| Flexion teardrop fracture | |
|---|---|
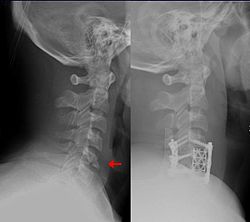 | |
| Teardrop fracture of the cervical spine before and after treatment with metal fixation | |
| Specialty | Orthopedic |
A flexion teardrop fracture is a fracture of the anteroinferior aspect of a cervical vertebral body due to flexion of the spine along with vertical axial compression. [1] The fracture continues sagittally through the vertebral body, and is associated with deformity of the body and subluxation or dislocation of the facet joints at the injured level. [2] A flexion teardrop fracture is usually associated with a spinal cord injury, often a result of displacement of the posterior portion of the vertebral body into the spinal canal. [3]
The flexion teardrop fracture should not be confused with a similar-looking vertebral fracture called "extension teardrop fracture". Both usually occur in the cervical spine, but as their names suggest, they result from different mechanisms (flexion-compression vs. hyperextension). Both are associated with a small fragment being broken apart from the anteroinferior corner of the affected vertebra. Flexion teardrop fractures usually involve instability in all elements of the spine at the injured level, commonly occur at the C4-C7 vertebra, and have a high association with spinal cord injury (in particular anterior cord syndrome). In comparison, the extension-type fracture occurs more commonly at C2 or C3, causes less if any disruption to the middle and posterior elements, and does not usually result in spinal cord injury (however, it may co-occur with more serious spine injuries). [2]