
Orthohantavirus is a genus of single-stranded, enveloped, negative-sense RNA viruses in the family Hantaviridae within the order Bunyavirales. Members of this genus may be called orthohantaviruses or simply hantaviruses.

Bunyavirales is an order of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses with mainly tripartite genomes. Member viruses infect arthropods, plants, protozoans, and vertebrates. It is the only order in the class Ellioviricetes. The name Bunyavirales derives from Bunyamwera, where the original type species Bunyamwera orthobunyavirus was first discovered. Ellioviricetes is named in honor of late virologist Richard M. Elliott for his early work on bunyaviruses.

An arenavirus is a bi- or trisegmented ambisense RNA virus that is a member of the family Arenaviridae. These viruses infect rodents and occasionally humans. A class of novel, highly divergent arenaviruses, properly known as reptarenaviruses, have also been discovered which infect snakes to produce inclusion body disease, mostly in boa constrictors. At least eight arenaviruses are known to cause human disease. The diseases derived from arenaviruses range in severity. Aseptic meningitis, a severe human disease that causes inflammation covering the brain and spinal cord, can arise from the lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Hemorrhagic fever syndromes, including Lassa fever, are derived from infections such as Guanarito virus, Junin virus, Lassa virus, Lujo virus, Machupo virus, Sabia virus, or Whitewater Arroyo virus. Because of the epidemiological association with rodents, some arenaviruses and bunyaviruses are designated as roboviruses.
Bwamba orthobunyavirus (BWAV) belongs to the genus Orthobunyavirus and the order Bunyavirales RNA viruses. BWAV is present in large parts of Africa, endemic in Mozambique, Tanzania and Uganda. It is transmitted to humans through mosquito bites and results in a brief benign generalised infection with headache, skin rash, diarrhea and joint pain and lasts 4–5 days. The animal reservoir of the virus includes birds, monkeys and donkeys.

Mardivirus is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Herpesviridae, in the subfamily Alphaherpesvirinae. Chickens, turkeys, and quail serve as natural hosts. There are six species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: Marek's disease, which causes asymmetric paralysis of one or more limbs, neurological symptoms, and development of multiple lymphomas that manifest as solid tumors. Gallid herpesvirus 2 is the only one of these viruses known to be pathogenic and due to the antigenic similarity between the three viruses the other two have been used to vaccinate against Marek's disease. These viruses have double stranded DNA genomes with no RNA intermediate.
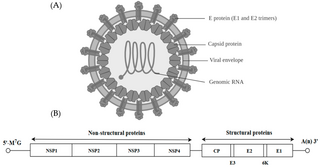
Alphavirus is a genus of RNA viruses, the sole genus in the Togaviridae family. Alphaviruses belong to group IV of the Baltimore classification of viruses, with a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genome. There are 32 alphaviruses, which infect various vertebrates such as humans, rodents, fish, birds, and larger mammals such as horses, as well as invertebrates. Alphaviruses that could infect both vertebrates and arthropods are referred dual-host alphaviruses, while insect-specific alphaviruses such as Eilat virus and Yada yada virus are restricted to their competent arthropod vector. Transmission between species and individuals occurs mainly via mosquitoes, making the alphaviruses a member of the collection of arboviruses – or arthropod-borne viruses. Alphavirus particles are enveloped, have a 70 nm diameter, tend to be spherical, and have a 40 nm isometric nucleocapsid.

Phlebovirus is one of twenty genera of the family Phenuiviridae in the order Bunyavirales. The genus contains 66 species. It derives its name from Phlebotominae, the vectors of member species Naples phlebovirus, which is said to be ultimately from the Greek phlebos, meaning "vein". The proper word for "vein" in ancient Greek is however phleps (φλέψ).

Andes orthohantavirus (ANDV), a species of Orthohantavirus, is a major causative agent of hantavirus cardiopulmonary syndrome (HCPS) and hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS) in South America. It is named for the Andes mountains of Chile and Argentina, where it was first discovered. Originating in the reservoir of rodents, Andes orthohantavirus is easily transmitted to humans who come into contact with infected rodents or their fecal droppings. However, infected rodents do not appear ill, so there is no readily apparent indicator to determine whether the rodent is infected or not. Additionally, Andes orthohantavirus, specifically, is the only hantavirus that can be spread by human to human contact via bodily fluids or long-term contact from one infected individual to a healthy person.

Orthobunyavirus is a genus of the Peribunyaviridae family in the order Bunyavirales. There are currently ~170 viruses recognised in this genus. These have been assembled into 103 species and 20 serogroups.
Dabie bandavirus, also called SFTS virus, is a tick-borne virus in the genus Bandavirus in the family Phenuiviridae, order Bunyavirales. The clinical condition it caused is known as severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS). SFTS is an emerging infectious disease that was first described in northeast and central China 2009 and now has also been discovered in Japan, South Korea, Vietnam and Taiwan in 2015. SFTS has a fatality rate of 12% and as high as over 30% in some areas. The major clinical symptoms of SFTS are fever, vomiting, diarrhea, multiple organ failure, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia and elevated liver enzyme levels. Another outbreak occurred in East China in the early half of 2020.
Schmallenberg orthobunyavirus, also called Schmallenberg virus, abbreviated SBV, is a virus that causes congenital malformations and stillbirths in cattle, sheep, goats, and possibly alpaca. It appears to be transmitted by midges, which are likely to have been most active in causing the infection in the Northern Hemisphere summer and autumn of 2011, with animals subsequently giving birth from late 2011. Schmallenberg virus falls in the Simbu serogroup of orthobunyaviruses. It is considered to be most closely related to the Sathuperi and Douglas viruses.
Sangassou orthohantavirus(SANGV) is single-stranded, negative-sense RNA virus species of the genus Orthohantavirus in the Bunyavirales order. It was first isolated in an African wood mouse (Hylomyscus simus) in the forest in Guinea, West Africa in 2010. It is named for the village near where the mouse was trapped. It is the first indigenous Murinae-associated African hantavirus to be discovered.
In 1954 the Hazara orthonairovirus, one of the 34 tick-borne viruses of the genus Orthonairovirus, was discovered in Pakistan in the Ixodes tick native to that region. Today this virus is studied in mice in an attempt to develop treatments for the highly pathogenic Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever virus.
Tahyna orthobunyavirus ("TAHV") is a viral pathogen of humans classified in the California encephalitis virus (CEV) serogroup of the Orthobunyavirus family in the order Bunyavirales, which is endemic to Europe, Asia, Africa and possibly China.
Batai orthobunyavirus (BATV) is a RNA virus belonging to order Bunyavirales, genus Orthobunyavirus.
Cache Valley orthobunyavirus (CVV) is a member of the order Bunyavirales, genus Orthobunyavirus, and serogroup Bunyamwera, which was first isolated in 1956 from Culiseta inornata mosquitos collected in Utah's Cache Valley. CVV is an enveloped arbovirus, nominally 80–120 nm in diameter, whose genome is composed of three single-stranded, negative-sense RNA segments. The large segment of related bunyaviruses is approximately 6800 bases in length and encodes a probable viral polymerase. The middle CVV segment has a 4463-nucleotide sequence and the smallest segment encodes for the nucleocapsid, and a second non-structural protein. CVV has been known to cause outbreaks of spontaneous abortion and congenital malformations in ruminants such as sheep and cattle. CVV rarely infects humans, but when they are infected it has caused encephalitis and multiorgan failure.
Phasmaviridae is a family of viruses with negative stranded RNA genomes associated with insect hosts. They are a member of the order Bunyavirales. Phasmaviruses were first discovered in phantom midges of the genus Chaoborus in 2014.

Phenuiviridae is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order Bunyavirales. Ruminants, camels, humans, and mosquitoes serve as natural hosts. Member genus Phlebovirus is the only genus of the family that has viruses that cause disease in humans except Dabie bandavirus.
Bunyaviridae nonstructural S proteins (NSs) are synthesized by viral DNA/RNA and do not play a role in the replication or the viral protein coating. The nonstructural S segment (NSs) created by Bunyaviridae virus family, are able to interact with the human immune system, in order to increase their replication in infected cells. Understanding this mechanism can have global health impacts.
Ngari virus (NRIV) is a single-stranded, negative sense, tri-segmented RNA virus. It is a subtype of the Bunyamwera virus (BUNV) and closely related to the Batai virus (BATV). NRIV is the only reassortment virus of the subtypes. There is evidence suggesting that NRIV stems from a naturally occurring reassortment event in which a host was infected with both BUNV and BATV. It is commonly found in areas that experience an outbreak of Rift Valley fever virus (RVFV)










