
Idiosepius is a genus of squids in the family Idiosepiidae. They are small, reaching mantle lengths of no more than about 21 mm (0.8 in); members of this genus represent no interest to commercial fisheries. They occur in tropical and temperate waters throughout the Indo-Pacific, primarily in association with seagrass and mangrove roots.
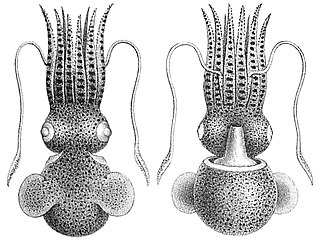
Euprymna stenodactyla is a species of bobtail squid.
Sepia aureomaculata is a species of cuttlefish native to the northwestern Pacific Ocean, specifically the Kii Channel, Tosa Bay, Hyuga-Nada, and the East China Sea. It lives at a depth of between 190 and 350 m.
Sepia erostrata is a species of cuttlefish native to the northwestern Pacific Ocean, specifically off western mainland Japan, from Sagami Bay to the Kii Peninsula. It inhabits subtidal, inshore habitats. It is the commonest species of cuttlefish occurring in rocky shorelines around Japanese coasts.
Sepia foliopeza is a species of cuttlefish native to the western Pacific Ocean, specifically the East China Sea and Taiwan. The depth range of S. foliopeza is unknown.

Semirossia tenera, also known as the lesser bobtail squid, is a widespread species of bobtail squid native to the northwest Atlantic Ocean. Its natural range covers the eastern coast of North America, from the northern Gulf of Maine to the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea. S. tenera is possibly also present in the southwest Atlantic, specifically off the coasts of Suriname, French Guiana, Brazil, and Uruguay, although the latter records are questionable.
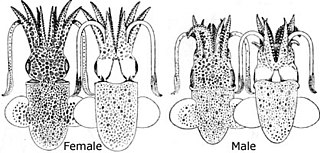
Rondeletiola minor, also known as the lentil bobtail, is a species of bobtail squid native to the eastern Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea. Its natural range covers the northwest of Spain, Portugal, and the eastern, central and western Mediterranean Sea to the southeastern Atlantic Benguela Current off Namibia.
Sepia subtenuipes is a species of cuttlefish native to the western Pacific Ocean, specifically the East China Sea and the Kii Channel in southwestern Japan. It lives at depths of 90 to 300 m.

Idiosepiidae, also known as the pygmy squids, is a family of squids in the superorder Decapodiformes. They are the smallest known squids.
Inioteuthis maculosa is a species of bobtail squid native to the Indo-Pacific. It occurs in the northern Indian Ocean, Persian Gulf, Arabian Sea, Bay of Bengal, Andaman Sea, and off India, Taiwan, the Philippines, and Indonesia.
Rossia bullisi, also known as the Gulf bobtail squid, is a species of bobtail squid native to the tropical western Atlantic Ocean, specifically the northern Gulf of Mexico and Straits of Florida.
Rossia moelleri is a species of bobtail squid native to the northern Atlantic Ocean and the Arctic Ocean, eastward to the Laptev Sea and westward to Amundsen Bay. It occurs off western and northeastern Greenland, northeastern Canada, Labrador, Spitsbergen, Jan Mayen, and in the Kara Sea. R. moelleri lives at depths from 17 to 250 m.
Rossia mollicella is a species of bobtail squid native to the western Pacific Ocean, south from Sendai Bay, Japan. It occurs on the outer continental shelf and in the upper bathyal zone. R. mollicella lives at depths from 729 to 805 m.

Iridoteuthis iris is a species of bobtail squid native to the northern central Pacific Ocean; it occurs near the Hawaiian Islands off the southeast and northwest Hancock, Colahan, and Kammu seamounts. There exists a doubtful record from the Ceram Sea. Unlike most other bobtail squid, I. iris is pelagic and lives in the open ocean.
Idiosepius minimus is a species of bobtail squid native to the "coast of Africa" where it occurs in shallow, inshore waters. Specimens collected under the junior synonyms I. biserialis and I. macrocheir were described from Mozambique. Since then, the further collecting effort off Mozambique has seen additional specimens gained. As a result it has been inferred that this species has a relatively restricted distribution since Idiosepius has not been recorded elsewhere in Africa.
Idiosepius picteti is a species of pygmy squid native to the Indo-Pacific waters off eastern Indonesia.

Xipholeptos is a genus of squid in the family Idiosepiidae. It is monotypic, being represented by the single species Xipholeptos notoides, commonly known as the southern pygmy squid. The species was originally classified as Idiosepius notoides. The southern pygmy squid is native to the southwestern Pacific Ocean, off southern and eastern Australia. It inhabits shallow, inshore waters. It has been recorded off the coasts of New South Wales, South Australia, Tasmania and Victoria.

Idiosepius paradoxus, also known as the northern pygmy squid, is a species of pygmy squid native to the western Pacific Ocean. This species can be found inhabiting shallow, inshore waters around central China, South Korea, and Japan.

Idiosepius pygmaeus, also known as the two-toned pygmy squid or tropical pygmy squid, is a species of bobtail squid native to the Indo-Pacific. It occurs in waters of the South China Sea, Japan, Philippines, Palau, Indonesia, Northern Mariana Islands, as well as northern and northeastern Australia. It inhabits shallow, inshore waters.

Sepiadarium austrinum, the southern bottletail squid, is a species of cuttlefish in the genus Sepiadarium. It was first described by S. Stillman Berry in 1921 based on a specimen found in St. Vincent Bay in South Australia.









