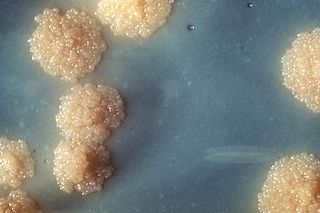
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, also known as Koch's bacillus, is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis. First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, M. tuberculosis has an unusual, waxy coating on its cell surface primarily due to the presence of mycolic acid. This coating makes the cells impervious to Gram staining, and as a result, M. tuberculosis can appear weakly Gram-positive. Acid-fast stains such as Ziehl–Neelsen, or fluorescent stains such as auramine are used instead to identify M. tuberculosis with a microscope. The physiology of M. tuberculosis is highly aerobic and requires high levels of oxygen. Primarily a pathogen of the mammalian respiratory system, it infects the lungs. The most frequently used diagnostic methods for tuberculosis are the tuberculin skin test, acid-fast stain, culture, and polymerase chain reaction.
Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis (MAP) is an obligate pathogenic bacterium in the genus Mycobacterium. It is often abbreviated M. paratuberculosis or M. avium ssp. paratuberculosis. It is the causative agent of Johne's disease, which affects ruminants such as cattle, and suspected causative agent in human Crohn's disease and rheumatoid arthritis. The type strain is ATCC 19698.
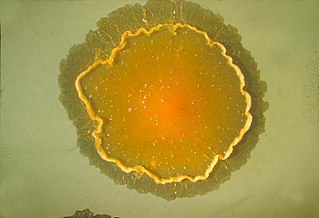
Mycobacterium marinum is a slow growing mycobacterium (SGM) belonging to the genus Mycobacterium and the phylum Actinobacteria. The strain marinum was first identified by Aronson in 1926 and it is observed as a pathogenic mycobacterium. For example, tuberculosis like infections in fish (mycobacteriosis) and skin lesions in humans.
Mycobacterium boenickei is a member of the Mycobacterium fortuitum third biovariant complex. They are rapidly growing ubiquitous environmental organisms that normally inhabit soil, dust and water. These organisms frequently are human pathogens that cause a wide spectrum of clinically significant disease. It is important for practitioners to be aware of these organisms as possible etiological agents, as they are resistant to most first-line anti-tuberculous agents.
Mycobacterium bohemicum is a species of the phylum Actinomycetota, belonging to the genus Mycobacterium.
Mycobacterium brisbanense is a member of the Mycobacterium fortuitum third biovariant complex. They are rapidly growing ubiquitous environmental organisms that normally inhabit soil, dust and water. These organisms frequently are human pathogens that cause a wide spectrum of clinically significant disease. It is important for practitioners to be aware of these organisms as possible etiological agents, as they are resistant to most first-line anti-tuberculous agents.

Mycobacteroides chelonae is a species of bacteria from the phylum Actinomycetota belonging to the genus Mycobacteroides. Mycobacteroides chelonae is a rapidly growing mycobacterium that is found all throughout the environment, including sewage and tap water. It can occasionally cause opportunistic infections of humans.
Mycobacterium chlorophenolicum is a species of the phylum Actinomycetota, belonging to the genus Mycobacterium.
Mycobacterium elephantis, a bacterium of the family Mycobacteriaceae, was discovered and isolated from a deceased elephant near India and may be linked to respiratory dysfunction. Organisms in the genus Mycobacterium are known to be aerobic and non-motile. Organisms within Mycobacterium belong to either the rapid growing group or the slow growing group. M. elephantis is classified as a rapid grower and relates most closely to Mycobacterium confluentis and Mycobacterium phlei.
Mycobacterium gordonae is a species of Mycobacterium named for Ruth E. Gordon. It is a species of the phylum Actinomycetota, belonging to the genus Mycobacterium.
Mycobacterium houstonense is a member of the Mycobacterium fortuitum third biovariant complex. The specific epithet houstonense refers to Houston, Texas, where the first isolate of the M. fortuitum third biovariant (sorbitol-positive) was identified.
Mycobacterium avium complex is a group of mycobacteria comprising Mycobacterium intracellulare and Mycobacterium avium that are commonly grouped because they infect humans together; this group, in turn, is part of the group of nontuberculous mycobacteria. These bacteria cause Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare infections or Mycobacterium avium complex infections in humans. These bacteria are common and are found in fresh and salt water, in household dust and in soil. MAC bacteria usually cause infection in those who are immunocompromised or those with severe lung disease.

Mycobacterium kansasii is a bacterium in the Mycobacterium genus. It is an environmental bacteria that causes opportunistic infections in humans, and is the one of the leading mycobacterial causes of human disease after tuberculosis and leprosy.
Mycobacterium montefiorense is a species of bacteria which cause granulomatous skin disease of moray eels. Sequence analysis, of the 16S rRNA gene reveals M. montefiorense is most closely related to Mycobacterium triplex, an opportunistic pathogen of humans.
Mycobacterium neworleansense is a member of the Mycobacterium fortuitum third biovariant complex.
Mycobacterium palustre is a slowly growing mycobacterium first isolated from an environmental source in Finland. It is potentially pathogenic, and has been isolated from human and veterinary clinical specimens.
Mycobacterium saskatchewanense is a species of Mycobacterium.
Mycobacterium parmense is a species of Mycobacterium.
Mycobacterium peregrinum is a species of Mycobacterium.
Mycobacterium rhodesiae is a species of Mycobacterium.



