
Mycobacterium is a genus of over 190 species in the phylum Actinomycetota, assigned its own family, Mycobacteriaceae. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis and leprosy in humans. The Greek prefix myco- means 'fungus', alluding to this genus' mold-like colony surfaces. Since this genus has cell walls with Gram-positive and Gram-negative features, acid-fast staining is used to emphasize their resistance to acids, compared to other cell types.
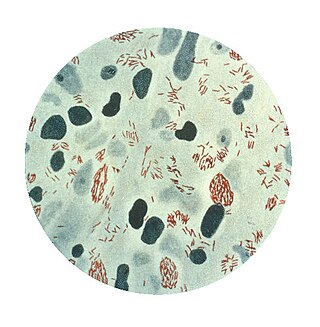
Mycobacterium leprae, is one of the two species of bacteria that cause Hansen’s disease (leprosy), a chronic but curable infectious disease that damages the peripheral nerves and targets the skin, eyes, nose, and muscles.
Adenitis is a general term for an inflammation of a gland. Often it is used to refer to lymphadenitis which is the inflammation of a lymph node.
Nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM), also known as environmental mycobacteria, atypical mycobacteria and mycobacteria other than tuberculosis (MOTT), are mycobacteria which do not cause tuberculosis or leprosy. NTM do cause pulmonary diseases that resemble tuberculosis. Mycobacteriosis is any of these illnesses, usually meant to exclude tuberculosis. They occur in many animals, including humans and are commonly found in soil and water.
Mycobacterium xenopi is a slow-growing scotochromogenic species of Mycobacterium. It was first reported by Schwabacher in 1959, having been isolated in lesions found on a Xenopus laevis, but the possibility of human infection was not confirmed until 1965. It has been cultured from hot and cold water taps, hospital hot water generators and storage tanks, and other environmental sources.

Buruli ulcer is an infectious disease characterized by the development of painless open wounds. The disease is limited to certain areas of the world, most cases occurring in Sub-Saharan Africa and Australia. The first sign of infection is a small painless nodule or area of swelling, typically on the arms or legs. The nodule grows larger over days to weeks, eventually forming an open ulcer. Deep ulcers can cause scarring of muscles and tendons, resulting in permanent disability.

Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare infection (MAI) is an atypical mycobacterial infection, i.e. one with nontuberculous mycobacteria or NTM, caused by Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC), which is made of two Mycobacterium species, M. avium and M. intracellulare. This infection causes respiratory illness in birds, pigs, and humans, especially in immunocompromised people. In the later stages of AIDS, it can be very severe. It usually first presents as a persistent cough. It is typically treated with a series of three antibiotics for a period of at least six months.
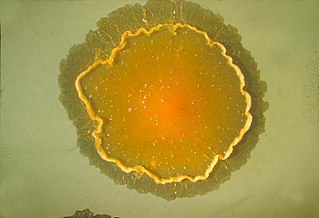
Mycobacterium marinum is a slow growing mycobacterium (SGM) belonging to the genus Mycobacterium and the phylum Actinobacteria. The strain marinum was first identified by Aronson in 1926 and it is observed as a pathogenic mycobacterium. For example, tuberculosis like infections in fish (mycobacteriosis) and skin lesions in humans.

Mycobacteroides abscessus is a species of rapidly growing, multidrug-resistant, nontuberculous mycobacteria that is a common soil and water contaminant. Although M. abscessus most commonly causes chronic lung infection and skin and soft tissue infection (SSTI), it can also cause infection in almost all human organs, mostly in patients with suppressed immune systems. Amongst NTM species responsible for disease, infection caused by M. abscessus complex are more difficult to treat due to antimicrobial drug resistance.
Mycobacterium boenickei is a member of the Mycobacterium fortuitum third biovariant complex. They are rapidly growing ubiquitous environmental organisms that normally inhabit soil, dust and water. These organisms frequently are human pathogens that cause a wide spectrum of clinically significant disease. It is important for practitioners to be aware of these organisms as possible etiological agents, as they are resistant to most first-line anti-tuberculous agents.
Mycobacterium brisbanense is a member of the Mycobacterium fortuitum third biovariant complex. They are rapidly growing ubiquitous environmental organisms that normally inhabit soil, dust and water. These organisms frequently are human pathogens that cause a wide spectrum of clinically significant disease. It is important for practitioners to be aware of these organisms as possible etiological agents, as they are resistant to most first-line anti-tuberculous agents.

Mycobacteroides chelonae is a species of bacteria from the phylum Actinomycetota belonging to the genus Mycobacteroides. Mycobacteroides chelonae is a rapidly growing mycobacterium that is found all throughout the environment, including sewage and tap water. It can occasionally cause opportunistic infections of humans.

Mycobacterium fortuitum is a nontuberculous species of the phylum Actinomycetota, belonging to the genus Mycobacterium.
Mycobacterium avium complex is a group of mycobacteria comprising Mycobacterium intracellulare and Mycobacterium avium that are commonly grouped because they infect humans together; this group, in turn, is part of the group of nontuberculous mycobacteria. These bacteria cause Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare infections or Mycobacterium avium complex infections in humans. These bacteria are common and are found in fresh and salt water, in household dust and in soil. MAC bacteria usually cause infection in those who are immunocompromised or those with severe lung disease.

Mycobacterium kansasii is a bacterium in the Mycobacterium genus. It is an environmental bacteria that causes opportunistic infections in humans, and is the one of the leading mycobacterial causes of human disease after tuberculosis and leprosy.
Mycobacterium mucogenicum
Etymology: mucogenicum, from the organism's highly mucoid appearance.
T-SPOT.TB is a type of ELISpot assay used for tuberculosis diagnosis, which belongs to the group of interferon gamma release assays. The test is manufactured by Oxford Immunotec in the UK. It is available in most European countries, the United States as well as various other countries. It was developed by researchers at the University of Oxford in England.
Tuberculous cellulitis is a skin condition resulting from infection with mycobacterium, and presenting as cellulitis.
Aquarium granuloma is a rare skin condition caused by a non-tubercular mycobacterium known as Mycobacterium marinum. Skin infections with M. marinum in humans are relatively uncommon, and are usually acquired from contact with contaminated swimming pools, aquariums or infected fish.
Mycolicibacterium agri is a species of bacteria from the phylum Actinomycetota that was first isolated from soil. It is non-pigmented and grows rapidly at 25–45 °C on Ogawa egg medium. It has also been isolated from a human skin infection, and raw milk M. agri is capable of degrading octocrylene.








