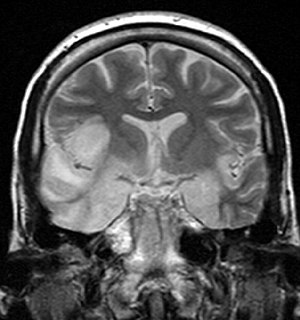
Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain. The severity can be variable with symptoms including headache, fever, confusion, a stiff neck, and vomiting. Complications may include seizures, hallucinations, trouble speaking, memory problems, and problems with hearing.

Flaviviridae is a family of viruses. Humans and other mammals serve as natural hosts. They are primarily spread through arthropod vectors. The family gets its name from the yellow fever virus, the type virus of Flaviviridae; flavus is Latin for "yellow", and yellow fever in turn was named because of its propensity to cause jaundice in victims. Currently, 89 species are in this family, divided among four genera. Diseases associated with this family include: hepatitis (hepaciviruses), hemorrhagic syndromes, fatal mucosal disease (pestiviruses), hemorrhagic fever, encephalitis, and the birth defect microcephaly (flaviviruses).

Viral meningitis, also known as aseptic meningitis, is a type of meningitis due to a viral infection. It results in inflammation of the meninges. Symptoms commonly include headache, fever, sensitivity to light and neck stiffness.
Tick-borne diseases, which afflict humans and other animals, are caused by infectious agents transmitted by tick bites. They are caused by infection with a variety of pathogens, including rickettsia and other types of bacteria, viruses, and protozoa. Because individual ticks can harbor more than one disease-causing agent, patients can be infected with more than one pathogen at the same time, compounding the difficulty in diagnosis and treatment. 16 tick-borne diseases of humans are known, of which four have been discovered since 2013.

Tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) is a virus associated with tick-borne encephalitis.
This is a shortened version of the tenth chapter of the ICD-10: Diseases of the respiratory system. It covers ICD codes J00 to J99. All versions of the ICD-10, including the most recent one (2019), can be browsed freely on the website of the World Health Organisation (WHO). The ICD-10 can also be downloaded in PDF-form.
This is a shortened version of the sixteenth chapter of the ICD-10: Certain conditions originating in the perinatal period. It covers ICD codes P00.0 to P96.9. All versions of the ICD-10, including the most recent one (2019), can be browsed freely on the website of the World Health Organisation (WHO). The ICD-10 can also be downloaded in PDF-form.

Meningoencephalitis, also known as herpes meningoencephalitis, is a medical condition that simultaneously resembles both meningitis, which is an infection or inflammation of the meninges, and encephalitis, which is an infection or inflammation of the brain.
Powassan virus (POWV) is a Flavivirus transmitted by ticks, found in North America and in the Russian Far East. It is named after the town of Powassan, Ontario, where it was identified in a young boy who eventually died from it. It can cause encephalitis, an infection of the brain. No vaccine or antiviral drug exists. Prevention of tick bites is the best precaution.
The Central Nervous System controls most of the functions of the body and mind. It comprises the brain, spinal cord and the nerve fibers that branch off to all parts of the body. The Central Nervous System viral diseases are caused by viruses that attack the CNS. Existing and emerging viral CNS infections are major sources of human morbidity and mortality. Virus infections usually begin in the peripheral tissues, and can invade the mammalian system by spreading into the peripheral nervous system and more rarely the CNS. CNS is protected by effective immune responses and multi-layer barriers, but some viruses enter with high-efficiency through the bloodstream and some by directly infecting the nerves that innervate the tissues. Most viruses that enter can be opportunistic and accidental pathogens, but some like herpes viruses and rabies virus have evolved in time to enter the nervous system efficiently, by exploiting the neuronal cell biology. While acute viral diseases come on quickly, chronic viral conditions have long incubation periods inside the body. Their symptoms develop slowly and follow a progressive, fatal course.

Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), also referred to as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), are infections that are commonly spread by sexual activity, especially vaginal intercourse, anal sex and oral sex. Many times STIs initially do not cause symptoms. This results in a greater risk of passing the disease on to others. Symptoms and signs of disease may include vaginal discharge, penile discharge, ulcers on or around the genitals, and pelvic pain. STIs can be transmitted to an infant before or during childbirth and may result in poor outcomes for the baby. Some STIs may cause problems with the ability to get pregnant.

Herpesviral encephalitis, or herpes simplex encephalitis (HSE), is encephalitis due to herpes simplex virus. It is estimated to affect at least 1 in 500,000 individuals per year, and some studies suggest an incidence rate of 5.9 cases per 100,000 live births.
Kemerovo tickborne viral fever is an aparalytic febrile illness accompanied by meningism following tick-bite. The causative agent is a zoonotic Orbivirus first described in 1963 in western Siberia by Mikhail Chumakov and coworkers. The virus has some 23 serotypes, and can occur in coinfections with other Orbiviruses and tick-transmitted encephalitis viruses, complicating the course of illness. Rodents and birds are the primary vertebrate hosts of the virus; Ixodes persulcatus ticks are a vector of the virus. Kemerovo and related viruses may be translocated distances in the environment by migratory birds.
The stages of HIV infection are acute infection, latency and AIDS. Acute infection lasts for several weeks and may include symptoms such as fever, swollen lymph nodes, inflammation of the throat, rash, muscle pain, malaise, and mouth and esophageal sores. The latency stage involves few or no symptoms and can last anywhere from two weeks to twenty years or more, depending on the individual. AIDS, the final stage of HIV infection, is defined by low CD4+ T cell counts, various opportunistic infections, cancers and other conditions.
In the United States, the National Notifiable Disease Surveillance System (NNDSS) is responsible for sharing information regarding notifiable diseases. As of 2020, the following are the notifiable diseases in the US as mandated by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention:
This is the first chapter of the ICD-11 MMS: Certain infectious or parasitic diseases. It covers ICD codes 1A00 to 1H0Z. The entities listed here are from the most recent revision of the ICD-11 MMS: version 04/2019. The full chapter can be browsed freely on the ICD-11 Browser of the website of the World Health Organization.