
Mycobacterium is a genus of over 190 species in the phylum Actinomycetota, assigned its own family, Mycobacteriaceae. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis and leprosy in humans. The Greek prefix myco- means 'fungus', alluding to this genus' mold-like colony surfaces. Since this genus has cell walls with Gram-positive and Gram-negative features, acid-fast staining is used to emphasize their resistance to acids, compared to other cell types.
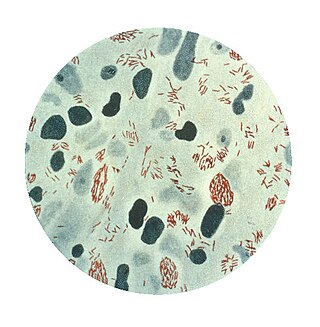
Mycobacterium leprae, is one of the two species of bacteria that cause Hansen’s disease (leprosy), a chronic but curable infectious disease that damages the peripheral nerves and targets the skin, eyes, nose, and muscles.
Mycolicibacterium alvei is a species of the phylum Actinomycetota, belonging to the genus Mycolicibacterium.
Mycobacterium brumae is a rapidly growing environmental mycobacterial species identified in 1993. Aside from one 2004 report of a catheter related bloodstream infection no other infections by this organism have been reported. It was first isolated from water, soil and one human sputum sample in Spain.
Mycobacterium caprae is a species of bacteria in the genus Mycobacterium and a member of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. The species is named after the caprines, the organisms from which M. caprae was first isolated. Prior to 2003, the species was referred to as Mycobacterium tuberculosis subsp. caprae. It is also synonymous with the name Mycobacterium bovis subsp. caprae.
Mycobacterium conceptionense is a non pigmented rapidly growing mycobacterium was first isolated from wound liquid outflow, bone tissue biopsy, and excised skin tissue from a 31-year-old woman who suffered an accidental open right tibia fracture and prolonged stay in a river. Etymology: conceptionense, pertaining to Hôpital de la Conception, the hospital where the first strain was isolated.
Mycobacterium cookii is a species of the phylum Actinomycetota, belonging to the genus Mycobacterium.
Mycobacterium diernhoferi is a species of the phylum Actinomycetota, belonging to the genus Mycobacterium.
Mycobacterium duvalii is a species of the phylum Actinomycetota, belonging to the genus Mycobacterium.
Mycobacterium elephantis, a bacterium of the family Mycobacteriaceae, was discovered and isolated from a deceased elephant near India and may be linked to respiratory dysfunction. Organisms in the genus Mycobacterium are known to be aerobic and non-motile. Organisms within Mycobacterium belong to either the rapid growing group or the slow growing group. M. elephantis is classified as a rapid grower and relates most closely to Mycobacterium confluentis and Mycobacterium phlei.
Mycobacterium genavense is a slow-growing species of the phylum Actinomycetota, belonging to the genus Mycobacterium.
Mycolicibacter hiberniae is a species of bacteria in the phylum Actinomycetota.

Mycobacterium kansasii is a bacterium in the Mycobacterium genus. It is an environmental bacteria that causes opportunistic infections in humans, and is the one of the leading mycobacterial causes of human disease after tuberculosis and leprosy.
Mycobacterium lacus is a species of bacteria in the genus Mycobacterium known to be a causative agent in immunocompetent individuals.
Mycobacterium vanbaalenii is a rapidly growing mycobacterium that can use polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. It was first isolated from petroleum-contaminated estuarine sediments and has been shown by 16S rRNA gene sequencing to be closely related to Mycobacterium aurum and Mycobacterium vaccae. M. vanbaalenii has potential use in the bioremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated environmental sites. Etymology: vanbaalenii of Van Baalen, in memory of Dr Chase Van Baalen, late Professor at The University of Texas Marine Science Institute, Port Aransas Marine Laboratory, Port Aransas, TX, USA.
Mycobacterium pyrenivorans is a scotochromogenic, rapidly growing mycobacterium, first isolated from an enrichment culture obtained from soil that was highly contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). The soil sample was collected on the site of a former coking plant at Ubach-Palenberg, Germany. Etymology: pyrenivorans; digesting pyrene.
Mycobacterium peregrinum is a species of Mycobacterium.
Mycobacterium novocastrense is a species of Mycobacterium.
Mycobacterium rhodesiae is a species of Mycobacterium.

Mycobacterium ulcerans is a species of bacteria found in various aquatic environments. The bacteria can infect humans and some other animals, causing persistent open wounds called Buruli ulcer. M. ulcerans is closely related to Mycobacterium marinum, from which it evolved around one million years ago, and more distantly to the mycobacteria which cause tuberculosis and leprosy.



