
Phenylalanine is an essential α-amino acid with the formula C
9H
11NO
2. It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of alanine. This essential amino acid is classified as neutral, and nonpolar because of the inert and hydrophobic nature of the benzyl side chain. The L-isomer is used to biochemically form proteins coded for by DNA. Phenylalanine is a precursor for tyrosine, the monoamine neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), and the biological pigment melanin. It is encoded by the messenger RNA codons UUU and UUC.
A gluten-free casein-free diet, also known as a gluten-free dairy-free diet, is a diet that does not include gluten, and casein. Despite an absence of scientific evidence, there have been advocates for the use of this diet as a treatment for autism and related conditions.

Tryptamine is an indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by an indole—a fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon. The structure of tryptamine is a shared feature of certain aminergic neuromodulators including melatonin, serotonin, bufotenin and psychedelic derivatives such as dimethyltryptamine (DMT), psilocybin, psilocin and others.

Alkylresorcinols (ARs), also known as resorcinolic lipids, are amphiphilic phenolic lipids characterised by a non-polar odd-numbered alkyl side chain with up to 27 carbon atoms attached to a polar resorcinol (1,3-dihydroxybenzene) ring.

Hartnup disease is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder affecting the absorption of nonpolar amino acids. Niacin is a precursor to nicotinamide, a necessary component of NAD+.

5-Hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) is the main metabolite of serotonin. The metabolic intermediate 5-hydroxyindoleacetaldehyde (5-HIAL) is formed from serotonin by monoamine oxidase (MAO) and then 5-HIAA is formed from 5-HIAL via aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH). In chemical analysis of urine samples, 5-HIAA is used to determine serotonin levels in the body.

Trace amines are an endogenous group of trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) agonists – and hence, monoaminergic neuromodulators – that are structurally and metabolically related to classical monoamine neurotransmitters. Compared to the classical monoamines, they are present in trace concentrations. They are distributed heterogeneously throughout the mammalian brain and peripheral nervous tissues and exhibit high rates of metabolism. Although they can be synthesized within parent monoamine neurotransmitter systems, there is evidence that suggests that some of them may comprise their own independent neurotransmitter systems.

Tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) is an enzyme (EC 1.14.16.4) involved in the synthesis of the monoamine neurotransmitter serotonin. Tyrosine hydroxylase, phenylalanine hydroxylase, and tryptophan hydroxylase together constitute the family of biopterin-dependent aromatic amino acid hydroxylases. TPH catalyzes the following chemical reaction

An aromatic amino acid is an amino acid that includes an aromatic ring.

Phenylacetylglutamine is a product formed by the conjugation of phenylacetate and glutamine. It is a common metabolite that occurs naturally in human urine.

Homeobox protein engrailed-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EN2 gene. It is a member of the engrailed gene family.
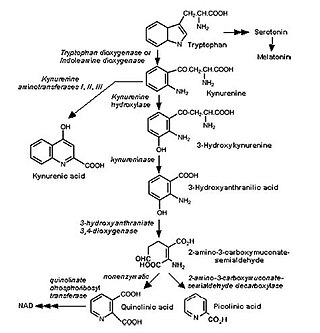
The kynurenine pathway is a metabolic pathway leading to the production of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+). Metabolites involved in the kynurenine pathway include tryptophan, kynurenine, kynurenic acid, xanthurenic acid, quinolinic acid, and 3-hydroxykynurenine. The kynurenine pathway is responsible for about 95% of total tryptophan catabolism. Disruption in the pathway is associated with certain genetic and psychiatric disorders.

3,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid is a dihydroxybenzoic acid. It is a colorless solid.

3,5-Dihydroxyphenylpropionoic acid is a metabolite of alkylresorcinols, first identified in human urine and can be quantified in urine and plasma, and may be an alternative, equivalent biomarker of whole grain wheat intake.
Auto-brewery syndrome (ABS) is a condition characterized by the fermentation of ingested carbohydrates in the gastrointestinal tract of the body caused by bacteria or fungi. ABS is a rare medical condition in which intoxicating quantities of ethanol are produced through endogenous fermentation within the digestive system. The organisms responsible for ABS include various yeasts and bacteria, including Saccharomyces cerevisiae, S. boulardii, Candida albicans, C. tropicalis, C. krusei, C. glabrata, C. parapsilosis, Kluyveromyces marxianus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Enterococcus faecium. These organisms use lactic acid fermentation or mixed acid fermentation pathways to produce an ethanol end product. The ethanol generated from these pathways is absorbed in the small intestine, causing an increase in blood alcohol concentrations that produce the effects of intoxication without the consumption of alcohol.
Paul Shattock is a British autism researcher and scientific consultant to the charity Education and Services for People with Autism, of which he is also the founder. He was formerly the director of the Autism Research Unit at the University of Sunderland. He is well known for his disputed research into dietary therapy and autism, having claimed that autistic children may have a "leaky gut" which allows certain peptides to enter the bloodstream, and claimed that they excrete unusually high levels thereof. As a result of this speculation, he has promoted the use of a gluten-free, casein-free diet to ameliorate the symptoms of autism, a theory he developed along with Kalle Reichelt. In addition, he has claimed that a protein found in milk may play a role in the etiology of autism. He is also the former president of the World Autism Organization.
The opioid excess theory postulates that autism is the result of a metabolic disorder in which opioid peptides produced through metabolism of gluten and casein pass through an abnormally permeable intestinal membrane and then proceed to exert an effect on neurotransmission through binding with opioid receptors. It is believed by advocates of this hypothesis that autistic children are unusually sensitive to gluten, which results in small bowel inflammation in these children, which in turn allows these opioid peptides to enter the brain.
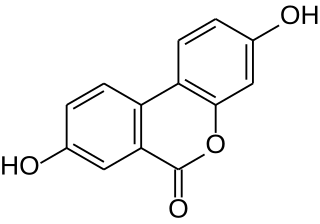
Urolithin A is a metabolite compound resulting from the transformation of ellagitannins by the gut bacteria. It belongs to the class of organic compounds known as benzo-coumarins or dibenzo-α-pyrones. Its precursors – ellagic acids and ellagitannins – are ubiquitous in nature, including edible plants, such as pomegranates, strawberries, raspberries, walnuts, and others.

3-Indolepropionic acid (IPA), or indole-3-propionic acid, has been studied for its therapeutic value in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. As of 2022 IPA shows potential in the treatment of this disease, though the therapeutic effect of IPA depends on dose and time of therapy initiation.

N-Acetyltaurine (NAcT) is an endogenous metabolite. Biochemically, N-acetyltaurine is formed as a result of an acetylation of taurine. The main substrate for this reaction is acetate. An increase of endogenous N-acetyltaurine concentrations was observed after the consumption of alcohol and after extended physical activity (ketoacidosis).

















