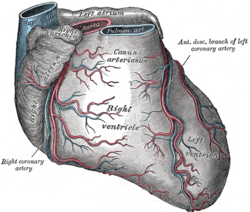
The aorta is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart, branching upwards immediately after, and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits at the aortic bifurcation into two smaller arteries. The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through the systemic circulation.
An infundibulum is a funnel-shaped cavity or organ.

The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest, called the mediastinum.

A heart valve is a biological one-way valve that allows blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart. Four valves are usually present in a mammalian heart and together they determine the pathway of blood flow through the heart. A heart valve opens or closes according to differential blood pressure on each side.

A ventricle is one of two large chambers located toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper heart that is smaller than a ventricle. Interventricular means between the ventricles, while intraventricular means within one ventricle.

A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the main pulmonary artery or pulmonary trunk from the heart, and the smallest ones are the arterioles, which lead to the capillaries that surround the pulmonary alveoli.

The pulmonary valve is a valve of the heart that lies between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery, and has three cusps. It is one of the four valves of the heart and one of the two semilunar valves, the other being the aortic valve. Similar to the aortic valve, the pulmonary valve opens in ventricular systole when the pressure in the right ventricle rises above the pressure in the pulmonary artery. At the end of ventricular systole, when the pressure in the right ventricle falls rapidly, the pressure in the pulmonary artery closes the pulmonary valve.

The ductus arteriosus, also called the ductus Botalli, named after the Italian physiologist Leonardo Botallo, is a blood vessel in the developing fetus connecting the trunk of the pulmonary artery to the proximal descending aorta. It allows most of the blood from the right ventricle to bypass the fetus's fluid-filled non-functioning lungs. Upon closure at birth, it becomes the ligamentum arteriosum.

Transposition of the great vessels (TGV) is a group of congenital heart defects involving an abnormal spatial arrangement of any of the great vessels: superior and/or inferior venae cavae, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins, and aorta. Congenital heart diseases involving only the primary arteries belong to a sub-group called transposition of the great arteries (TGA), which is considered the most common congenital heart lesion that presents in neonates.

Persistent truncus arteriosus (PTA), often referred to simply as truncus arteriosus, is a rare form of congenital heart disease that presents at birth. In this condition, the embryological structure known as the truncus arteriosus fails to properly divide into the pulmonary trunk and aorta. This results in one arterial trunk arising from the heart and providing mixed blood to the coronary arteries, pulmonary arteries, and systemic circulation. For the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11), the International Paediatric and Congenital Cardiac Code (IPCCC) was developed to standardize the nomenclature of congenital heart disease. Under this system, English is now the official language, and persistent truncus arteriosus should properly be termed common arterial trunk.
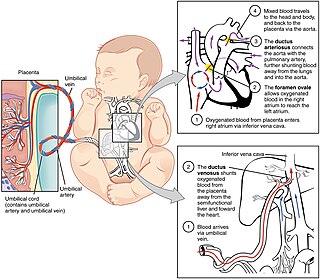
In humans, the circulatory system is different before and after birth. The fetal circulation is composed of the placenta, umbilical blood vessels encapsulated by the umbilical cord, heart and systemic blood vessels. A major difference between the fetal circulation and postnatal circulation is that the lungs are not used during the fetal stage resulting in the presence of shunts to move oxygenated blood and nutrients from the placenta to the fetal tissue. At birth, the start of breathing and the severance of the umbilical cord prompt various changes that quickly transform fetal circulation into postnatal circulation.
In cardiology, the cardiac skeleton, also known as the fibrous skeleton of the heart, is a high-density homogeneous structure of connective tissue that forms and anchors the valves of the heart, and influences the forces exerted by and through them. The cardiac skeleton separates and partitions the atria from the ventricles .The heart's cardiac skeleton comprises four dense connective tissue rings that encircle the mitral and tricuspid atrioventricular (AV) canals and extend to the origins of the pulmonary trunk and aorta. This provides crucial support and structure to the heart while also serving to electrically isolate the atria from the ventricles.
The great arteries are the primary arteries that carry blood away from the heart, which include:

The aortic arch, arch of the aorta, or transverse aortic arch is the part of the aorta between the ascending and descending aorta. The arch travels backward, so that it ultimately runs to the left of the trachea.

The bulbus cordis is a part of the developing heart that lies ventral to the primitive ventricle after the heart assumes its S-shaped form. The superior end of the bulbus cordis is also called the conotruncus.

A ventricular outflow tract is a portion of either the left ventricle or right ventricle of the heart through which blood passes in order to enter the great arteries.

The truncus arteriosus is a structure that is present during embryonic development. It is an arterial trunk that originates from both ventricles of the heart that later divides into the aorta and the pulmonary trunk.
The heart is the first functional organ in a vertebrate embryo. There are 5 stages to heart development.
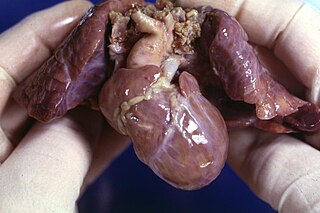
Hypoplastic right heart syndrome or HRHS is a congenital heart defect in which the structures on the right side of the heart, particularly the right ventricle, are underdeveloped. This defect causes inadequate blood flow to the lungs, and thus a cyanotic infant.

Heart development, also known as cardiogenesis, refers to the prenatal development of the heart. This begins with the formation of two endocardial tubes which merge to form the tubular heart, also called the primitive heart tube. The heart is the first functional organ in vertebrate embryos.