
A spirochaete or spirochete is a member of the phylum Spirochaetes, which contains distinctive diderm (double-membrane) gram-negative bacteria, most of which have long, helically coiled cells. Spirochaetes are chemoheterotrophic in nature, with lengths between 3 and 500 μm and diameters around 0.09 to at least 3 μm.
Tick-borne diseases, which afflict humans and other animals, are caused by infectious agents transmitted by tick bites. They are caused by infection with a variety of pathogens, including rickettsia and other types of bacteria, viruses, and protozoa. Because individual ticks can harbor more than one disease-causing agent, patients can be infected with more than one pathogen at the same time, compounding the difficulty in diagnosis and treatment. 16 tick-borne diseases of humans are known, of which four have been discovered since 2013.
Relapsing fever is a vector-borne disease caused by infection with certain bacteria in the genus Borrelia, which is transmitted through the bites of lice or soft-bodied ticks.
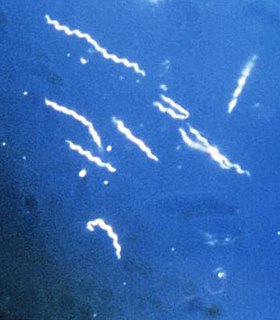
Borrelia is a genus of bacteria of the spirochete phylum. It causes Lyme disease, also called Lyme borreliosis, a zoonotic, vector-borne disease transmitted primarily by ticks and by lice, depending on the species of bacteria. The genus is named after French biologist Amédée Borrel (1867–1936), who first documented the distinction between a species of Borrelia, B. anserina, and the other known type of spirochete at the time, Treponema pallidum. This bacterium must be viewed using dark-field microscopy, which make the cells appear white against a dark background. Borrelia species are grown in Barbour-Stoenner-Kelly medium. Of 52 known species of Borrelia, 20 are members of the Lyme disease group, 29 belong to the relapsing fever group, and two are members of a genetically distinct third group typically found in reptiles. The Lyme disease group has been proposed to be split based on genetic diversity and moved to their own genus, Borelliella, but this change is not widely accepted. This bacterium uses hard and soft ticks and lice as vectors. Testing for the presence of the bacteria in a human includes two-tiered serological testing, including immunoassays and immunoblotting.

Wilhelm Burgdorfer was an American scientist born and educated in Basel, Switzerland, considered an international leader in the field of medical entomology. He discovered the bacterial pathogen that causes Lyme disease, a spirochete named Borrelia burgdorferi in his honor.

Lyme disease, or borreliosis, is caused by spirochetal bacteria from the genus Borrelia, which has 52 known species. Three main species are the main causative agents of the disease in humans, while a number of others have been implicated as possibly pathogenic. Borrelia species in the species complex known to cause Lyme disease are collectively called Borrelia burgdorferisensu lato (s.l.) not to be confused with the single species in that complex Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto which is responsible for nearly all cases of Lyme disease in North America.

Borrelia hermsii is a spirochete bacterium that has been implicated as a cause of tick-borne relapsing fever. It is spread by the soft-bodied tick Ornithodoros hermsi.

Borrelia recurrentis is a species of Borrelia, a spirochaete bacterium associated with relapsing fever. B. recurrentis is usually transmitted from person to person by the human body louse. Since the 1800s, the body louse has been known as its only known vector.
American tick bite fever is a spotted fever disease caused by the tick-borne bacterium Rickettsia parkeri. Symptoms may include a fever, red spots on the skin throughout the body, and an eschar at the site of the tick-bite.
Rickettsia parkeri is a Gram-negative intracellular bacterium. R. parkeri causes mild spotted fever disease in humans,, characterized by headache, rash, fever, and an eschar at the site of tick attachment. It is transmitted via tick bite and found mainly in the Western Hemisphere. Doxycycline and chloramphenicol are the most common drugs of choice for reducing the symptoms associated with disease caused by R. parkeri.

Amblyomma maculatum is a species of tick in the genus Amblyomma. Immatures usually infest small mammals and birds that dwell on the ground; cotton rats may be particularly favored hosts. Some recorded hosts include:

Ornithodoros hermsi is a species of soft tick. It can be infected with Borrelia hermsii.
Borrelia duttoni, formerly known as Spirochaeta duttoni, is a species of Borrelia.

Ornithodoros moubata, commonly known as the African hut tampan or the eyeless tampan, is a species of tick in the family Argasidae. It is an ectoparasite and vector of relapsing fever in humans, and African swine fever in pigs.
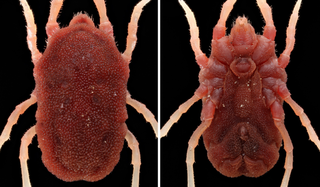
Ornithodoros turicata, commonly referred to as the relapsing fever tick, is a soft tick found in the midwestern and southwestern United States. It is a known vector of Borrelia turicatae, a spirochete responsible for tick-borne relapsing fever in humans. Additionally, vector competence for the transmission of Leptospira pomona, the agent of canine jaundice, has been demonstrated in a laboratory setting.
Borrelia miyamotoi is a spirochete bacterium in the genus Borrelia. A zoonotic bacterium, B. miyamotoi can be transferred to humans through the hard (Ixodes) ticks, the same tick species that spread B. burgdorferi, the causative agent of Lyme disease, and Babesia microti, the causative agent of babesiosis. Although infection can cause some similar symptoms including fever, headache, fatigue, and muscle aches, acute Lyme disease often presents with rash, while infection with B. miyamotoi does not; it remains unclear whether B. miyamotoi causes a relapsing fever syndrome.

Joseph Everett Dutton was a British Parasitologist who discovered one of the trypanosomes that cause sleeping sickness. He died in the Congo Free State at the age of 30 from tick fever, or African relapsing fever, while investigating the disease, which is caused by a spirillum that was later named Borrelia duttoni.
Borrelia turicatae is a bacterial species of the spirochaete class of the genus Borrelia. It is one of the relapsing fever spirochaetes, which are globally distributed yet understudied agents of tick-borne relapsing fever. The tick vector Ornithodoros turicata transmits B. turicatae, which causes relapsing fever, an arthropod-borne infection of humans and other mammals caused by different Borrelia species. B. turicatae is long and spiral-shaped, as is typical for all spirochaetes. It is a Gram-negative bacterium and visible with light microscopy. Few epidemiological studies have been performed and few molecular data exist for B. turicatae and its arthropod vector O. turicata.
Borrelia coriaceae is a species of spirochete bacteria and member of the genus Borrelia. Strains of this species have been isolated from the soft tick Ornithodoros coriaceus and from mule deer.
The Asian monitor lizard tick, is a hard-bodied tick of the genus Amblyomma. It is found in India, Thailand, Taiwan and Sri Lanka. Adults parasitize various reptiles such as varanids and snakes. These ticks are potential vectors of spotted fever group (SFG) rickettsiae.









