Related Research Articles

Harlequin-type ichthyosis is a genetic disorder that results in thickened skin over nearly the entire body at birth. The skin forms large, diamond/trapezoid/rectangle-shaped plates that are separated by deep cracks. These affect the shape of the eyelids, nose, mouth, and ears and limit movement of the arms and legs. Restricted movement of the chest can lead to breathing difficulties. These plates fall off over several weeks. Other complications can include premature birth, infection, problems with body temperature, and dehydration. The condition is the most severe form of ichthyosis, a group of genetic disorders characterised by scaly skin.

Cardiofaciocutaneous (CFC) syndrome is an extremely rare genetic disorder, and is one of the RASopathies. It was first described in 1986.

Darier's disease (DAR) is a rare, inherited skin disorder that presents with multiple greasy, crusting, thick brown bumps that merge into patches. It is an autosomal dominant disorder discovered by French dermatologist Ferdinand-Jean Darier.

Gunther disease is a congenital form of erythropoietic porphyria. The word porphyria originated from the Greek word porphura. Porphura actually means "purple pigment", which, in suggestion, the color that the body fluid changes when a person has Gunther's disease. It is a rare, autosomal recessive metabolic disorder affecting heme, caused by deficiency of the enzyme uroporphyrinogen cosynthetase. It is extremely rare, with a prevalence estimated at 1 in 1,000,000 or less. There have been times that prior to birth of a fetus, Gunther's disease has been shown to lead to anemia. In milder cases patients have not presented any symptoms until they have reached adulthood. In Gunther's disease, porphyrins are accumulated in the teeth and bones and an increased amount are seen in the plasma, bone marrow, feces, red blood cells, and urine.

Meleda disease (MDM) or "mal de Meleda", also called Mljet disease, keratosis palmoplantaris and transgradiens of Siemens, is an extremely rare autosomal recessive congenital skin disorder in which dry, thick patches of skin develop on the soles of the hands and feet, a condition known as palmoplantar hyperkeratosis. Meleda Disease is a skin condition which usually can be identified not long after birth. This is a genetic condition but it is very rare. The hands and feet usually are the first to show signs of the disease but the disease can advance to other parts of the body. Signs of the disease include thickening of the skin, on hands and soles of feet, which can turn red in color. There currently is no cure and treatment is limited, but Acitretin can be used in severe cases.
Cyclic neutropenia (CyN) is a rare hematologic disorder and form of congenital neutropenia that tends to occur approximately every three weeks and lasting for few days at a time due to changing rates of neutrophil production by the bone marrow. It causes a temporary condition with a low absolute neutrophil count and because the neutrophils make up the majority of circulating white blood cells it places the body at severe risk of inflammation and infection. In comparison to severe congenital neutropenia, it responds well to treatment with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (filgrastim), which increases the neutrophil count, shortens the cycle length, as well decreases the severity and frequency of infections.
Severe congenital neutropenia (SCN), also often known as Kostmann syndrome or disease, is a group of rare disorders that affect myelopoiesis, causing a congenital form of neutropenia, usually without other physical malformations. SCN manifests in infancy with life-threatening bacterial infections. It causes severe pyogenic infections. It can be caused by autosomal dominant inheritance of the ELANE gene, autosomal recessive inheritance of the HAX1 gene. There is an increased risk of leukemia and myelodysplastic cancers.
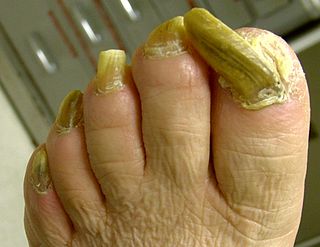
Onychogryphosis is a hypertrophy that may produce nails resembling claws or a ram's horn.
Dyschromatosis universalis hereditaria is a type of pigmentation disorder of the skin. It is characterized by dark and light spots formed like lace in a generalized distribution.
Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata is a rare developmental brain disorder characterized by abnormally short arms and legs (rhizomelia), seizures, recurrent respiratory tract infections and congenital cataracts.

Kindler syndrome is a rare congenital disease of the skin caused by a mutation in the KIND1 gene.

White sponge nevus (WSN) is an autosomal dominant condition of the oral mucosa. It is caused by a mutations in certain genes coding for keratin, which causes a defect in the normal process of keratinization of the mucosa. This results in lesions which are thick, white and velvety on the inside of the cheeks within the mouth. Usually, these lesions are present from birth or develop during childhood. The condition is entirely harmless, and no treatment is required.

Epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica or dystrophic EB (DEB) is an inherited disease affecting the skin and other organs.

Milroy's disease (MD) is a familial disease characterized by lymphedema, commonly in the legs, caused by congenital abnormalities in the lymphatic system. Disruption of the normal drainage of lymph leads to fluid accumulation and hypertrophy of soft tissues.

Ichthyosis bullosa of Siemens is a type of familial, autosomal dominant ichthyosis, a rare skin disorder. It is also known as bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma of Siemens or ichthyosis exfoliativa. It is a genetic disorder with no known cure which is estimated to affect about 1 in 500,000 people.
Trichorrhexis invaginata is a distinctive hair shaft abnormality that may occur sporadically, either in normal hair or with other hair shaft abnormalities, or regularly as a marker for Netherton syndrome. The primary defect appears to be abnormal keratinization of the hair shaft in the keratogenous zone, allowing for intussusception of the fully keratinized and hard distal shaft into the incompletely keratinized and soft proximal portion of the shaft.

Marinesco–Sjögren syndrome (MSS), sometimes spelled Marinescu–Sjögren syndrome, is a rare autosomal recessive disorder.
Congenital generalized lipodystrophy is an extremely rare autosomal recessive condition, characterized by an extreme scarcity of fat in the subcutaneous tissues. It is a type of lipodystrophy disorder where the magnitude of fat loss determines the severity of metabolic complications. Only 250 cases of the condition have been reported, and it is estimated that it occurs in 1 in 10 million people worldwide.
Howel–Evans syndrome is an extremely rare condition involving thickening of the skin in the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet (hyperkeratosis). This familial disease is associated with a high lifetime risk of esophageal cancer. For this reason, it is sometimes known as tylosis with oesophageal cancer (TOC).
For chromosome 20, R-spondin 4 is a protein in humans that is encoded by the RSPO4 gene. This gene encodes a member of the R-spondin family of proteins that share a common domain organization consisting of a signal peptide, cysteine-rich/furin-like domain, thrombospondin domain and a C-terminal basic region. The encoded protein may be involved in activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways. Mutations in this gene are associated with anonychia congenita. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants.[provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009].
References
- ↑ MacGilchrist, Claire (2020). "3. The skin and nails in podiatry". In Burrow, J. Gordon; Rome, Keith; Padhiar, Nat (eds.). Neale's Disorders of the Foot and Ankle (9th ed.). Elsevier. p. 52. ISBN 978-0-7020-6504-0.
- ↑ James, William D.; Elston, Dirk; Treat, James R.; Rosenbach, Misha A.; Neuhaus, Isaac (2020). "33. Diseases of the skin appendages". Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology (13th ed.). Edinburgh: Elsevier. p. 782. ISBN 978-0-323-54753-6.
- ↑ Khan TN, Klar J, Nawaz S, Jameel M, Tariq M, Malik NA, Baig SM, Dahl N (2012) Novel missense mutation in the RSPO4 gene in congenital hyponychia and evidence for a polymorphic initiation codon (p.M1I). BMC Med Genet 13(1):120