
Acne, also known as acne vulgaris, is a long-term skin condition that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and possible scarring. It primarily affects skin with a relatively high number of oil glands, including the face, upper part of the chest, and back. The resulting appearance can lead to lack of confidence, anxiety, reduced self-esteem, and, in extreme cases, depression or thoughts of suicide.

Cosmetics are composed of mixtures of chemical compounds derived from either natural sources or synthetically created ones. Cosmetics have various purposes. Those designed for personal care and skin care can be used to cleanse or protect the body and skin. Cosmetics designed to enhance or alter one's appearance (makeup) can be used to conceal blemishes, enhance one's natural features, add color to a person's face, or change the appearance of the face entirely to resemble a different person, creature or object. Cosmetics can also be designed to add fragrance to the body.

Seborrhoeic dermatitis is a long-term skin disorder. Symptoms include flaky, scaly, greasy, and occasionally itchy and inflamed skin. Areas of the skin rich in oil-producing glands are often affected including the scalp, face, and chest. It can result in social or self-esteem problems. In babies, when the scalp is primarily involved, it is called cradle cap. Seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp may be described in lay terms as dandruff due to the dry, flaky character of the skin. However, as dandruff may refer to any dryness or scaling of the scalp, not all dandruff is seborrhoeic dermatitis. Seborrhoeic dermatitis is sometimes inaccurately referred to as seborrhoea.

Contact dermatitis is a type of acute or chronic inflammation of the skin caused by exposure to chemical or physical agents. Symptoms of contact dermatitis can include itchy or dry skin, a red rash, bumps, blisters, or swelling. These rashes are not contagious or life-threatening, but can be very uncomfortable.

Rosacea is a long-term skin condition that typically affects the face. It results in redness, pimples, swelling, and small and superficial dilated blood vessels. Often, the nose, cheeks, forehead, and chin are most involved. A red, enlarged nose may occur in severe disease, a condition known as rhinophyma.

Benzoyl peroxide is a chemical compound (specifically, an organic peroxide) with structural formula (C6H5−C(=O)O−)2, often abbreviated as (BzO)2. In terms of its structure, the molecule can be described as two benzoyl (C6H5−C(=O)−, Bz) groups connected by a peroxide (−O−O−). It is a white granular solid with a faint odour of benzaldehyde, poorly soluble in water but soluble in acetone, ethanol, and many other organic solvents. Benzoyl peroxide is an oxidizer, which is principally used as in the production of polymers.

Clobetasol propionate is a corticosteroid used to treat skin conditions such as eczema, contact dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, and psoriasis. It is applied to the skin as a cream, ointment, or shampoo. Use should be short term and only if other weaker corticosteroids are not effective. Use is not recommended in rosacea or perioral dermatitis.

Perioral dermatitis, also known as periorificial dermatitis, is a common type of skin rash. Symptoms include multiple small (1–2 mm) bumps and blisters sometimes with background redness and scale, localized to the skin around the mouth and nostrils. Less commonly the eyes and genitalia may be involved. It can be persistent or recurring and resembles particularly rosacea and to some extent acne and allergic dermatitis. The term "dermatitis" is a misnomer because this is not an eczematous process.

Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a form of contact dermatitis that is the manifestation of an allergic response caused by contact with a substance; the other type being irritant contact dermatitis (ICD).

Lotion is a low-viscosity topical preparation intended for application to the skin. By contrast, creams and gels have higher viscosity, typically due to lower water content. Lotions are applied to external skin with bare hands, a brush, a clean cloth, or cotton wool.

Skin care or skincare is a range of practices that support skin integrity, enhance its appearance, and relieve skin conditions. They can include nutrition, avoidance of excessive sun exposure, and appropriate use of emollients. Practices that enhance appearance include the use of cosmetics, botulinum, exfoliation, fillers, laser resurfacing, microdermabrasion, peels, retinol therapy, and ultrasonic skin treatment. Skin care is a routine daily procedure in many settings, such as skin that is either too dry or too moist, and prevention of dermatitis and prevention of skin injuries.

Amcinonide is a topical glucocorticoid used to treat itching, redness and swelling associated with several dermatologic conditions such as atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis. Amcinonide can also be classified as a multi-functional small molecule corticosteroid, which has been approved by the FDA and is currently marketed as an ointment, lotion, or cream. It acts as both a transcription factor for responses to glucocorticoids and modulator for other transcription factors while also regulating phospholipase A2 activity.

Acneiform eruptions, or acne mimicking eruptions, are a group of skin conditions characterized by small bumps resembling acne. Typically, these bumps are mostly of similar size. Some bumps may be bigger or contain fluid. Generally, blackheads and whiteheads are absent. It tends to appear suddenly, with the chest and back most frequently affected.
Acne aestivalis also called as acne mallorca, is a special kind of polymorphous light eruption induced by ultra violet A radiation. This condition is said to be seasonal, usually affecting people in springtime and goes away in autumn when there is less sun light. This photo induced skin reaction leads to a mono-morphous eruption that consists of multiple, uniform, red, papular lesions. This skin reaction is classified as a delayed-type hypersensitivity because the onset is 24–72 hours after sun exposure. The condition equally affects men and women between the ages of 20–40 years old with no prior history of acne vulgaris. The eruption is unusual because it spares the face but it affects the lateral aspects of the upper arms, shoulder girdle, back, and chest. This condition's pathogenesis is not very well understood but scientists believe it an unfortunate side effect that results from a strong immune response to potentially cancer-causing cell damage.

Neonatal acne, also known as acne neonatorum, is a type of acne that develops in newborns, typically before 6 weeks of life. It presents with open and closed comedones on the cheeks, chin and forehead.
Eyelid dermatitis is commonly related to atopic dermatitis or allergic contact dermatitis. Volatile substances, tosylamide, epoxy hardeners, insect sprays, and lemon peel oil may be implicated, with many cases of eyelid contact dermatitis being caused by substances transferred by the hands to the eyelids.

A pimple or zit is a kind of comedo that results from excess sebum and dead skin cells getting trapped in the pores of the skin. In its aggravated state, it may evolve into a pustule or papule. Pimples can be treated by acne medications, antibiotics, and anti-inflammatories prescribed by a physician, or various over the counter remedies purchased at a pharmacy.
Infantile acne is a form of acne that begins in very young children. Typical symptoms include inflammatory and noninflammatory lesions, papules and pustules most commonly present on the face. No cause of infantile acne has been established but it may be caused by increased sebaceous gland secretions due to elevated androgens, genetics and the fetal adrenal gland causing increased sebum production. Infantile acne can resolve by itself by age 1 or 2. However, treatment options include topical benzyl peroxide, topical retinoids and topical antibiotics in most cases.

Irritant folliculitis is an inflammation of the hair follicle. It characteristically presents with small red bumps in the skin at sites of occlusion, pressure, friction, or hair removal; typically around the beard area in males, pubic area and lower legs of females, or generally the inner thighs and bottom. An associated itch may or may not be present. Pseudofolliculitis barbae is a type of irritant folliculitis in the beard area.
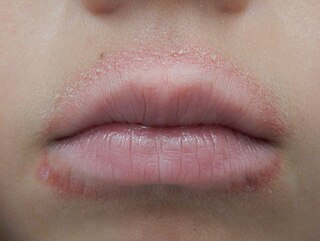
Lip licker's dermatitis is a type of skin inflammation around the lips due to damage by saliva from repetitive lip licking and is classified as a subtype of irritant contact cheilitis. The resulting scaling, redness, chapping, and crusting makes a well-defined ring around the lips. The rash may extend as far as the tongue can reach and usually does not occur at the corners of the mouth. It commonly occurs during winter months but some people can have it year-round if lip licking is a chronic habit.
















