
Interferons (IFNs) are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten their anti-viral defenses.

In structural biology, a protein subunit is a single protein molecule that assembles with other protein molecules to form a protein complex. Some naturally occurring proteins have a relatively small number of subunits and therefore described as oligomeric, for example hemoglobin or DNA polymerase. Others may consist of a very large number of subunits and therefore described as multimeric, for example microtubules and other cytoskeleton proteins. The subunits of a multimeric protein may be identical, homologous or totally dissimilar and dedicated to disparate tasks.
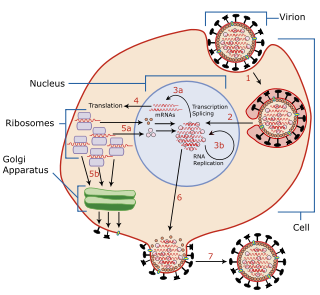
Viral replication is the formation of biological viruses during the infection process in the target host cells. Viruses must first get into the cell before viral replication can occur. Through the generation of abundant copies of its genome and packaging these copies, the virus continues infecting new hosts. Replication between viruses is greatly varied and depends on the type of genes involved in them. Most DNA viruses assemble in the nucleus while most RNA viruses develop solely in cytoplasm.
Lentivirus is a genus of retroviruses that cause chronic and deadly diseases characterized by long incubation periods, in the human and other mammalian species. The best known lentivirus is the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), which causes AIDS. Lentiviruses are also hosted in apes, cows, goats, horses, cats, and sheep. Recently, lentiviruses have been found in monkeys, lemurs, Malayan flying lemur, rabbits, and ferrets. Lentiviruses and their hosts have worldwide distribution. Lentiviruses can integrate a significant amount of viral cDNA into the DNA of the host cell and can efficiently infect nondividing cells, so they are one of the most efficient methods of gene delivery. Lentiviruses can become endogenous (ERV), integrating their genome into the host germline genome, so that the virus is henceforth inherited by the host's descendants.

Transcription factor Sp1, also known as specificity protein 1* is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SP1 gene.

Human Herpes Virus (HHV) Infected Cell Polypeptide 0 (ICP0) is a protein, encoded by the DNA of herpes viruses. It is produced by herpes viruses during the earliest stage of infection, when the virus has recently entered the host cell; this stage is known as the immediate-early or α ("alpha") phase of viral gene expression. During these early stages of infection, ICP0 protein is synthesized and transported to the nucleus of the infected host cell. Here, ICP0 promotes transcription from viral genes, disrupts structures in the nucleus known as nuclear dots or promyelocytic leukemia (PML) nuclear bodies, and alters the expression of host and viral genes in combination with a neuron specific protein. At later stages of cellular infection, ICP0 relocates to the cell cytoplasm to be incorporated into new virion particles.

Tectiviridae is a family of viruses with three genera. Gram-negative bacteria serve as natural hosts. There are currently four species in this genus including the type species Enterobacteria phage PRD1. Tectiviruses have no head-tail structure, but are capable of producing tail-like tubes of ~ 60×10 nm upon adsorption or after chloroform treatment. The name is derived from Latin tectus.

Interferon regulatory factor 3, also known as IRF3, is an interferon regulatory factor.
NSP1, the product of rotavirus gene 5, is a nonstructural RNA-binding protein that contains a cysteine-rich region and is a component of early replication intermediates. RNA-folding predictions suggest that this region of the NSP1 mRNA can interact with itself, producing a stem-loop structure similar to that found near the 5'-terminus of the NSP1 mRNA.

WEE1 homolog , also known as WEE1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the WEE1 gene.

Interferon regulatory factor 7, also known as IRF7, is a member of the interferon regulatory factor family of transcription factors.

G2/mitotic-specific cyclin-B2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCNB2 gene.

Host cell factor 1, also known as VP16-accessory protein, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HCFC1 gene.

Interferon regulatory factor 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IRF5 gene.

Interferon-induced transmembrane protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFITM1 gene. IFITM1 has also recently been designated CD225. This protein has several additional names: fragilis, IFI17 [interferon-induced protein 17], 9-27 [Interferon-inducible protein 9-27] and Leu13.

Vpu is an accessory protein that in HIV is encoded by the vpu gene. Vpu stands for "Viral Protein U". The Vpu protein acts in the degradation of CD4 in the endoplasmic reticulum and in the enhancement of virion release from the plasma membrane of infected cells. Vpu induces the degradation of the CD4 viral receptor and therefore participates in the general downregulation of CD4 expression during the course of HIV infection. Vpu-mediated CD4 degradation is thought to prevent CD4-Env binding in the endoplasmic reticulum in order to facilitate proper Env assembly into virions. It is found in the membranes of infected cells, but not the virus particles themselves.
Vpx is a virion-associated protein encoded by human immunodeficiency virus type 2 HIV-2 and most simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) strains, but that is absent from HIV-1. It is similar in structure to the protein Vpr that is carried by SIV and HIV-2 as well as HIV-1. Vpx is one of five accessory proteins carried by lentiviruses that enhances viral replication by inhibiting host antiviral factors.
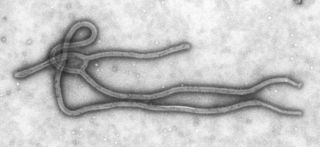
A negative-sense single-stranded RNA virus is a virus that uses negative sense, single-stranded RNA as its genetic material. Single stranded RNA viruses are classified as positive or negative depending on the sense or polarity of the RNA. The negative viral RNA is complementary to the mRNA and must be converted to a positive RNA by RNA polymerase before translation. Therefore, the purified RNA of a negative sense virus is not infectious by itself, as it needs to be converted to a positive sense RNA for replication. These viruses belong to Group V on the Baltimore classification.
BZLF1 is an immediate-early viral gene of the Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) of the Herpes Virus Family, which induces cancers and infects primarily the B-cells of 95% of the human population. This gene produces the expression of other EBV genes in other stages of disease progression, and is involved in converting the virus from the latent to the lytic form.















