Related Research Articles

Rotavirus is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses in the family Reoviridae. Rotaviruses are the most common cause of diarrhoeal disease among infants and young children. Nearly every child in the world is infected with a rotavirus at least once by the age of five. Immunity develops with each infection, so subsequent infections are less severe; adults are rarely affected. There are nine species of the genus, referred to as A, B, C, D, F, G, H, I and J. Rotavirus A, the most common species, causes more than 90% of rotavirus infections in humans. Rotavirus E, which is seen in pigs, has not been confirmed as a distinct species.

Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the common cold, while more lethal varieties can cause SARS, MERS and COVID-19. In cows and pigs they cause diarrhea, while in mice they cause hepatitis and encephalomyelitis.

An enterotoxin is a protein exotoxin released by a microorganism that targets the intestines.

A viral protein is both a component and a product of a virus. Viral proteins are grouped according to their functions, and groups of viral proteins include structural proteins, nonstructural proteins, regulatory proteins, and accessory proteins. Viruses are non-living and do not have the means to reproduce on their own, instead depending on their host cell's resources in order to reproduce. Thus, viruses do not code for many of their own viral proteins, and instead use the host cell's machinery to produce the viral proteins they require for replication.

H5N1 genetic structure is the molecular structure of the H5N1 virus's RNA.
The NS1 influenza protein (NS1) is a viral nonstructural protein encoded by the NS gene segments of type A, B and C influenza viruses. Also encoded by this segment is the nuclear export protein (NEP), formally referred to as NS2 protein, which mediates the export of influenza virus ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complexes from the nucleus, where they are assembled.

The Coronavirus packaging signal is a conserved cis-regulatory element found in Betacoronavirus. It has an important role in regulating the packaging of the viral genome into the capsid. As part of the viral life cycle, within the infected cell, the viral genome becomes associated with viral proteins and assembles into new infective progeny viruses. This process is called packaging and is vital for viral replication.
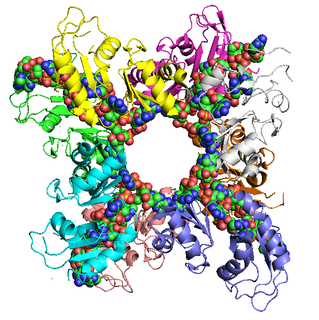
Poly(A)-binding protein is a RNA-binding protein which triggers the binding of eukaryotic initiation factor 4 complex (eIF4G) directly to the poly(A) tail of mRNA which is 200-250 nucleotides long. The poly(A) tail is located on the 3' end of mRNA and was discovered by Mary Edmonds, who also characterized the poly-A polymerase enzyme that generates the poly(a) tail. The binding protein is also involved in mRNA precursors by helping polyadenylate polymerase add the poly(A) nucleotide tail to the pre-mRNA before translation. The nuclear isoform selectively binds to around 50 nucleotides and stimulates the activity of polyadenylate polymerase by increasing its affinity towards RNA. Poly(A)-binding protein is also present during stages of mRNA metabolism including nonsense-mediated decay and nucleocytoplasmic trafficking. The poly(A)-binding protein may also protect the tail from degradation and regulate mRNA production. Without these two proteins in-tandem, then the poly(A) tail would not be added and the RNA would degrade quickly.

Rotavirus translation, the process of translating mRNA into proteins, occurs in a different way in Rotaviruses. Unlike the vast majority of cellular proteins in other organisms, in Rotaviruses the proteins are translated from capped but nonpolyadenylated mRNAs. The viral nonstructural protein NSP3 specifically binds the 3'-end consensus sequence of viral mRNAs and interacts with the eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF4G. The Rotavirus replication cycle occurs entirely in the cytoplasm. Upon virus entry, the viral transcriptase synthesizes capped but nonpolyadenylated mRNA The viral mRNAs bear 5' and 3' untranslated regions (UTR) of variable length and are flanked by two different sequences common to all genes.

RoXaN also known as ZC3H7B, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZC3H7B gene. RoXaN is a protein that contains tetratricopeptide repeat and leucine-aspartate repeat as well as zinc finger domains. This protein also interacts with the rotavirus non-structural protein NSP3.
NSP1 (NS53), the product of rotavirus gene 5, is a nonstructural RNA-binding protein that contains a cysteine-rich region and is a component of early replication intermediates. RNA-folding predictions suggest that this region of the NSP1 mRNA can interact with itself, producing a stem-loop structure similar to that found near the 5'-terminus of the NSP1 mRNA.

NSP2 (NS35), is a rotavirus nonstructural RNA-binding protein that accumulates in cytoplasmic inclusions (viroplasms) and is required for genome replication. NSP2 is closely associated in vivo with the viral replicase. The non-structural protein NSP5 plays a role in the structure of viroplasms mediated by its interaction with NSP2.

Rotavirus protein NSP3 (NS34) is bound to the 3' end consensus sequence of viral mRNAs in infected cells.
The rotavirus nonstructural protein NSP4 was the first viral enterotoxin discovered. It induces diarrhea and causes Ca2+-dependent transepithelial secretion.
NSP5 encoded by genome segment 11 of group A rotaviruses. In virus-infected cells NSP5 accumulates in the viroplasms. NSP5 has been shown to be autophosphorylated. Interaction of NSP5 with NSP2 was also demonstrated. In rotavirus-infected cells, the non-structural proteins NSP5 and NSP2 localize in complexes called viroplasms, where replication and assembly occur and they can drive the formation of viroplasm-like structures in the absence of other rotaviral proteins and rotavirus replication.
Gene 11 of Rotavirus encodes a nonstructural protein, NSP5 and also encodes NSP6, from an out of phase open reading frame. In contrast to the other rotavirus non-structural proteins, NSP6 was found to have a high rate of turnover, being completely degraded within 2h of synthesis. NSP6 was found to be a sequence independent nucleic acid binding protein, with similar affinities for ssRNA and dsRNA.

Nonstructural protein 2 (NS2) is a viral protein found in the hepatitis C virus. It is also produced by influenza viruses, and is alternatively known as the nuclear export protein (NEP).
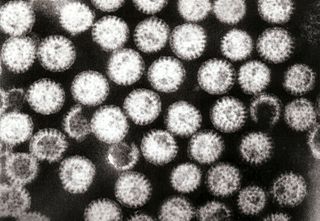
Rotavirus gastroenteritis is the most common cause of severe diarrhoea among infants and young children. It is caused by Rotavirus, a genus of double-stranded RNA virus in the family Reoviridae. By the age of five, nearly every child in the world has been infected with rotavirus at least once. However, with each infection, immunity develops, and subsequent infections are less severe; adults are rarely affected. There are five species of this virus, referred to as A, B, C, D, and E. Rotavirus A, the most common, causes more than 90% of infections in humans.
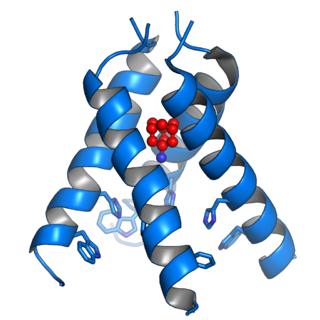
Viroporins are small and usually hydrophobic multifunctional viral proteins that modify cellular membranes, thereby facilitating virus release from infected cells. Viroporins are capable of assembling into oligomeric ion channels or pores in the host cell's membrane, rendering it more permeable and thus facilitating the exit of virions from the cell. Many viroporins also have additional effects on cellular metabolism and homeostasis mediated by protein-protein interactions with host cell proteins. Viroporins are not necessarily essential for viral replication, but do enhance growth rates. They are found in a variety of viral genomes but are particularly common in RNA viruses. Many viruses that cause human disease express viroporins. These viruses include hepatitis C virus, HIV-1, influenza A virus, poliovirus, respiratory syncytial virus, and SARS-CoV.

ORF1ab refers collectively to two open reading frames (ORFs), ORF1a and ORF1b, that are conserved in the genomes of nidoviruses, a group of viruses that includes coronaviruses. The genes express large polyproteins that undergo proteolysis to form several nonstructural proteins with various functions in the viral life cycle, including proteases and the components of the replicase-transcriptase complex (RTC). The two ORFs are related by a programmed ribosomal frameshift that allows the ribosome to continue translating past the stop codon at the end of ORF1a, in a -1 reading frame. The resulting polyproteins are known as pp1a and pp1ab.
References
- ↑ Viral+Nonstructural+Proteins at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)