In genetics and biochemistry, sequencing means to determine the primary structure of an unbranched biopolymer. Sequencing results in a symbolic linear depiction known as a sequence which succinctly summarizes much of the atomic-level structure of the sequenced molecule.
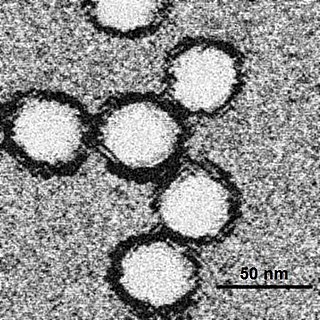
West Nile fever is an infection by the West Nile virus, which is typically spread by mosquitoes. In about 80% of infections people have few or no symptoms. About 20% of people develop a fever, headache, vomiting, or a rash. In less than 1% of people, encephalitis or meningitis occurs, with associated neck stiffness, confusion, or seizures. Recovery may take weeks to months. The risk of death among those in whom the nervous system is affected is about 10 percent.
A convulsion is a medical condition where the body muscles contract and relax rapidly and repeatedly, resulting in uncontrolled shaking. Because epileptic seizures typically include convulsions, the term convulsion is often used as a synonym for seizure. However, not all epileptic seizures result in convulsions, and not all convulsions are caused by epileptic seizures. Non-epileptic convulsions have no relation with epilepsy, and are caused by non-epileptic seizures.

Viral meningitis, also known as aseptic meningitis, is a type of meningitis due to a viral infection. It results in inflammation of the meninges. Symptoms commonly include headache, fever, sensitivity to light and neck stiffness.
Viral load, also known as viral burden, is a numerical expression of the quantity of virus in a given volume of fluid, including biological and environmental specimens. It is not to be confused with viral titre or viral titer, which depends on the assay. When an assay for measuring the infective virus particle is done, viral titre often refers to the concentration of infectious viral particles, which is different from the total viral particles. Viral load is measured using body fluids sputum and blood plasma. As an example of environmental specimens, the viral load of norovirus can be determined from run-off water on garden produce. Norovirus has not only prolonged viral shedding and has the ability to survive in the environment but a minuscule infectious dose is required to produce infection in humans: less than 100 viral particles.

Roseola, also known as sixth disease, is an infectious disease caused by certain types of human herpes viruses. Most infections occur before the age of three. Symptoms vary from absent to the classic presentation of a fever of rapid onset followed by a rash. The fever generally lasts for three to five days, while the rash is generally pink and lasts for less than three days. Complications may include febrile seizures, with serious complications being rare.
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis (LCM) is a rodent-borne viral infectious disease that presents as aseptic meningitis, encephalitis or meningoencephalitis. Its causative agent is lymphocytic choriomeningitis mammarenavirus (LCMV), a member of the family Arenaviridae. The name was coined by Charles Armstrong in 1934.

Aseptic meningitis is the inflammation of the meninges, a membrane covering the brain and spinal cord, in patients whose cerebral spinal fluid test result is negative with routine bacterial cultures. Aseptic meningitis is caused by viruses, mycobacteria, spirochetes, fungi, medications, and cancer malignancies. The testing for both meningitis and aseptic meningitis is mostly the same. A cerebrospinal fluid sample is taken by lumbar puncture and is tested for leukocyte levels to determine if there is an infection and goes on to further testing to see what the actual cause is. The symptoms are the same for both meningitis and aseptic meningitis but the severity of the symptoms and the treatment can depend on the certain cause.

Oropouche fever is a tropical viral infection transmitted by biting midges and mosquitoes from the blood of sloths to humans. This disease is named after the region where it was first discovered and isolated at the Trinidad Regional Virus Laboratory in 1955 by the Oropouche River in Trinidad and Tobago. Oropouche fever is caused by a specific arbovirus, the Oropouche virus (OROV), of the Bunyaviridae family.

Phlebovirus is one of twenty genera of the family Phenuiviridae in the order Bunyavirales. The genus contains 66 species. It derives its name from Phlebotominae, the vectors of member species Naples phlebovirus, which is said to be ultimately from the Greek phlebos, meaning "vein". The proper word for "vein" in ancient Greek is however phleps (φλέψ).

Astroviruses are a type of virus that was first discovered in 1975 using electron microscopes following an outbreak of diarrhea in humans. In addition to humans, astroviruses have now been isolated from numerous mammalian animal species and from avian species such as ducks, chickens, and turkey poults. Astroviruses are 28–35 nm diameter, icosahedral viruses that have a characteristic five- or six-pointed star-like surface structure when viewed by electron microscopy. Along with the Picornaviridae and the Caliciviridae, the Astroviridae comprise a third family of nonenveloped viruses whose genome is composed of plus-sense, single-stranded RNA. Astrovirus has a non-segmented, single stranded, positive sense RNA genome within a non-enveloped icosahedral capsid. Human astroviruses have been shown in numerous studies to be an important cause of gastroenteritis in young children worldwide. In animals, Astroviruses also cause infection of the gastrointestinal tract but may also result in encephalitis, hepatitis (avian) and nephritis (avian).
Mitochondrially encoded tRNA histidine, also known as MT-TH, is a transfer RNA which, in humans, is encoded by the mitochondrial MT-TH gene.
Dabie bandavirus, also called SFTS virus, is a tick-borne virus in the genus Bandavirus in the family Phenuiviridae, order Bunyavirales. The clinical condition it caused is known as severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS). SFTS is an emerging infectious disease that was first described in northeast and central China 2009 and now has also been discovered in Japan, South Korea, Vietnam and Taiwan in 2015. SFTS has a fatality rate of 12% and as high as over 30% in some areas. The major clinical symptoms of SFTS are fever, vomiting, diarrhea, multiple organ failure, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia and elevated liver enzyme levels. Another outbreak occurred in East China in the early half of 2020.
Heartland bandavirus, sometimes called Heartland virus (HRTV), is a tick-borne phlebovirus of the Bhanja virus serocomplex discovered in 2009. The lone star tick transmits the virus to people when feeding on blood. As of 2017, only five states in the Central United States have reported 20 human infections, namely Arkansas, Indiana, Missouri, Oklahoma, and Tennessee; symptoms resemble those of two other tick-borne infections ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis. The reservoir host is unknown, but deer, raccoon, coyotes, and moose in 13 different states have antibody titers against the virus. By 2023 over 50 human infections were reported in at least eleven states.

Molecular diagnostics is a collection of techniques used to analyze biological markers in the genome and proteome, and how their cells express their genes as proteins, applying molecular biology to medical testing. In medicine the technique is used to diagnose and monitor disease, detect risk, and decide which therapies will work best for individual patients, and in agricultural biosecurity similarly to monitor crop- and livestock disease, estimate risk, and decide what quarantine measures must be taken.

Bourbon virus is an RNA virus in the genus Thogotovirus of the family Orthomyxoviridae, which is similar to Dhori virus and Batken virus. It was first identified in 2014 in a man from Bourbon County, Kansas, United States, who died after being bitten by ticks. The case is the eighth report of human disease associated with a thogotovirus globally, and the first in the Western hemisphere. As of May 2015, a case was discovered in Stillwater, Oklahoma, and relatively little is known about the virus. No specific treatment or vaccine is available. The virus is suspected to be transmitted by ticks or insects, and avoidance of bites is recommended to reduce risk of infection. In June 2017 a 58-year-old female Missouri State Park employee died from an infection of the Bourbon virus after it had been misdiagnosed for a significant period of time.
The Punta Toro virus is a member of the genus Phlebovirus of the order Bunyavirales. It was initially isolated from patients in Colombia and two key patients in Panama. Two individual serotypes of PTV were isolated from these patients, PTV-Adames (A) and PTV-Balliet (B), with PTV-A appearing to be more virulent. PTV is considered to be relatively contained to the Americas with no cases being reported outside of this region. Along with a few other human pathogenic Phleboviruses, PTV is considered to be a significant virus in terms of public health as little information is known about its clinical effects and with further research underway, PTV could have unforeseen impacts on health and virology.
Whitewater Arroyo mammarenavirus (WWAV) is a zoonotic Arenavirus associated with hemorrhagic fever with liver failure.

Middelburg virus (MIDV) is an alphavirus of the Old World Group that has likely endemic and zoonotic potential. It is of the viral family Togaviridae. It was isolated from mosquitos in 1957 in South Africa, MDIV antigens have now been found in livestock, horses, and humans.
Clinical metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) is the comprehensive analysis of microbial and host genetic material in clinical samples from patients by next-generation sequencing. It uses the techniques of metagenomics to identify and characterize the genome of bacteria, fungi, parasites, and viruses without the need for a prior knowledge of a specific pathogen directly from clinical specimens. The capacity to detect all the potential pathogens in a sample makes metagenomic next generation sequencing a potent tool in the diagnosis of infectious disease especially when other more directed assays, such as PCR, fail. Its limitations include clinical utility, laboratory validity, sense and sensitivity, cost and regulatory considerations.









