
Dandruff is a skin condition that mainly affects the scalp. Symptoms include flaking and sometimes mild itchiness. It can result in social or self-esteem problems. A more severe form of the condition, which includes inflammation of the skin, is known as seborrhoeic dermatitis.
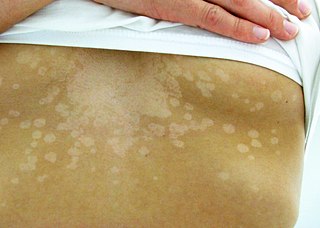
Tinea versicolor is a condition characterized by a skin eruption on the trunk and proximal extremities. The majority of tinea versicolor is caused by the fungus Malassezia globosa, although Malassezia furfur is responsible for a small number of cases. These yeasts are normally found on the human skin and become troublesome only under certain circumstances, such as a warm and humid environment, although the exact conditions that cause initiation of the disease process are poorly understood.

Folliculitis is the infection and inflammation of one or more hair follicles. The condition may occur anywhere on hair covered skin. The rash may appear as pimples that come to white tips on the face, chest, back, arms, legs, buttocks, or head.

A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest number on the face and scalp, but also on all parts of the skin except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. In the eyelids, meibomian glands, also called tarsal glands, are a type of sebaceous gland that secrete a special type of sebum into tears. Surrounding the female nipple, areolar glands are specialized sebaceous glands for lubricating the nipple. Fordyce spots are benign, visible, sebaceous glands found usually on the lips, gums and inner cheeks, and genitals.
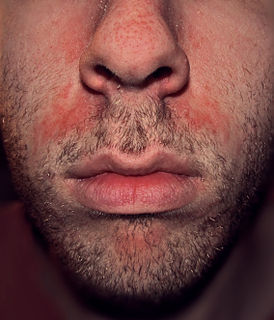
Seborrhoeic dermatitis, also known as seborrhoea, is a long-term skin disorder. Symptoms include red, scaly, greasy, itchy, and inflamed skin. Areas of the skin rich in oil-producing glands are often affected including the scalp, face, and chest. It can result in social or self-esteem problems. In babies, when the scalp is primarily involved, it is called cradle cap. Dandruff is a milder form of the condition without inflammation.

Malassezia is a genus of fungi. Malassezia is naturally found on the skin surfaces of many animals, including humans. In occasional opportunistic infections, some species can cause hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation on the trunk and other locations in humans. Allergy tests for this fungus are available.
Skin disorders are among the most common health problems in dogs, and have many causes. The condition of a dog's skin and coat are also an important indicator of its general health. Skin disorders of dogs vary from acute, self-limiting problems to chronic or long-lasting problems requiring life-time treatment. Skin disorders may be primary or secondary in nature, making diagnosis complicated.
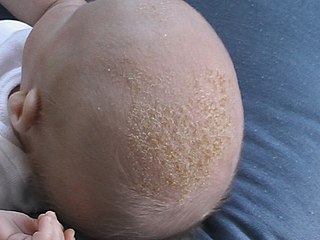
Cradle cap causes crusty or oily scaly patches on a baby's scalp. The condition is not painful or itchy, but it can cause thick white or yellow scales that are not easy to remove. Cradle cap most commonly begins sometime in the first three months but can occur in later years. Similar symptoms in older children are more likely to be dandruff than cradle cap. The rash is often prominent around the ear, the eyebrows or the eyelids. It may appear in other locations as well, where it is called infantile seborrhoeic dermatitis. Cradle cap is just a special - and more benign - case of this condition. The exact cause of cradle cap is not known. Cradle cap is not spread from person to person (contagious). It is also not caused by poor hygiene. It is not an allergy, and it is not dangerous. Cradle cap often lasts a few months. In some children, the condition can last until age 2 or 3.

Azelaic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOOC(CH2)7COOH. This saturated dicarboxylic acid exists as a white powder. It is found in wheat, rye, and barley. It is a precursor to diverse industrial products including polymers and plasticizers, as well as being a component of a number of hair and skin conditioners.
Eosinophilic folliculitis is an itchy rash with an unknown cause that is most common among individuals with HIV, though it can occur in HIV-negative individuals where it is known by the eponym Ofuji disease. EF consists of itchy red bumps (papules) centered on hair follicles and typically found on the upper body, sparing the abdomen and legs. The name eosinophilic folliculitis refers to the predominant immune cells associated with the disease (eosinophils) and the involvement of the hair follicles.

Malassezia furfur is a species of yeast that is naturally found on the skin surfaces of humans and some other mammals. It is associated with a variety of dermatological conditions caused by fungal infections, notably seborrhoeic dermatitis and tinea versicolor. As an opportunistic pathogen, it has further been associated with dandruff, malassezia folliculitis, pityriasis versicolor, and tinea circinata, as well as catheter-related fungemia and pneumonia in patients receiving hematopoietic transplants. The fungus can also affect other animals, including dogs.
Acne medicamentosa is acne that is caused or aggravated by medication. Because acne is generally a disorder of the pilosebaceous units caused by hormones, the medications that trigger acne medicamentosa most frequently are hormone analogs. It is also often caused by corticosteroids; in this case, it is referred to as steroid acne.
Hidradenitis is any disease in which the histologic abnormality is primarily an inflammatory infiltrate around the eccrine glands. This group includes neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis and recurrent palmoplantar hidradenitis.

Cutis verticis gyrata is a medical condition usually associated with thickening of the scalp. People show visible folds, ridges or creases on the surface of the top of the scalp. The number of folds can vary from two to roughly ten and are typically soft and spongy. These folds cannot be corrected with pressure. The condition typically affects the central and rear regions of the scalp, but sometimes can involve the entire scalp.

Microsporum audouinii is an anthropophilic fungus in the genus Microsporum. It is a type of dermatophyte that colonizes keratinized tissues causing infection. The fungus is characterized by its spindle-shaped macroconidia, clavate microconidia as well as its pitted or spiny external walls.
Anti-seborrheics are drugs effective in seborrheic dermatitis. Selenium sulfide, zinc pyrithione, corticosteroids, imidazole antifungals, and salicylic acid are common anti-seborrheics.
Mycobiota are a group of all the fungi present in a particular geographic region or habitat type.
Malassezia pachydermatis is a zoophilic yeast in the division Basidiomycota. It was first isolated in 1925 by Fred Weidman, and has been named pachydermatis Greek for "thick-skin" after the original sample taken from an Indian rhinoceros with severe exfoliative dermatitis. Within the genus Malassezia, M. pachydermatis is most closely related to the species M. furfur. A commensal fungus, it can be found within the microflora of healthy mammals such as humans, cats and dogs, However, it is capable of acting as an opportunistic pathogen under special circumstances and has been seen to cause skin and ear infections, most often occurring in canines.
Malassezia sympodialis is a species in the genus Malassezia. It is characterized by a pronounced lipophily, unilateral, percurrent or sympodial budding and an irregular, corrugated cell wall ultrastructure. It is one of the most common species found on the skin of healthy and diseased individuals. It is considered to be part of the skin's normal human microbiota and begins to colonize the skin of humans shortly after birth. Malassezia sympodialis, often has a symbiotic or commensal relationship with its host, but it can act as a pathogen causing a number of different skin diseases, such as atopic dermatitis.











