
Cutthroat eels are a family, Synaphobranchidae, of eels, the only members of the suborder Synaphobranchoidei. They are found worldwide in temperate and tropical seas.
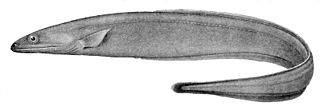
The grey cutthroat eel, Synaphobranchus affinis, is a cutthroat eel. It was originally described by Albert Günther in 1877. It lives a benthic lifestyle, inhabiting the continental slope and global deep waters including near Portugal, Canary Islands, Morocco, Japan, Australia, and others. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which has been found at depths ranging from 300 to 2300 meters and at temperatures ranging from 3.3 - 11.3 °C. Males can grow to a length of up to 110 centimeters. It is primarily a scavenger, however it also actively hunts small fish and crustaceans.

Ilyophis is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Synaphobranchidae, the cutthroat eels. These eels are found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans.
Coloconger cadenati is an eel in the family Colocongridae. It was described by Robert H. Kanazawa in 1961. It is a marine, deep-water dwelling eel which is known from Senegal to the Gulf of Guinea in the eastern Atlantic Ocean. It is known from a depth range of 270–600 m. Males can reach a maximum total length of 90 cm. The diet of C. cadenati consists primarily of benthic crustaceans.

The short-tooth sawpalate is an eel in the family Serrivomeridae. It was described by Johannes Schmidt in 1916 in its larval form, originally under the genus Leptocephalus, and later as a subspecies of Serrivomer sector by Roule & Bertin in 1929. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the eastern central and western central Atlantic Ocean, including the Strait of Gibraltar, Cape Verde, the United States, the Bahamas and Bermuda, as well as the Strait of Gibraltar, Cape Verde, Canada and the United States. It dwells at a depth range of 150 to 6,000 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 65 centimetres (26 in).
Atractodenchelys phrix, known under the common name "arrowtooth eel" is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Catherine H. Robins and Charles Richard Robins in 1970. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from its type locality in the eastern Caribbean, in the western central Atlantic Ocean. It is known to dwell at a depth range of 385–425 metres.

Dysomma anguillare, the shortbelly eel, stout moray, mustard eel or arrowtooth eel, is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Keppel Harcourt Barnard in 1923. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the western Atlantic Ocean and Indo-Western Pacific, including the United States, Venezuela, South Africa, Zanzibar, and Japan. It lives at a depth range of 30 to 270 metres, and inhabits muddy sediments in coastal waters and large rivermouths. Males can reach a maximum total length of 52 centimetres (20 in).
Dysomma brevirostre, the pignosed arrowtooth eel or batnose eel, is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Luigi Facciolà in 1887. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the eastern and western Atlantic Ocean, including Madeira Island, the Gulf of Guinea, the Ligurian Sea, Italy, and Florida and Hawaii, USA. It dwells at a depth range of 200 to 1,000 metres, and inhabits soft sediments on the continental slope. Males can reach a maximum total length of 30 centimetres (12 in).
Dysomma fuscoventralis is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Christine Karrer and Wolfgang Klausewitz in 1982. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is endemic to the Red Sea. It dwells at a depth range of 750–1425 metres.
Dysommina proboscideus is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Einar Hagbart Martin Lea in 1913. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from the eastern central Atlantic Ocean. It is known to dwell at a depth of 150 metres.
Histiobranchus australis, the southern cut-throat eel is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Regan in 1913. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the southern Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 950 to 3,001 metres, and leads a benthic lifestyle. Males can reach a maximum total length of 62.8 centimetres (24.7 in), while females can reach a maximum TL of 67.0 centimetres (26.4 in).
Ilyophis arx is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Catherine H. Robins in 1976. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the eastern Pacific and northeastern Atlantic Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 1,790 to 3,225 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 44.7 centimetres (17.6 in).
Ilyophis nigeli is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Yuri Nikolaevich Shcherbachev and Kenneth J. Sulak in 1997. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from Japan, in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. It is known to dwell at a depth range of 700 to 1,800 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 51.3 centimetres (20.2 in).
Ilyophis robinsae is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Yuri Nikolaevich Shcherbachev and Kenneth J. Sulak in 1997. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Philippines, in the Indo-West Pacific. It is known to dwell at depths of 4,800 metres (15,700 ft) to 5,180 metres (16,990 ft). Males can reach a maximum total length of 34.8 centimetres (13.7 in).
Ilyophis saldanhai is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Emma Stanislavovna Karmovskaya and Nikolai Vasilyevich Parin in 1999, and is the most recently described of the six species in the genus Ilyophis. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the western central Atlantic Ocean. It is known to dwell at a depth of 3,020 metres (9,910 ft).
Meadia abyssalis, the abyssal cutthroat eel, is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Toshiji Kamohara in 1938. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific, including Brazil, the Hancock Seamount, the Hawaiian and Society islands, Japan, Mauritius, and Réunion. It is found off the continental slope, and dwells at a depth range of 100–329 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 73 centimetres.
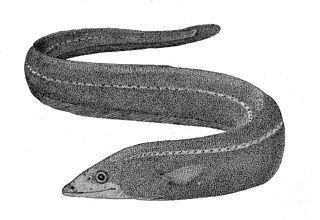
The shortdorsal cutthroat eel is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1887. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific and western central Atlantic Ocean, including Zanzibar, Maldives, Australia, Japan, Suriname, and the Gulf of Mexico. It dwells at a depth range of 900 to 3,000 metres, most often between 1,000 to 2,500 metres, and leads a benthic lifestyle, inhabiting the continental slope. Males can reach a maximum total length of 111 centimetres (44 in).
Synaphobranchus dolichorhynchus is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Einar Hagbart Martin Lea in 1913, originally under the genus Leptocephalus. It is a marine, subtropical eel which is known solely from larval specimens discovered in the northern Atlantic Ocean. It is known to dwell at a depth range of 100 to 150 metres.

The Kaup's arrowtooth eel is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by James Yate Johnson in 1862. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Indo-Western Pacific and eastern and western Atlantic Ocean, including the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Cape Verde, the Western Sahara, Nigeria, Namibia, South Africa, Greenland, France, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, the United Kingdom, Ireland, the Philippines, Portugal, Spain, the Bahamas, Brazil, Canada, Cuba, Japan, Australia, Mauritania, Morocco, and Hawaii. It dwells at a depth range of 120 to 4,800 metres, most often between 400 and 2,200 metres, and inhabits the upper abyssal zone on the continental slope. It is intolerant of the temperatures of higher waters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 100 centimetres (39 in).
Synaphobranchus oregoni is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Peter Henry John Castle in 1960. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the western central Atlantic Ocean, including the Bahamas, Trinidad and Tobago, Mexico, and the United States. It dwells at a depth range of 512 to 1,900 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 111 centimetres (44 in).





