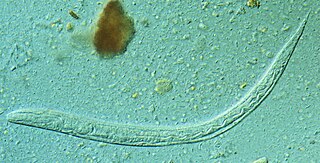
Strongyloides stercoralis is a human pathogenic parasitic roundworm causing the disease strongyloidiasis. Its common name in the US is threadworm. In the UK and Australia, however, the term threadworm can also refer to nematodes of the genus Enterobius, otherwise known as pinworms.
The order Ascaridida includes several families of parasitic roundworms with three "lips" on the anterior end. They were formerly placed in the subclass Rhabditia by some, but morphological and DNA sequence data rather unequivocally assign them to the Spiruria. The Oxyurida and Rhigonematida are occasionally placed in the Ascaridida as superfamily Oxyuroidea, but while they seem indeed to be Spiruria, they are not as close to Ascaris as such a treatment would place them. These "worms" contain a number of important parasites of humans and domestic animals.

Mebendazole (MBZ), sold under the brand name Vermox among others, is a medication used to treat a number of parasitic worm infestations. This includes ascariasis, pinworm infection, hookworm infections, guinea worm infections, hydatid disease, and giardia, among others. It is taken by mouth.

Secernentea was a class of nematodes in the Classical Phylogeny System and is no longer in use. This morphological-based classification system has been replaced by the Modern Phylogeny system, where taxonomy assignment is based on small subunit ribosomal DNA.

Helminthic therapy, an experimental type of immunotherapy, is the treatment of autoimmune diseases and immune disorders by means of deliberate infestation with a helminth or with the eggs of a helminth. Helminths are parasitic worms such as hookworms, whipworms, and threadworms that have evolved to live within a host organism on which they rely for nutrients. These worms are members of two phyla: nematodes, which are primarily used in human helminthic therapy, and flat worms (trematodes).
The soil-transmitted helminths are a group of intestinal parasites belonging to the phylum Nematoda that are transmitted primarily through contaminated soil. They are so called because they have a direct life cycle which requires no intermediate hosts or vectors, and the parasitic infection occurs through faecal contamination of soil, foodstuffs and water supplies. The adult forms are essentially parasites of humans, causing soil-transmitted helminthiasis (STH), but also infect domesticated mammals. The juveniles are the infective forms and they undergo tissue-migratory stages during which they invade vital organs such as lungs and liver. Thus the disease manifestations can be both local and systemic. The geohelminths together present an enormous infection burden on humanity, amounting to 135,000 deaths every year, and persistent infection of more than two billion people.
Dientamoebiasis is a medical condition caused by infection with Dientamoeba fragilis, a single-cell parasite that infects the lower gastrointestinal tract of humans. It is an important cause of traveler's diarrhea, chronic abdominal pain, chronic fatigue, and failure to thrive in children.
Gyrinicola batrachiensis are nematode parasites that are members of the order Oxyurida. Members of this order are also known as pinworms. These organisms are nematodes that feed on micro-particles in the gut of vertebrates and invertebrates. Oxyurida is further separated into two superfamilies: Oxyuroidea and Thelastomatoidea, which are parasites of vertebrates and invertebrates respectively. Oxyuroidea is composed on three families: Pharyngodonidae; parasites of herbivorous vertebrates, and Oxyuridae and Heteroxynematidae; parasites of mammals and some birds.

Subclass Spiruria comprises mostly parasitic secernentean nematodes. In an alternate classification, they are treated as suborder Spirurina, with the orders listed here being ranked as infraorders.

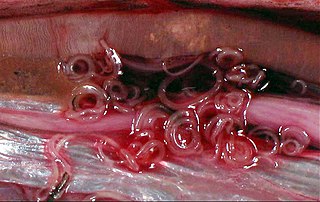
The pinworm, also known as threadworm or seatworm, is a parasitic worm. It is a nematode (roundworm) and a common intestinal parasite or helminth, especially in humans. The medical condition associated with pinworm infestation is known as pinworm infection (enterobiasis) or less precisely as oxyuriasis in reference to the family Oxyuridae.
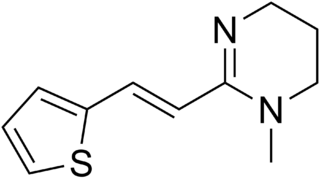
Pyrantel is a medication used to treat a number of parasitic worm infections. This includes ascariasis, hookworm infections, enterobiasis, trichostrongyliasis, and trichinellosis. It is taken by mouth.

The nematodes, roundworms or eelworms constitute the phylum Nematoda. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Most species are free-living, feeding on microorganisms, but there are many that are parasitic. The parasitic worms (helminths) are the cause of soil-transmitted helminthiases.
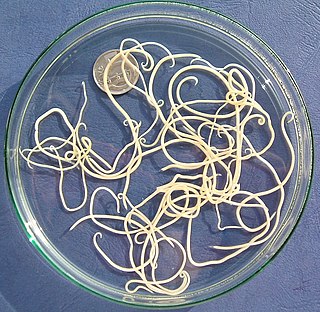
The suborder Ascaridina contains the bulk of the Ascaridida, parasitic roundworms with three "lips" on the anterior end. The Ascaridida were formerly placed in the subclass Rhabditia by some, but morphological and DNA sequence data rather unequivocally assigns them to the Spiruria. The Oxyurida and Rhigonematida are occasionally placed in the Ascaridina as superfamily Oxyuroidea, but while they seem indeed to be Spiruria, they are not as close to Ascaris as such a treatment would place them.

Archaeoparasitology, a multi-disciplinary field within paleopathology, is the study of parasites in archaeological contexts. It includes studies of the protozoan and metazoan parasites of humans in the past, as well as parasites which may have affected past human societies, such as those infesting domesticated animals.

Oxyuridae is a family of nematode worms of the class Secernentea. It consists of eight genera, one of which contains the human pinworm.
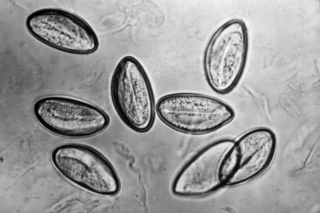
Pinworm infection, also known as enterobiasis, is a human parasitic disease caused by the pinworm, Enterobius vermicularis. The most common symptom is itching in the anal area. The period of time from swallowing eggs to the appearance of new eggs around the anus is 4 to 8 weeks. Some people who are infected do not have symptoms.

Vermiculation is a surface pattern of dense but irregular lines, so called from the Latin vermiculus meaning "little worm" because the shapes resemble worms, worm-casts, or worm tracks in mud or wet sand. The word may be used in a number of contexts for patterns that have little in common. The adjective vermiculated is more often used than the noun.
E. vermicularis may refer to:

Dientamoeba fragilis is a species of single-celled excavates found in the gastrointestinal tract of some humans, pigs and gorillas. It causes gastrointestinal upset in some people, but not in others. It is an important cause of travellers diarrhoea, chronic diarrhoea, fatigue and, in children, failure to thrive. Despite this, its role as a "commensal, pathobiont, or pathogen" is still debated. D. fragilis is one of the smaller parasites that are able to live in the human intestine. Dientamoeba fragilis cells are able to survive and move in fresh feces but are sensitive to aerobic environments. They dissociate when in contact or placed in saline, tap water or distilled water.















