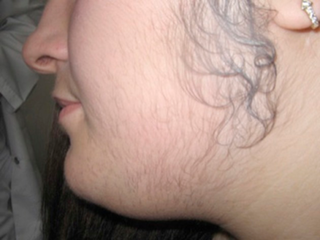
Hirsutism is excessive body hair on parts of the body where hair is normally absent or minimal. The word is from early 17th century: from Latin hirsutus meaning "hairy". It usually refers to a male pattern of hair growth in a female that may be a sign of a more serious medical condition, especially if it develops well after puberty. Cultural stigma against hirsutism can cause much psychological distress and social difficulty. Discrimination based on facial hirsutism often leads to the avoidance of social situations and to symptoms of anxiety and depression.

Hyperpigmentation is the darkening of an area of skin or nails caused by increased melanin.

Menkes disease (MNK), also known as Menkes syndrome, is an X-linked recessive disorder caused by mutations in genes coding for the copper-transport protein ATP7A, leading to copper deficiency. Characteristic findings include kinky hair, growth failure, and nervous system deterioration. Like all X-linked recessive conditions, Menkes disease is more common in males than in females. The disorder was first described by John Hans Menkes in 1962.

Hypertrichosis is an abnormal amount of hair growth over the body. The two distinct types of hypertrichosis are generalized hypertrichosis, which occurs over the entire body, and localized hypertrichosis, which is restricted to a certain area. Hypertrichosis can be either congenital or acquired later in life. The excess growth of hair occurs in areas of the skin with the exception of androgen-dependent hair of the pubic area, face, and axillary regions.

Physical urticaria is a distinct subgroup of urticaria (hives) that are induced by an exogenous physical stimulus rather than occurring spontaneously. There are seven subcategories that are recognized as independent diseases. Physical urticaria is known to be painful, itchy and physically unappealing; it can recur for months to years.

Pityriasis lichenoides represents a distinct subset of inflammatory skin disorders that includes pityriasis lichenoides chronica, febrile ulceronecrotic Mucha-Habermann disease, and pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta (PLEVA).
Eosinophilic folliculitis is an itchy rash with an unknown cause that is most common among individuals with HIV, though it can occur in HIV-negative individuals where it is known by the eponym Ofuji disease. EF consists of itchy red bumps (papules) centered on hair follicles and typically found on the upper body, sparing the abdomen and legs. The name eosinophilic folliculitis refers to the predominant immune cells associated with the disease (eosinophils) and the involvement of the hair follicles.
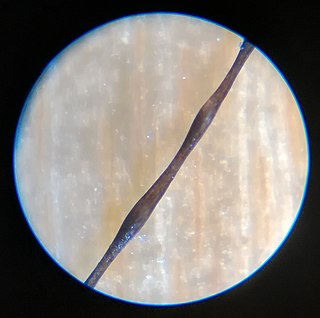
Monilethrix is a rare autosomal dominant hair disease that results in short, fragile, broken hair that appears beaded. It comes from the Latin word for necklace (monile) and the Greek word for hair (thrix). Hair becomes brittle, and breaks off at the thinner parts between the beads. It appears as a thinning or baldness of hair and was first described in 1897 by Walter Smith

White piedra is a mycosis of the hair caused by several species of fungi in the genus Trichosporon. It is characterized by soft nodules composed of yeast cells and arthroconidia that encompass hair shafts.

Pili torti is characterized by short and brittle hairs that appear flattened and twisted when viewed through a microscope.

Piedraia hortae is a superficial fungus that exists in the soils of tropical and subtropical environments and affects both sexes of all ages. The fungus grows very slowly, forming dark hyphae, which contain chlamydoconidia cells and black colonies when grown on agar. Piedraia hortae is a dermatophyte and causes a superficial fungal infection known as black piedra, which causes the formation of black nodules on the hair shaft and leads to progressive weakening of the hair. The infection usually infects hairs on the scalp and beard, but other varieties tend to grow on pubic hairs. The infection is usually treated with cutting or shaving of the hair and followed by the application of anti-fungal and topical agents. The fungus is used for cosmetic purposes to darken hair in some societies as a symbol of attractiveness.
Median nail dystrophy, also known as dystrophia unguis mediana canaliformis, median canaliform dystrophy of Heller, and solenonychia consists of longitudinal splitting or canal formation in the midline of the nail, a split which often resembles a fir tree, occurring at the cuticle and proceeding outward as the nail grows.
Disseminate and recurrent infundibulofolliculitis, also called disseminate and recurrent infundibular folliculitis or Hitch and Lund disease, is a rare follicular skin condition that presents with irregularly shaped papules pierced by hair, is mildly itchy at times, and is chronic with recurrent exacerbations.

Trichoscopy is a method of hair and scalp evaluation and is used for diagnosing hair and scalp diseases. The method is based on dermoscopy. In trichoscopy hair and scalp structures may be visualized at many-fold magnification. Currently magnifications ranging from 10-fold to 70-fold are most popular in research and clinical practice.
Actinic granuloma (AG) was first described by O'Brien in 1975 as a rare granulomatous disease. Lesions appear on sun-exposed areas, usually on the face, neck, and scalp, with a slight preference for middle-aged women. They are typically asymptomatic, single or multiple, annular or polycyclic lesions measuring up to 6 cm in diameter, with slow centrifugal expansion, an erythematous elevated edge, and a hypopigmented, atrophic center.
Progressive nodular histiocytosis is a cutaneous condition clinically characterized by the development of two types of skin lesions: superficial papules and deeper larger subcutaneous nodules. Progressive nodular histiocytosis was first reported in 1978 by Taunton et al. It is a subclass of non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis and a subgroup of xanthogranuloma.

Airbag dermatitis is skin irritation secondary to the deployment of airbags. The diagnosis of "air bag dermatitis" is relatively recent; the first case was reported in 1994.
Infantile acne is a form of acne that begins in very young children. Typical symptoms include inflammatory and noninflammatory lesions, papules and pustules most commonly present on the face. No cause of infantile acne has been established but it may be caused by increased sebaceous gland secretions due to elevated androgens, genetics and the fetal adrenal gland causing increased sebum production. Infantile acne can resolve by itself by age 1 or 2. However, treatment options include topical benzyl peroxide, topical retinoids and topical antibiotics in most cases.

Prepubertal hypertrichosis, also known as childhood hypertrichosis, is a cutaneous condition characterized by increased hair growth, found in otherwise healthy infants and children. Prepubertal hypertrichosis is a cosmetic condition and does not affect any other health aspect. Individuals with this condition may suffer with low self esteem and mental health issues due to societal perceptions of what a "normal" appearance should be. The mechanism of prepubertal hypertrichosis is unclear, but causes may include genetics, systemic illnesses, or medications.
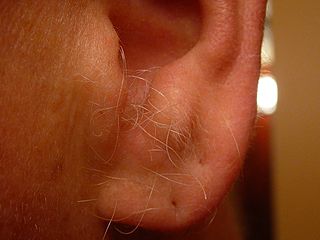
Ear hair is the terminal hair arising from folliculary cartilage inside the external auditory meatus in humans. In its broader sense, ear hair may also include the fine vellus hair covering much of the ear, particularly at the prominent parts of the anterior ear, or even the abnormal hair growth as seen in hypertrichosis and hirsutism. Medical research on the function of ear hair is currently very scarce.














