| Papulonecrotic tuberculid | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
Papulonecrotic tuberculid is usually an asymptomatic, chronic skin disorder, presenting in successive crops, skin lesions symmetrically distributed on the extensor extremities. [1] :337 [2]
| Papulonecrotic tuberculid | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
Papulonecrotic tuberculid is usually an asymptomatic, chronic skin disorder, presenting in successive crops, skin lesions symmetrically distributed on the extensor extremities. [1] :337 [2]

A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment.

Hyperpigmentation is the darkening of an area of skin or nails caused by increased melanin.

Tuberculosis verrucosa cutis is a rash of small, red papular nodules in the skin that may appear 2–4 weeks after inoculation by Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a previously infected and immunocompetent individual.

Scrofuloderma is a skin condition caused by tuberculous involvement of the skin by direct extension, usually from underlying tuberculous lymphadenitis.

Epidermolysis bullosa simplex (EBS), is a disorder resulting from mutations in the genes encoding keratin 5 or keratin 14.
Lichen spinulosus is a rare skin disorder characterized by follicular keratotic papules that are grouped into large patches. It is a variant of keratosis pilaris named for its resemblance to a patch of lichen.
Tropical acne is unusually severe acne occurring in the tropics during seasons when the weather is hot and humid.

Periorbital dermatitis is a skin condition, a variant of perioral dermatitis, occurring on the lower eyelids and skin adjacent to the upper and lower eyelids.
Prurigo gestationis is an eruption consisting of pruritic, excoriated papules of the proximal limbs and upper trunk, most often occurring between the 20th and 34th week of gestation.
Impetigo herpetiformis is a form of severe pustular psoriasis occurring in pregnancy which may occur during any trimester.
Erosive pustular dermatitis of the scalp presents with pustules, erosions, and crusts on the scalp of primarily older Caucasian females, and on biopsy, has a lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate with or without foreign body giant cells and pilosebaceous atrophy.
Keratosis pilaris atrophicans faciei begins in infancy as follicular papules with perifollicular erythema. Initially, the lesions are restricted to the lateral eyebrows, but with time spread to involve the cheeks and forehead, and may also be associated with keratosis pilaris on the extremities and buttocks.
Primary inoculation tuberculosis is a skin condition that develops at the site of inoculation of tubercle bacilli into a tuberculosis-free individual.
Tuberculosis cutis orificialis is a form of cutaneous tuberculosis that occurs at the mucocutaneous borders of the nose, mouth, anus, urinary meatus, and vagina, and on the mucous membrane of the mouth or tongue.
Lichen scrofulosorum is a rare tuberculid that presents as a lichenoid eruption of minute papules in children and adolescents with tuberculosis. The lesions are usually asymptomatic, closely grouped, skin-colored to reddish-brown papules, often perifollicular and are mainly found on the abdomen, chest, back, and proximal parts of the limbs. The eruption is usually associated with a strongly positive tuberculin reaction. Of the three tuberculids, the incidence of lichen scrofulosorum was found to be the lowest (2%) in a large study conducted in Hong Kong. This highlights its rarity and significance as an important marker of undetected tuberculosis.
Aquarium granuloma is a skin condition caused by Mycobacterium marinum, characterized by a skin lesion that presents roughly three weeks after exposure.
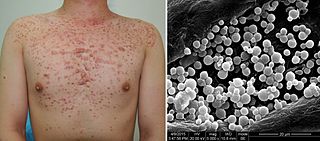
Malassezia folliculitis or Pityrosporum folliculitis, is a skin condition caused by infection by Malassezia yeast.
Cutaneous actinomycosis is a chronic disease that affects the deep subcutaneous tissue of the skin. Caused by an anaerobic, Gram-positive, filamentous type of bacteria in the genus Actinomyces, invasion of the soft tissue leads to the formation of abnormal channels leading to the skin surface that discharge pale yellow sulfur granules.

Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia refers to a groups of benign cutaneous disorders characterized by collections of lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells in the skin. Conditions included in this groups are:

Tuberculous gumma is a skin condition characterized histologically by massive necrosis. Restated, this is a skin condition that results from hematogenous dissemination of mycobacteria from a primary focus, resulting in firm, nontender erythematous nodules that soften, ulcerate, and form sinuses.
| Classification |
|
|---|