Related Research Articles

Chorioretinitis is an inflammation of the choroid and retina of the eye. It is a form of posterior uveitis. If only the choroid is inflamed, not the retina, the condition is termed choroiditis. The ophthalmologist's goal in treating these potentially blinding conditions is to eliminate the inflammation and minimize the potential risk of therapy to the patient.

Histoplasmosis is a disease caused by the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum. Symptoms of this infection vary greatly, but the disease affects primarily the lungs. Occasionally, other organs are affected; called disseminated histoplasmosis, it can be fatal if left untreated.

A granuloma is an aggregation of macrophages that forms in response to chronic inflammation. This occurs when the immune system attempts to isolate foreign substances that it is otherwise unable to eliminate. Such substances include infectious organisms including bacteria and fungi, as well as other materials such as foreign objects, keratin, and suture fragments.
Hepatosplenomegaly is the simultaneous enlargement of both the liver (hepatomegaly) and the spleen (splenomegaly). Hepatosplenomegaly can occur as the result of acute viral hepatitis, infectious mononucleosis, and histoplasmosis or it can be the sign of a serious and life-threatening lysosomal storage disease. Systemic venous hypertension can also increase the risk for developing hepatosplenomegaly, which may be seen in those patients with right-sided heart failure.
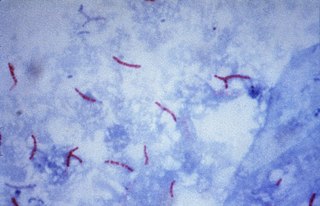
Ziehl–Neelsen staining is a type of acid-fast stain, first introduced by Paul Ehrlich. Ziehl–Neelsen staining is a bacteriological stain used to identify acid-fast organisms, mainly Mycobacteria. It is named for two German doctors who modified the stain: the bacteriologist Franz Ziehl (1859–1926) and the pathologist Friedrich Neelsen (1854–1898).

Parotitis is an inflammation of one or both parotid glands, the major salivary glands located on either side of the face, in humans. The parotid gland is the salivary gland most commonly affected by inflammation.

Mycoses are infectious diseases caused by pathogenic fungi. They include fungal infections of the skin, just under the skin and ones that are more deep or widespread such as histoplasmosis and blastomycosis. They include yeast infections such as candidiasis and pityriasis versicolor, and include several other opportunistic fungal infections such as aspergillosis and mucormycosis. Several, including sporotrichosis, chromoblastomycosis and mycetoma are neglected.
Voriconazole, sold under the brand name Vfend among others, is an antifungal medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. This includes aspergillosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, penicilliosis, and infections by Scedosporium or Fusarium. It can be taken by mouth or used by injection into a vein.
The CDC Classification System for HIV Infection is the medical classification system used by the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to classify HIV disease and infection. The system is used to allow the government to handle epidemic statistics and define who receives US government assistance.
Talaromycosis is an infection caused by Talaromyces marneffei. The disease is endemic exclusively to southeast Asia. The disease usually affects people with a weakened immune system; healthy people are rarely affected. Talaromycosis often presents with non-specific symptoms and with skin bumps that are usually small and painless and usually affect the face and neck. The infection is thought to be acquired by inhaling the pathogen from the environment, however, the environmental source of the organism is not known. The disease is treatable with antifungal medications. The disease is likely to end in death if not treated.

Presumed ocular histoplasmosis syndrome (POHS) is a syndrome affecting the eye, which is characterized by peripheral atrophic chorioretinal scars, atrophy or scarring adjacent to the optic disc and maculopathy.

Histoplasma is a genus of dimorphic fungi commonly found in bird and bat fecal material. Histoplasma contains a few species, including—Histoplasma capsulatum—the causative agent of histoplasmosis; and Histoplasma capsulatum var. farciminosum, causing epizootic lymphangitis in horses.

Histoplasma capsulatum is a species of dimorphic fungus. Its sexual form is called Ajellomyces capsulatus. It can cause pulmonary and disseminated histoplasmosis.

Guano is the accumulated excrement of seabirds and bats. As a manure, guano is a highly effective fertilizer due to its exceptionally high content of nitrogen, phosphate, and potassium: key nutrients essential for plant growth. Guano was also, to a lesser extent, sought for the production of gunpowder and other explosive materials.
Primary pulmonary histoplasmosis is caused by inhalation of Histoplasma capsulatum spores, and approximately 10% of people with this acute infection develop erythema nodosum.
Progressive disseminated histoplasmosis is an infection caused by Histoplasma capsulatum, and most people who develop this severe form of histoplasmosis are immunocompromised or taking systemic corticosteroids. Skin lesions are present in approximately 6% of patients with dissemination.
African histoplasmosis is a fungal infection caused by Histoplasma capsulatumvar. duboisii, or Histoplama duboisii (Hcd). Disease has been most often reported in Uganda, Nigeria, Zaire and Senegal, as Hcd is exclusive to Africa. In human disease it manifests differently than histoplasmosis, most often involving the skin and bones and rarely involving the lungs. Also unlike Hcc, Hcd has been reported to rarely present in those with HIV, likely due to underreporting. However, this along with the differences in Hcc and Hcd have been disputed.
Histoplasma duboisii is a saprotrophic fungus responsible for the invasive infection known as African histoplasmosis. This species is a close relative of Histoplasma capsulatum, the agent of classical histoplasmosis, and the two occur in similar habitats. Histoplasma duboisii is restricted to continental Africa and Madagascar, although scattered reports have arisen from other places usually in individuals with an African travel history. Like, H. capsulatum, H. duboisii is dimorphic – growing as a filamentous fungus at ambient temperature and a yeast at body temperature. It differs morphologically from H. capsulatum by the typical production of a large-celled yeast form. Both agents cause similar forms of disease, although H. duboisii predominantly causes cutaneous and subcutaneous disease in humans and non-human primates. The agent responds to many antifungal drug therapies used to treat serious fungal diseases.
Charlotte Catherine Campbell was an American medical mycologist.
Emmonsiosis, also known as emergomycosis, is a systemic fungal infection that can affect the lungs, generally always affects the skin and can become widespread. The lesions in the skin look like small red bumps and patches with a dip, ulcer and dead tissue in the centre.
References
- ↑ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.