethe disease is a rare recessive genetic disorder, with approximately 400 reported cases since its discovery. It was first officially reported in 1929 by Erich Urbach and Camillo Wiethe, although cases may be recognized dating back as early as 1908.
Nutritional deficiency eczema is a pattern of eczema with localized, thickened, scaling patches that have some characteristics of nummular eczema, seborrheic dermatitis, and neurodermatitis that may be seen in alcoholics.
Junctional epidermolysis bullosa is a skin condition characterized by blister formation within the lamina lucida of the basement membrane zone.
Narcotic dermopathy is a skin condition caused by the injection of drugs intravenously, resulting in thrombosed, cordlike, thickened veins at the site of injection.
Acanthoma fissuratum is a cutaneous condition characterized by local thickening of the skin in response to pressure caused by an eyeglass frame.
Diabetic cheiroarthropathy, also known as Diabetic stiff hand syndrome or limited joint mobility syndrome, is a cutaneous condition characterized by waxy, thickened skin and limited joint mobility of the hands and fingers, leading to flexion contractures, a condition associated with diabetes mellitus and it is observed in roughly 30% of diabetic patients with longstanding disease. It can be a predictor for other diabetes-related complications and was one of the earliest known complications of diabetes, first documented in 1974.














