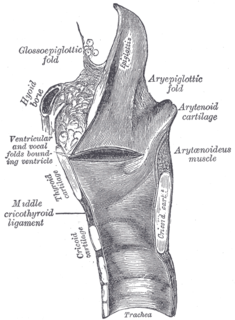
| Laryngeal ventricle | |
|---|---|
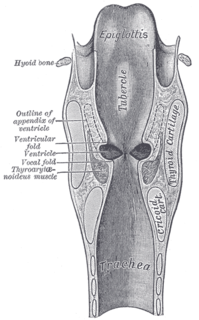
 Coronal section of larynx and upper part of trachea, with Ventricle labeled at center left. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ventriculus laryngis |
| TA | A06.2.09.010 |
| FMA | 64171 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
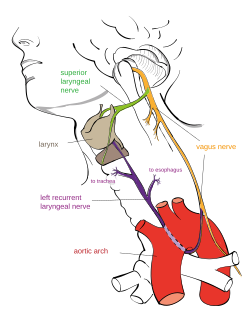
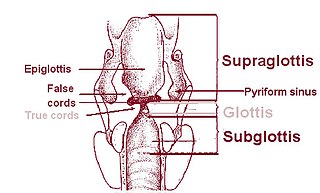
The laryngeal ventricle, (also called the ventricle of the larynx, laryngeal sinus, or Morgagni's sinus) [1] is a fusiform fossa, situated between the vestibular and vocal folds on either side, and extending nearly their entire length. There is also a sinus of Morgagni in the pharynx.
In anatomy, a fossa is a depression or hollow, usually in a bone, such as the hypophyseal fossa. Some examples include:

The vestibular fold is one of two thick folds of mucous membrane, each enclosing a narrow band of fibrous tissue, the vestibular ligament, which is attached in front to the angle of the thyroid cartilage immediately below the attachment of the epiglottis, and behind to the antero-lateral surface of the arytenoid cartilage, a short distance above the vocal process.
In the pharynx, the sinus of Morgagni is the enclosed space between the upper border of the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle, the base of the skull and the pharyngeal aponeurosis.
Contents
The fossa is bounded, above, by the free crescentic edge of the vestibular ligament; below, by the straight margin of the vocal fold and laterally, by the mucous membrane covering the corresponding thyroarytenoid muscle.

A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at various body openings such as the eyes, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lip, vagina, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated.

The thyroarytenoid muscle is a broad, thin muscle that forms the body of the vocal fold and that supports the wall of the ventricle and its appendix. It functions to relax the vocal folds.
The anterior part of the ventricle leads up by a narrow opening into a pouch-like diverticulum, a mucous membranous sac of variable size called the appendix of the laryngeal ventricle. The appendix (also called the laryngeal saccule, pouch or Hilton's pouch) extends vertically from the laryngeal ventricle. It runs between the vestibular fold, thyroarytenoid muscle, and thyroid cartilage, and is conical, bending slightly backward. It is covered in roughly seventy mucous glands. The muscles surrounding the appendix compress it until mucus is secreted to lubricate the vocal folds.
A diverticulum is the medical or biological term for an outpouching of a hollow structure in the body. Depending upon which layers of the structure are involved, they are described as being either true or false.

The thyroid cartilage is the largest of the nine cartilages that make up the laryngeal skeleton, the cartilage structure in and around the trachea that contains the larynx. It does not completely encircle the larynx; only the cricoid cartilage does.