
Athlete's foot, known medically as tinea pedis, is a common skin infection of the feet caused by a fungus. Signs and symptoms often include itching, scaling, cracking and redness. In rare cases the skin may blister. Athlete's foot fungus may infect any part of the foot, but most often grows between the toes. The next most common area is the bottom of the foot. The same fungus may also affect the nails or the hands. It is a member of the group of diseases known as tinea.

Griseofulvin is an antifungal medication used to treat a number of types of dermatophytoses (ringworm). This includes fungal infections of the nails and scalp, as well as the skin when antifungal creams have not worked. It is taken by mouth.
Dermatophyte is a common label for a group of fungus of Arthrodermataceae that commonly causes skin disease in animals and humans. Traditionally, these anamorphic mold genera are: Microsporum, Epidermophyton and Trichophyton. There are about 40 species in these three genera. Species capable of reproducing sexually belong in the teleomorphic genus Arthroderma, of the Ascomycota. As of 2019 a total of nine genera are identified and new phylogenetic taxonomy has been proposed.

Tinea corporis is a fungal infection of the body, similar to other forms of tinea. Specifically, it is a type of dermatophytosis that appears on the arms and legs, especially on glabrous skin; however, it may occur on any superficial part of the body.

Tinea capitis is a cutaneous fungal infection (dermatophytosis) of the scalp. The disease is primarily caused by dermatophytes in the genera Trichophyton and Microsporum that invade the hair shaft. The clinical presentation is typically single or multiple patches of hair loss, sometimes with a 'black dot' pattern, that may be accompanied by inflammation, scaling, pustules, and itching. Uncommon in adults, tinea capitis is predominantly seen in pre-pubertal children, more often boys than girls.

Tinea barbae is a fungal infection of the hair. Tinea barbae is due to a dermatophytic infection around the bearded area of men. Generally, the infection occurs as a follicular inflammation, or as a cutaneous granulomatous lesion, i.e. a chronic inflammatory reaction. It is one of the causes of folliculitis. It is most common among agricultural workers, as the transmission is more common from animal-to-human than human-to-human. The most common causes are Trichophyton mentagrophytes and T. verrucosum.

Dermatophytosis, also known as tinea and ringworm, is a fungal infection of the skin, that may affect skin, hair, and nails. Typically it results in a red, itchy, scaly, circular rash. Hair loss may occur in the area affected. Symptoms begin four to fourteen days after exposure. The types of dermatophytosis are typically named for area of the body that they affect. Multiple areas can be affected at a given time.

The KOH Test for Candida albicans, also known as a potassium hydroxide preparation or KOH prep, is a quick, inexpensive fungal test to differentiate dermatophytes and Candida albicans symptoms from other skin disorders like psoriasis and eczema.

Trichophyton rubrum is a dermatophytic fungus in the phylum Ascomycota. It is an exclusively clonal, anthropophilic saprotroph that colonizes the upper layers of dead skin, and is the most common cause of athlete's foot, fungal infection of nail, jock itch, and ringworm worldwide. Trichophyton rubrum was first described by Malmsten in 1845 and is currently considered to be a complex of species that comprises multiple, geographically patterned morphotypes, several of which have been formally described as distinct taxa, including T. raubitschekii, T. gourvilii, T. megninii and T. soudanense.

Trichophyton is a genus of fungi, which includes the parasitic varieties that cause tinea, including athlete's foot, ringworm, jock itch, and similar infections of the nail, beard, skin and scalp. Trichophyton fungi are molds characterized by the development of both smooth-walled macro- and microconidia. Macroconidia are mostly borne laterally directly on the hyphae or on short pedicels, and are thin- or thick-walled, clavate to fusiform, and range from 4 to 8 by 8 to 50 μm in size. Macroconidia are few or absent in many species. Microconidia are spherical, pyriform to clavate or of irregular shape, and range from 2 to 3 by 2 to 4 μm in size.

Microsporum audouinii is an anthropophilic fungus in the genus Microsporum. It is a type of dermatophyte that colonizes keratinized tissues causing infection. The fungus is characterized by its spindle-shaped macroconidia, clavate microconidia as well as its pitted or spiny external walls.
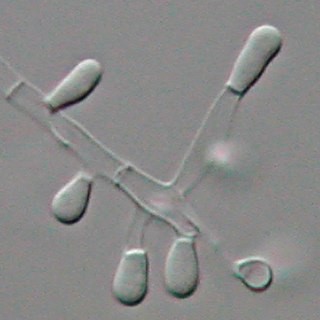
Trichophyton tonsurans is a fungus in the family Arthrodermataceae that causes ringworm infection of the scalp. It was first recognized by David Gruby in 1844. Isolates are characterized as the "–" or negative mating type of the Arthroderma vanbreuseghemii complex. This species is thought to be conspecific with T. equinum, although the latter represents the "+" mating strain of the same biological species Despite their biological conspecificity, clones of the two mating types appear to have undergone evolutionary divergence with isolates of the T. tonsurans-type consistently associated with Tinea capitis whereas the T. equinum-type, as its name implies, is associated with horses as a regular host. Phylogenetic relationships were established in isolates from Northern Brazil, through fingerprinting polymorphic RAPD and M13 markers. There seems to be lower genomic variability in the T. tonsurans species due to allopatric divergence. Any phenotypic density is likely due to environmental factors, not genetic characteristics of the fungus.

Majocchi's granuloma is a skin condition characterized by deep, pustular plaques, and is a form of tinea corporis. It is a localized form of fungal folliculitis. Lesions often have a pink and scaly central component with pustules or folliculocentric papules at the periphery. The name comes from Domenico Majocchi, who discovered the disorder in 1883. Majocchi was a professor of dermatology at the University of Parma and later the University of Bologna. This disease is most commonly caused by filamentous fungi in the genus Trichophyton.
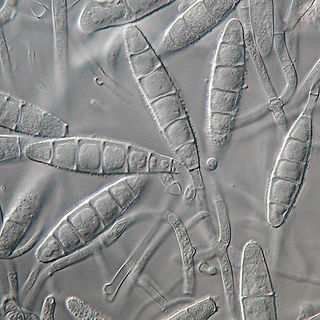
Microsporum gypseum is a soil-associated dermatophyte that occasionally is known to colonise and infect the upper dead layers of the skin of mammals. The name refers to an asexual "form-taxon" that has been associated with four related biological species of fungi: the pathogenic taxa Arthroderma incurvatum, A. gypsea, A. fulva and the non-pathogenic saprotroph A. corniculata. More recent studies have restricted M. gypseum to two teleomorphic species A. gypseum and A. incurvatum. The conidial states of A. fulva and A. corniculata have been assigned to M. fulvum and M. boullardii. Because the anamorphic states of these fungi are so similar, they can be identified reliably only by mating. Two mating strains have been discovered, "+" and "–". The classification of this species has been based on the characteristically rough-walled, blunt, club-shaped, multicelled macroconidia. Synonyms include Achorion gypseum, Microsporum flavescens, M. scorteum, and M. xanthodes. There has been past nomenclatural confusion in the usage of the generic names Microsporum and Microsporon.
Trichophyton concentricum is an anthropophilic dermatophyte believed to be an etiological agent of a type of skin mycosis in humans, evidenced by scaly cutaneous patches on the body known as tinea imbricata. This fungus has been found mainly in the Pacific Islands and South America.
Microsporum nanum is a pathogenic fungus in the family Arthrodermataceae. It is a type of dermatophyte that causes infection in dead keratinized tissues such as skin, hair, and nails. Microsporum nanum is found worldwide and is both zoophilic and geophilic. Animals such as pigs and sheep are the natural hosts for the fungus; however, infection of humans is also possible. Majority of the human cases reported are associated with pig farming. The fungus can invade the skin of the host; if it is scratched off by the infected animal, the fungus is still capable of reproducing in soil.

Microsporum gallinae is a fungus of the genus Microsporum that causes dermatophytosis, commonly known as ringworm. Chickens represent the host population of Microsporum gallinae but its opportunistic nature allows it to enter other populations of fowl, mice, squirrels, cats, dogs and monkeys. Human cases of M. gallinae are rare, and usually mild, non-life-threatening superficial infections.

Favus or tinea favosa is the severe form of tinea capitis, a skin infectious disease caused by the dermatophyte fungus Trichophyton schoenleinii. Typically the species affects the scalp, but occasionally occurs as onychomycosis, tinea barbae, or tinea corporis.
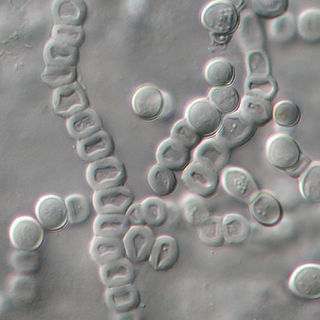
Trichophyton verrucosum, commonly known as the cattle ringworm fungus, is a dermatophyte largely responsible for fungal skin disease in cattle, but is also a common cause of ringworm in donkeys, dogs, goat, sheep, and horses. It has a worldwide distribution, however human infection is more common in rural areas where contact with animals is more frequent, and can cause severe inflammation of the afflicted region. Trichophyton verrucosum was first described by Emile Bodin in 1902.
















