Related Research Articles

Mycobacterium is a genus of Actinobacteria, given its own family, the Mycobacteriaceae. Over 190 species are recognized in this genus. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis and leprosy in humans. The Greek prefix myco- means "fungus," alluding to the way mycobacteria have been observed to grow in a mold-like fashion on the surface of cultures. It is acid fast and cannot be stained by the Gram stain procedure.
Nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM), also known as environmental mycobacteria, atypical mycobacteria and mycobacteria other than tuberculosis (MOTT), are mycobacteria which do not cause tuberculosis or leprosy. NTM do cause pulmonary diseases that resemble tuberculosis. Mycobacteriosis is any of these illnesses, usually meant to exclude tuberculosis. They occur in many animals, including humans.
The Runyon classification of nontuberculous mycobacteria based on the rate of growth, production of yellow pigment and whether this pigment was produced in the dark or only after exposure to light.

Mycobacterium abscessus complex (MABSC) is a group of rapidly growing, multidrug-resistant, nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) species that are common soil and water contaminants. Although M. abscessus complex most commonly causes chronic lung infection and skin and soft tissue infection (SSTI), the complex can also cause infection in almost all human organs, mostly in patients with suppressed immune systems. Amongst NTM species responsible for disease, infection caused by M. abscessus complex are more difficult to treat due to antimicrobial drug resistance.
Mycobacterium boenickei is a member of the Mycobacterium fortuitum third biovariant complex. They are rapidly growing ubiquitous environmental organisms that normally inhabit soil, dust and water. These organisms frequently are human pathogens that cause a wide spectrum of clinically significant disease. It is important for practitioners to be aware of these organisms as possible etiological agents, as they are resistant to most first-line anti-tuberculous agents.
Mycobacterium bolletii is a bacterial species of the phylum Actinobacteria and the genus Mycobacterium. It was named in honor of Claude Bollet, a famous clinical microbiologist and taxonomist.
Mycobacterium brisbanense is a member of the Mycobacterium fortuitum third biovariant complex. They are rapidly growing ubiquitous environmental organisms that normally inhabit soil, dust and water. These organisms frequently are human pathogens that cause a wide spectrum of clinically significant disease. It is important for practitioners to be aware of these organisms as possible etiological agents, as they are resistant to most first-line anti-tuberculous agents.
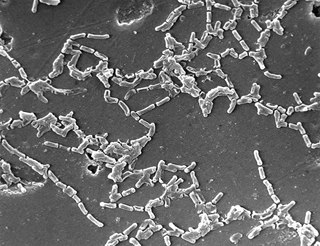
Mycobacterium chelonae is a species of the phylum Actinobacteria, belonging to the genus Mycobacterium. Mycobacterium chelonae is a rapidly growing mycobacterium, that is found all throughout the environment including sewage and tap water. It can occasionally cause opportunistic infections of humans.
Mycobacterium conceptionense is a non pigmented rapidly growing mycobacterium was first isolated from wound liquid outflow, bone tissue biopsy, and excised skin tissue from a 31-year-old woman who suffered an accidental open right tibia fracture and prolonged stay in a river. Etymology: conceptionense, pertaining to Hôpital de la Conception, the hospital where the first strain was isolated.

Mycobacterium cosmeticum is a rapidly growing mycobacterium that was first isolated from cosmetic patients and sites performing cosmetic procedures.

Mycobacterium fortuitum is a nontuberculous species of the phylum Actinobacteria, belonging to the genus Mycobacterium.
Mycobacterium goodii is an acid-fast bacterial species in the phylum Actinobacteria and the genus Mycobacterium.
Mycobacterium houstonense is a member of the Mycobacterium fortuitum third biovariant complex. The specific epithet houstonense refers to Houston, Texas, where the first isolate of the M. fortuitum third biovariant (sorbitol-positive) was identified.
Mycobacterium mucogenicum
Etymology: mucogenicum, from the organism's highly mucoid appearance.
Mycobacterium neworleansense is a member of the Mycobacterium fortuitum third biovariant complex.
The MCAG group is a group of Mycobacteria.
Mycobacterium peregrinum is a species of Mycobacterium.
Mycobacterium novocastrense is a species of Mycobacterium.
Mycobacterium rhodesiae is a species of Mycobacterium.
Mycobacterium stephanolepidis is an acid fast, rod-shaped bacteria that can form either round or smooth colonies, without pigmentation. The species name is derived from the fish that it was first discovered for infecting, Stephanolepis cirrhifer. This species grows on Middlebrook 7H11 agar or egg slants after being incubated for 3–5 days at 30 °C. Mycobacterium stephanolepidis has catalase activity and urease activity, intermediate for iron uptake. The organism fails to show Tween 80 hydrolysis, nitrate reduction, or arylsulfatase activity. It does not gro on Middlebrook 7H11 agar with picric acid. It has very little growth with 5% salt." M. stephanolepidis is "susceptible to clarithromycin, doxycycline, and ciprofloxacin." It displays either intermediate and/or resistant to the anitbiotics rifampicin, streptomycin, kanamycin and amikacin.
References
- ↑ Esteban J, Ortiz-Pérez A (December 2009). "Current treatment of atypical mycobacteriosis". Expert Opin Pharmacother. 10 (17): 2787–99. doi:10.1517/14656560903369363. PMID 19929702. S2CID 9877696.
- ↑ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.