| Infraglottic cavity | |
|---|---|
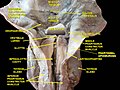
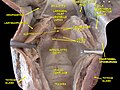
 Cut through the larynx of a horse 1 hyoid bone 2 epiglottis 3 vestibular fold 4 vocal fold 5 Ventricularis muscle 6 ventricle of larynx 7 Vocalis muscle 8 thyroid cartilage lamina 9 Cricoid cartilage 10 infraglottic cavity 11 first bronchial tube cartilage 12 bronchial tube | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | cavitas infraglottica |
| TA98 | A06.2.09.018 |
| TA2 | 3211 |
| FMA | 55311 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The infraglottic cavity is the portion of the larynx situated inferior to the glottis. [1] It is situated between the vocal cords (superior limit), and the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage (inferior limit) [2] where it is continuous with the trachea. [1]
Contents
On transverse section, the infraglottic cavity appears elliptical in shape superiorly, and circular in shape inferiorly. It is wider inferiorly. The walls of the infraglottic cavity are lined with respiratory epithelium. Structural support is provided by the cricothyroid ligament above, and the cricoid cartilage below. [2]