
The larynx, commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about 4–5 centimeters in diameter. The larynx houses the vocal cords, and manipulates pitch and volume, which is essential for phonation. It is situated just below where the tract of the pharynx splits into the trachea and the esophagus. The word 'larynx' comes from the Ancient Greek word lárunx ʻlarynx, gullet, throatʼ.
Articles related to anatomy include:

The hyoid bone is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebra.

The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior and middle cerebral circulation.
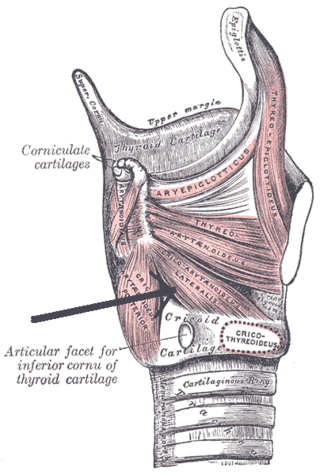
The lateral cricoarytenoid is an intrinsic muscle of the larynx. It attaches at the cricoid cartilage anteriorly, and at the arytenoid cartilage of the same side posteriorly. It is innervated by the recurrent laryngeal nerve. It acts to close the rima glottidis, thus closing the airway.

The posterior cricoarytenoid muscle is a intrinsic muscle of the larynx. It arises from the cricoid cartilage; it inserts onto the arytenoid cartilage of the same side. It is innervated by the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Each acts to open the vocal folds by pulling the vocal fold of the same side laterally. It participates in the production of sounds.

The cricoid cartilage, or simply cricoid or cricoid ring, is the only complete ring of cartilage around the trachea. It forms the back part of the voice box and functions as an attachment site for muscles, cartilages, and ligaments involved in opening and closing the airway and in producing speech.
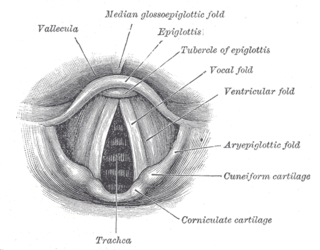
The laryngeal inlet is the opening that connects the pharynx and the larynx.

The thyrohyoid muscle is a small skeletal muscle of the neck. Above, it attaches onto the greater cornu of the hyoid bone; below, it attaches onto the oblique line of the thyroid cartilage. It is innervated by fibres derived from the cervical spinal nerve 1 that run with the hypoglossal nerve to reach this muscle. The thyrohyoid muscle depresses the hyoid bone and elevates the larynx during swallowing. By controlling the position and shape of the larynx, it aids in making sound.

The anterior longitudinal ligament is a ligament that extends across the anterior/ventral aspect of the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs the spine.

The thyroarytenoid muscle is a broad, thin muscle that forms the body of the vocal fold and that supports the wall of the ventricle and its appendix. It functions to shorten the vocal folds.

The lateral thyrohyoid ligament is a round elastic cord, which forms the posterior border of the thyrohyoid membrane and passes between the tip of the superior cornu of the thyroid cartilage and the extremity of the greater cornu of the hyoid bone. The internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve typical lies lateral to this ligament.

The thyrohyoid membrane is a broad, fibro-elastic sheet of the larynx. It connects the upper border of the thyroid cartilage to the hyoid bone.
The superior thyroid artery arises from the external carotid artery just below the level of the greater cornu of the hyoid bone and ends in the thyroid gland.

The superior laryngeal nerve is a branch of the vagus nerve. It arises from the middle of the inferior ganglion of the vagus nerve and additionally receives a sympathetic branch from the superior cervical ganglion.

The medial surface of the labyrinth of ethmoid consists of a thin lamella, which descends from the under surface of the cribriform plate, and ends below in a free, convoluted margin, the middle nasal concha.

The portion of the cavity of the larynx above the vestibular fold is called the laryngeal vestibule; it is wide and triangular in shape, its base or anterior wall presenting, however, about its center the backward projection of the tubercle of the epiglottis. It contains the vestibular folds, and between these and the vocal folds are the laryngeal ventricles.

The laryngeal ventricle, is a fusiform fossa, situated between the vestibular and vocal folds on either side, and extending nearly their entire length. There is also a sinus of Morgagni in the pharynx.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The pharynx is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea. It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food to the esophagus and air to the larynx. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx.
















