Related Research Articles

The ulna or ulnal bone is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the wrist, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of the forearm as the little finger. It runs parallel to the radius, the other long bone in the forearm. The ulna is longer and the radius is shorter, but the radius is thicker and the ulna is thinner. Therefore, the ulna is considered to be the smaller bone of the two bones in the lower arm. The corresponding bone in the lower leg is the fibula.

The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial compartment of the forearm and the associated joints and overlying skin.

In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius and the carpus and; (3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as wrist joints. This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, bracelet lines, the flexor retinaculum, and the extensor retinaculum.
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus.

The radius or radial bone is one of the two large bones of the forearm, the other being the ulna. It extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist and runs parallel to the ulna. The ulna is longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. The radius is a long bone, prism-shaped and slightly curved longitudinally.
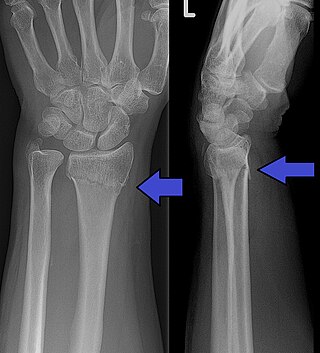
A distal radius fracture, also known as wrist fracture, is a break of the part of the radius bone which is close to the wrist. Symptoms include pain, bruising, and rapid-onset swelling. The ulna bone may also be broken.

The Galeazzi fracture is a fracture of the distal third of the radius with dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint. It classically involves an isolated fracture of the junction of the distal third and middle third of the radius with associated subluxation or dislocation of the distal radio-ulnar joint; the injury disrupts the forearm axis joint.

Madelung's deformity is usually characterized by malformed wrists and wrist bones and is often associated with Léri-Weill dyschondrosteosis. It can be bilateral or just in the one wrist. It has only been recognized within the past hundred years. Named after Otto Wilhelm Madelung (1846–1926), a German surgeon, who described it in detail, it was noted by others. Guillaume Dupuytren mentioned it in 1834, Auguste Nélaton in 1847, and Joseph-François Malgaigne in 1855.

The oblique cord is a ligament between the ulnar and radius bones in the forearm near the elbow. It takes the form of a small, flattened band, extending distally and laterally, from the lateral side of the ulnar tuberosity at the base of the coronoid process to the radius a little below the radial tuberosity. Its fibers run in the opposite direction to those of the Interosseous membrane of the forearm.

The distal radioulnar articulation is a synovial pivot joint between the two bones in the forearm; the radius and ulna. It is one of two joints between the radius and ulna, the other being the proximal radioulnar articulation. The joint features an articular disc, and is reinforced by the palmar and dorsal radioulnar ligaments.

The anterior interosseous nerve is a branch of the median nerve that supplies the deep muscles on the anterior of the forearm, except the ulnar (medial) half of the flexor digitorum profundus. Its nerve roots come from C8 and T1.

The interosseous membrane of the forearm is a fibrous sheet that connects the interosseous margins of the radius and the ulna. It is the main part of the radio-ulnar syndesmosis, a fibrous joint between the two bones.

The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is formed by the triangular fibrocartilage discus (TFC), the radioulnar ligaments (RULs) and the ulnocarpal ligaments (UCLs).

The Monteggia fracture is a fracture of the proximal third of the ulna with dislocation of the proximal head of the radius. It is named after Giovanni Battista Monteggia.

The humeroradial joint is the joint between the head of the radius and the capitulum of the humerus, is a limited ball-and-socket joint, hinge type of synovial joint.

The elbow is the region between the upper arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa, and the lateral and the medial epicondyles of the humerus. The elbow joint is a hinge joint between the arm and the forearm; more specifically between the humerus in the upper arm and the radius and ulna in the forearm which allows the forearm and hand to be moved towards and away from the body. The term elbow is specifically used for humans and other primates, and in other vertebrates forelimb plus joint is used.

A supracondylar humerus fracture is a fracture of the distal humerus just above the elbow joint. The fracture is usually transverse or oblique and above the medial and lateral condyles and epicondyles. This fracture pattern is relatively rare in adults, but is the most common type of elbow fracture in children. In children, many of these fractures are non-displaced and can be treated with casting. Some are angulated or displaced and are best treated with surgery. In children, most of these fractures can be treated effectively with expectation for full recovery. Some of these injuries can be complicated by poor healing or by associated blood vessel or nerve injuries with serious complications.

An ulna fracture is a break in the ulna bone, one of the two bones in the forearm. It is often associated with a fracture of the other forearm bone, the radius.

Wrist osteoarthritis is gradual loss of articular cartilage and hypertrophic bone changes (osteophytes). While in many joints this is part of normal aging (senescence), in the wrist osteoarthritis usually occurs over years to decades after scapholunate interosseous ligament rupture or an unhealed fracture of the scaphoid. Characteristic symptoms including pain, deformity and stiffness. Pain intensity and incapability are notably variable and do not correspond with arthritis severity on radiographs.

The muscles of the thumb are nine skeletal muscles located in the hand and forearm. The muscles allow for flexion, extension, adduction, abduction and opposition of the thumb. The muscles acting on the thumb can be divided into two groups: The extrinsic hand muscles, with their muscle bellies located in the forearm, and the intrinsic hand muscles, with their muscles bellies located in the hand proper.
References
- 1 2 3 Essex Lopresti fracture at Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics online
- ↑ Essex-Lopresti, P (May 1951). "Fractures of the radial head with distal radio-ulnar dislocation: report of two cases". J Bone Joint Surg Br. 33B (2): 244–7. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.33B2.244. PMID 14832324.
- ↑ Edwards, GS Jr.; Jupiter JB (Sep 1988). "Radial head fractures with acute radioulnar dislocation. Essex-Lopresti revisited". Clin Orthop Relat Res (234): 61–9. PMID 3409602.