Related Research Articles

True frogs is the common name for the frog family Ranidae. They have the widest distribution of any frog family. They are abundant throughout most of the world, occurring on all continents except Antarctica. The true frogs are present in North America, northern South America, Europe, Africa, and Asia. The Asian range extends across the East Indies to New Guinea and a single species, the Australian wood frog, has spread into the far north of Australia.

Rana is a genus of frogs commonly known as the Holarctic true frogs, pond frogs or brown frogs. Members of this genus are found through much of Eurasia and western North America. Many other genera were formerly included here. These true frogs are usually largish species characterized by their slim waists and wrinkled skin; many have thin ridges running along their backs, but they generally lack "warts" as in typical toads. They are excellent jumpers due to their long, slender legs. The typical webbing found on their hind feet allows for easy movement through water. Coloration is mostly greens and browns above, with darker and yellowish spots.

Palaeobatrachus is an extinct genus of frogs from Europe that existed from the middle Eocene to the middle Pleistocene, spanning almost 50 million years. They were obligately aquatic, and would have not spent much time on dry land. They are one of two genera and by far the largest genus in the family Palaeobatrachidae, which are considered to be members of Pipimorpha, related to the South American-African family Pipidae, which includes the African clawed frog and Surinam toad.

Icaronycteris is an extinct genus of microchiropteran (echolocating) bat that lived in the early Eocene, approximately 52.2 million years ago, making it the earliest known definitive bat. Four exceptionally preserved specimens, among the best preserved bat fossils, are known from the Green River Formation of North America. The best known species is I. index. Fragmentary material from France has also been tentatively placed within Icaronycteris as the second species I. menui. I. sigei is based on well-preserved fragments of dentaries and lower teeth found in Western India. In 2023, the species I. gunnelli also from the Green River Formation was distinguished from I. index, and I. menui and I. sigei were proposed to be removed from the genus due to them not being closely related.
Birbalomys is an extinct genus of rodent from Asia.

Ailuravus is a genus of prehistoric rodents in the family Ischyromyidae.

The common green frog is a frog species of in the true frog family Ranidae; some sources still use the old name Rana erythraea. It lives in Southeast Asia and is also known as green paddy frog, red-eared frog or leaf frog. The last name, however, commonly refers to the Neotropical tree frogs which make up the subfamily Phyllomedusinae. These are not closely related to H. erythraea, belonging to family Hylidae instead.

Rana sauteri is a species of true frog endemic to Taiwan. It inhabits low-altitude hill forests and the associated streams. It is an endangered species threatened by habitat loss due to agriculture and infrastructure development. Common names recorded for Rana sauteri include Kanshirei Village frog, Taiwan groove-toed frog, Sauter's brown frog, and Taiwan pseudotorrent frog.
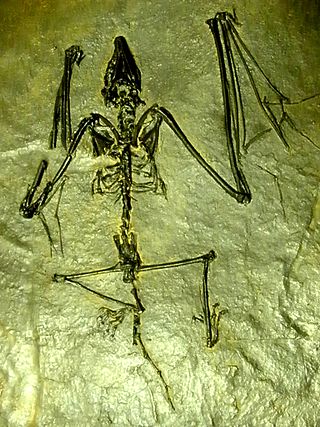
Archaeonycteris is an archaic bat genus whose fossilised remains have been found in Germany, France, England and India.
Eobarbourula delfinoi is an extinct toad which existed in what is now Gujarat, India, during the Middle Ypresian age of the early Eocene. It was described by Annelise Folie, Rajendra S. Rana, Kenneth D. Rose, Ashok Sahni, Kishor Kumar, Lachham Singh and Thierry Smith in 2012, and is the only species in the genus Eobarbourula. The name of the genus is a combination of "Eo", referring to the epoch in which the animal existed, and Barbourula, the generic name of the jungle toads, while the specific epithet refers to Massimo Delfino, an Italian paleontologist.
Indohyaenodon is an extinct genus of placental mammals from family Indohyaenodontidae within extinct order Hyaenodonta, that lived during the early Eocene in India.

Mercurana is a genus of arboreal frogs belonging to the family Rhacophoridae. The genus was named from the only known species Mercurana myristicapalustris, which was described in 2013 from the Western Ghats of Kerala, India. The generic name was derived from and given as a tribute to Freddie Mercury, the late vocalist of the British rock band Queen, in combination with the Latin name for "frog". The frog is different from other related frogs in that it has extensively webbed toes, lives only in swampy lowlands, and lays its eggs on mud with which it carefully mixes leaf litter.
Cambaytherium is an extinct genus of placental mammals in the family Cambaytheriidae whose fossils were found in an open pit coal mine located in Gujarat, India. The mine was a treasure trove full of teeth and bones, over 200 of which were identified as belonging to Cambaytherium thewissi. The fossils were dated to the Early Eocene, 54.5 million years ago, making them slightly younger than the oldest known fossils belonging to the order Perissodactyla.
Asiadapis is a genus of adapiform primate that lived in India's Cambay Shale Formation during the early Eocene (Ypresian). It has two known species, Asiadapis cambayensis and Asiadapis tapiensis.
Marcgodinotius is a genus of adapiform primate that lived in Asia during the early Eocene. It is a monotypic genus, the only species being Marcgodinotius indicus. Another adapiform primate Suratius robustus was found in the same horizon. Anthrasimias may be a junior synonym of Marcgodinotius and Anthrasimias gujaratensis a junior synonym of Marcgodinotius indicus.
Indiagama is an extinct genus of agamid lizard known from the type species Indiagama gujarata from the early Eocene of India. Indiagama was named in 2013 on the basis of a single lower jaw from the Cambay Shale in Gujarat. The rectangular shape of its teeth distinguish it from all other agamids, living and extinct.
Suratagama is an extinct genus of agamid lizard known from the type species Suratagama neeraae from the early Eocene of India. It was named in 2013 on the basis of three isolated jaw bones from the Cambay Shale in Gujarat.
Heterodontagama is an extinct genus of iguanian lizard from the Early Eocene of India. It belongs to the extinct family Priscagamidae, which is otherwise only known from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia. The type species Heterodontagama borsukae was named in 2013 from several isolated upper and lower jaws found in an exposure of the Cambay Shale in an open-pit coal mine in Gujarat.
Vastanavis is a genus of parrot-like bird that lived in what is now western India in the Early Eocene. It contains two species, Vastanavis eocaena and Vastanavis cambayensis; both are known from the Cambay Formation. Vastanavis was at least semi-zygodactyl, and most likely arboreal.
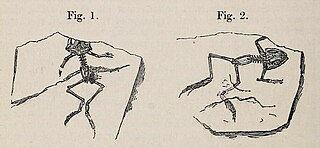
Indobatrachus is an extinct genus of frog known from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) of India. It contains a single species, Indobatrachus pusillus.
References
- 1 2 Annelise Folie; Rajendra S. Rana; Kenneth D. Rose; Ashok Sahni; Kishor Kumar; Lachham Singh; Thierry Smith (2012). "Early Eocene frogs from Vastan Lignite Mine, Gujarat, India". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 58 (3): 511–524. doi: 10.4202/app.2011.0063 .