![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Silicone</span> Family of polymers of the repeating form [R2Si–O–SiR2]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/37/Caulking.jpg/320px-Caulking.jpg)
In organosilicon and polymer chemistry, a silicone or polysiloxane is a polymer composed of repeating units of siloxane. They are typically colorless oils or rubber-like substances. Silicones are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medicine, cooking utensils, thermal insulation, and electrical insulation. Some common forms include silicone oil, grease, rubber, resin, and caulk.
In polymer science, the polymer chain or simply backbone of a polymer is the main chain of a polymer. Polymers are often classified according to the elements in the main chains. The character of the backbone, i.e. its flexibility, determines the properties of the polymer. For example, in polysiloxanes (silicone), the backbone chain is very flexible, which results in a very low glass transition temperature of −123 °C. The polymers with rigid backbones are prone to crystallization in thin films and in solution. Crystallization in its turn affects the optical properties of the polymers, its optical band gap and electronic levels.

In chemistry, catenation is the bonding of atoms of the same element into a series, called a chain. A chain or a ring shape may be open if its ends are not bonded to each other, or closed if they are bonded in a ring. The words to catenate and catenation reflect the Latin root catena, "chain".
In chemistry, a nitride is an inorganic compound of nitrogen. The "nitride" anion, N3- ion, is very elusive but compounds of nitride are numerous, although rarely naturally occurring. Some nitrides have a found applications, such as wear-resistant coatings (e.g., titanium nitride, TiN), hard ceramic materials (e.g., silicon nitride, Si3N4), and semiconductors (e.g., gallium nitride, GaN). The development of GaN-based light emitting diodes was recognized by the 2014 Nobel Prize in Physics. Metal nitrido complexes are also common.

In organosilicon chemistry, a siloxane is an organic compound containing a functional group of two silicon atoms bound to an oxygen atom: Si−O−Si. The parent siloxanes include the oligomeric and polymeric hydrides with the formulae H[OSiH2]nOH and [OSiH2]n. Siloxanes also include branched compounds, the defining feature of which is that each pair of silicon centres is separated by one oxygen atom. The siloxane functional group forms the backbone of silicones [−R2Si−O−SiR2−]n, the premier example of which is polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). The functional group R3SiO− is called siloxy. Siloxanes are manmade and have many commercial and industrial applications because of the compounds’ hydrophobicity, low thermal conductivity, and high flexibility.
In inorganic chemistry, chlorosilanes are a group of reactive, chlorine-containing chemical compounds, related to silane and used in many chemical processes. Each such chemical has at least one silicon-chlorine bond. Trichlorosilane is produced on the largest scale. The parent chlorosilane is silicon tetrachloride.

Borazine, also known as borazole, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula B3H6N3. In this cyclic compound, the three BH units and three NH units alternate. The compound is isoelectronic and isostructural with benzene. For this reason borazine is sometimes referred to as “inorganic benzene”. Like benzene, borazine is a colourless liquid with an aromatic odor.
In organic chemistry, hydroboration refers to the addition of a hydrogen-boron bond to certain double and triple bonds involving carbon. This chemical reaction is useful in the organic synthesis of organic compounds.

Ammonia borane, also called borazane, is the chemical compound with the formula H3NBH3. The colourless or white solid is the simplest molecular boron-nitrogen-hydride compound. It has attracted attention as a source of hydrogen fuel, but is otherwise primarily of academic interest.

Silanes are saturated chemical compounds with the empirical formula SixHy. They are hydrosilanes, a class of compounds that includes compounds with Si−H and other Si−X bonds. All contain tetrahedral silicon and terminal hydrides. They only have Si−H and Si−Si single bonds. The bond lengths are 146.0 pm for a Si−H bond and 233 pm for a Si−Si bond. The structures of the silanes are analogues of the alkanes, starting with silane, SiH4, the analogue of methane, continuing with disilane Si2H6, the analogue of ethane, etc. They are mainly of theoretical or academic interest.
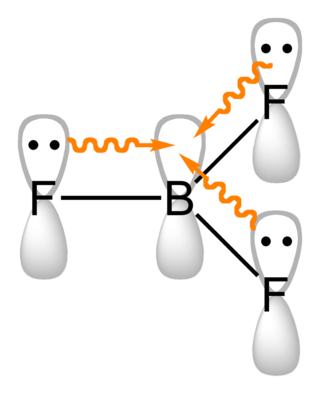
Boron compounds are compounds containing the element boron. In the most familiar compounds, boron has the formal oxidation state +3. These include oxides, sulfides, nitrides, and halides.
Dimethyldichlorosilane is a tetrahedral, organosilicon compound with the formula Si(CH3)2Cl2. At room temperature it is a colorless liquid that readily reacts with water to form both linear and cyclic Si-O chains. Dimethyldichlorosilane is made on an industrial scale as the principal precursor to dimethylsilicone and polysilane compounds.

A silsesquioxane is an organosilicon compound with the chemical formula [RSiO3/2]n. Silsesquioxanes are colorless solids that adopt cage-like or polymeric structures with Si-O-Si linkages and tetrahedral Si vertices. Silsesquioxanes are members of polyoctahedral silsesquioxanes ("POSS"), which have attracted attention as preceramic polymer precursors to ceramic materials and nanocomposites. Diverse substituents (R) can be attached to the Si centers. The molecules are unusual because they feature an inorganic silicate core and an organic exterior. The silica core confers rigidity and thermal stability.
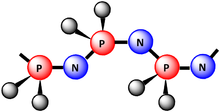
In organosilicon chemistry, polysilazanes are polymers in which silicon and nitrogen atoms alternate to form the basic backbone. Since each silicon atom is bound to two separate nitrogen atoms and each nitrogen atom to two silicon atoms, both chains and rings of the formula [R2Si−NR]n occur. R can be hydrogen atoms or organic substituents. If all substituents R are hydrogen atoms, the polymer is designated as perhydropolysilazane, polyperhydridosilazane, or inorganic polysilazane ([H2Si−NH]n). If hydrocarbon substituents are bound to the silicon atoms, the polymers are designated as Organopolysilazanes. Molecularly, polysilazanes [R2Si−NH]n are isoelectronic with and close relatives to polysiloxanes [R2Si−O]n (silicones).
Polysilicon hydrides are polymers containing only silicon and hydrogen. They have the formula where 0.2 ≤ n ≤ 2.5 and x is the number of monomer units. The polysilicon hydrides are generally colorless or pale-yellow/ocher powders that are easily hydrolyzed and ignite readily in air. The surfaces of silicon prepared by MOCVD using silane (SiH4) consist of a polysilicon hydride.

Polysilanes are organosilicon compounds with the formula (R2Si)n. They are relatives of traditional organic polymers but their backbones are composed of silicon atoms. They exhibit distinctive optical and electrical properties. They are mainly used as precursors to silicon carbide. The simplest polysilane would be (SiH2)n, which is mainly of theoretical, not practical interest.
IUPAC Polymer Nomenclature are standardized naming conventions for polymers set by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and described in their publication "Compendium of Polymer Terminology and Nomenclature", which is also known as the "Purple Book". Both the IUPAC and Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS) make similar naming recommendations for the naming of polymers.
Borane, also known as borine, is an unstable and highly reactive molecule with the chemical formula BH
3. The preparation of borane carbonyl, BH3(CO), played an important role in exploring the chemistry of boranes, as it indicated the likely existence of the borane molecule. However, the molecular species BH3 is a very strong Lewis acid. Consequently, it is highly reactive and can only be observed directly as a continuously produced, transitory, product in a flow system or from the reaction of laser ablated atomic boron with hydrogen. It normally dimerizes to diborane in the absence of other chemicals.

Smart inorganic polymers (SIPs) are hybrid or fully inorganic polymers with tunable (smart) properties such as stimuli responsive physical properties (shape, conductivity, rheology, bioactivity, self-repair, sensing etc.). While organic polymers are often petrol-based, the backbones of SIPs are made from elements other than carbon which can lessen the burden on scarce non-renewable resources and provide more sustainable alternatives. Common backbones utilized in SIPs include polysiloxanes, polyphosphates, and polyphosphazenes, to name a few.
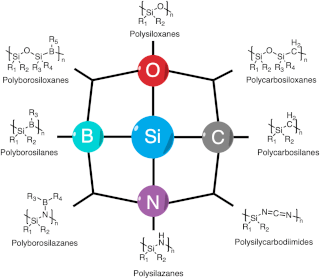
Polymer derived ceramics (PDCs) are ceramic materials formed by the pyrolysis of preceramic polymers, usually under inert atmosphere.



![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Silicone</span> Family of polymers of the repeating form [R2Si–O–SiR2]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/37/Caulking.jpg/320px-Caulking.jpg)









