Theravāda is the most commonly accepted name of Buddhism's oldest existing school. The school's adherents, termed Theravādins, have preserved their version of Gautama Buddha's teaching or dhamma in the Pāli Canon for over two millennia.

Fo Guang Shan (FGS) (Chinese: 佛光山; pinyin: Fó guāng shān; lit. 'Buddha's Light Mountain') is an international Chinese Mahāyāna Buddhist organization and monastic order based in Taiwan that practices Humanistic Buddhism whose roots are traced to the Linji school of Chan Buddhism. The headquarters, Fo Guang Shan Monastery, is located in Dashu District, Kaohsiung, and is the largest Buddhist monastery in Taiwan. The organization is also one of the largest charity organizations in Taiwan. The organization's counterpart for laypeople is known as the Buddha's Light International Association.

Thammasat University is a public research university in Thailand with campuses in Tha Phra Chan, Rangsit, Pattaya and Lampang Province. As of 2019, Thammasat University has over 33,000 students enrolled in 33 faculties, colleges, institutes and 2,700 academic staff.
Free education is education funded through government spending or charitable organizations rather than tuition funding. Many models of free higher education have been proposed. Primary school and other comprehensive or compulsory education is free in many countries. Tertiary education is also free in certain countries, including post-graduate studies in the Nordic countries. The Article 13 of International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights ensures the right to free education at primary education and progressive introduction of it at secondary and higher education as the right to education.

Buddhadasa was a Thai Buddhist monk. Known as an innovative reinterpreter of Buddhist doctrine and Thai folk beliefs, he fostered a reformation in conventional religious perceptions in his home country, Thailand, as well as abroad. He developed a personal view that those who have penetrated the essential nature of religions consider "all religions to be inwardly the same", while those who have the highest understanding of dhamma feel "there is no religion".

Buddhism in Thailand is largely of the Theravada school, which is followed by roughly 93.4 percent of the population. Thailand has the second largest Buddhist population in the world, after China, with approximately 64 million Buddhists. Buddhism in Thailand has also become integrated with folk religion (Bon), Hinduism from millennia of Indian influence, and Chinese religions from the large Thai Chinese population. Buddhist temples in Thailand are characterized by tall golden stupas, and the Buddhist architecture of Thailand is similar to that in other Southeast Asian countries, particularly Cambodia and Laos, with which Thailand shares cultural and historical heritages. Thai Buddhism also shares many similarities with Sri Lankan Buddhism. Thailand, Cambodia, Myanmar, Sri Lanka and Laos are countries with Theravada Buddhist majorities.

Theravada Buddhism is the largest religion in Laos, which is practiced by 66% of the population. Lao Buddhism is a unique version of Theravada Buddhism and is at the basis of ethnic Lao culture. Buddhism in Laos is often closely tied to animist beliefs and belief in ancestral spirits, particularly in rural areas.
Geshe or geshema is a Tibetan Buddhist academic degree for monks and nuns. The degree is emphasized primarily by the Gelug lineage, but is also awarded in the Sakya and Bön traditions. The equivalent geshema degree is awarded to women.

Education in Sri Lanka has a long history that dates back two millennia. While the Constitution of Sri Lanka does not provide free education as a fundamental right, the constitution mentions that 'the complete eradication of illiteracy and the assurance to all persons of the right to universal and equal access to education at all levels" in its section on directive principles of state policy at (27. Sri Lanka's population had an adult literacy rate of 96.3% in 2015, which is above average by world and regional standards. Computer literacy in 2017 28.3% and phone users in 2017 105%, website users 32% in 2017. Education plays a major part in the life and culture of the country, which dates back to 543 BC. Sri Lanka's modern educational system modeled after Christian missionary system was brought about by its integration into the British Empire in the 19th century. Education currently falls under the control of both the Central Government and the Provincial Councils, with some responsibilities lying with the Central Government and the Provincial Council having autonomy for others.
Payap University, established in 1974, is a private and non-profit institution founded by the Foundation of the Church of Christ in Thailand. Payap University is a liberal arts and pre-professional school offering a doctoral degree in peacebuilding, master's degrees in divinity, linguistics, TESOL, law, business administration and music, and bachelor degrees in communication arts, information technology, accountancy, business administration, economics, nursing, law, and Christian theology. Payap University is a founding member of the Association of Private Higher Education Institutions of Thailand and an active member of the Association of Christian Universities and Colleges in Asia, as well as the Association of Southeast Asian Institutions of Higher Learning.
P. A. Payutto, also known by his current monastic title, Somdet Phra Buddhaghosacariya, is a well-known Thai Buddhist monk, an intellectual, and a prolific writer.
Woodenfish Foundation, previously known as "Woodenfish Project," is an international Buddhist educational NGO with operations in the United States and China. Yifa founded the "Woodenfish Project" in 2002 at Fo Guang Shan in Kaohsiung, Taiwan. The initial flagship program, "Humanistic Buddhist Monastic Life Program" aims to allow students from around the world to authentically experience Humanistic Buddhism for one month each summer within a monastic context.

Buddhism is a major religion in Hong Kong and has been greatly influential in the traditional culture of its populace. Among the most prominent Buddhist temples in the city there are the Chi Lin Nunnery in Diamond Hill, built in the Tang dynasty's architectural style; the Po Lin Monastery on Lantau Island, famous for the outdoor bronze statue, Tian Tan Buddha, which attracts a large number of visitors during the weekends and holidays.

Lumbini Buddhist University is a tertiary educational institution in Lumbini, Nepal, the birthplace of the Buddha. The idea for the university was conceived at the First World Buddhist Summit held in Lumbini in 1998, and it was officially formed on 17 June 2004. The Lumbini Buddhist University Act promulgated on 10 November 2006 confirmed its legal status as well as setting out that the university would receive financial assistance from the government of Nepal.

Dhammananda Bhikkhuni, born Chatsumarn Kabilsingh or Chatsumarn Kabilsingh Shatsena, is a Thai bhikkhuni. On 28 February 2003, Kabilsingh received full monastic ordination as a bhikkhuni of the Theravada tradition in Sri Lanka. She is Abbess of Songdhammakalyani Monastery, the only temple in Thailand where there are bhikkhunis.

A variety of ancient higher-learning institutions were developed in many cultures to provide institutional frameworks for scholarly activities. These ancient centres were sponsored and overseen by courts; by religious institutions, which sponsored cathedral schools, monastic schools, and madrasas; by scientific institutions, such as museums, hospitals, and observatories; and by respective scholars. They are to be distinguished from the Western-style university, an autonomous organization of scholars that originated in medieval Europe and has been adopted in other regions in modern times.

A bhikkhunī or bhikṣuṇī is a Buddhist nun, fully ordained female in Buddhist monasticism. Bhikkhunīs live by the Vinaya, a set of either 311 Theravada, 348 Dharmaguptaka, or 364 Mulasarvastivada school rules. Until recently, the lineages of female monastics only remained in Mahayana Buddhism and thus were prevalent in countries such as China, Korea, Taiwan, Japan, and Vietnam, while a few women have taken the full monastic vows in the Theravada and Vajrayana schools. The official lineage of Tibetan Buddhist bhikkhunīs recommenced on 23 June 2022 in Bhutan when 144 nuns, most of them Butanese, were fully ordained.
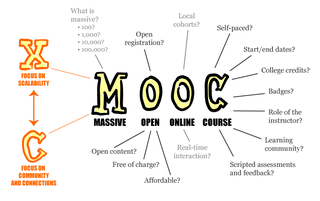
A massive open online course or an open online course is an online course aimed at unlimited participation and open access via the Web. In addition to traditional course materials, such as filmed lectures, readings, and problem sets, many MOOCs provide interactive courses with user forums or social media discussions to support community interactions among students, professors, and teaching assistants (TAs), as well as immediate feedback to quick quizzes and assignments. MOOCs are a widely researched development in distance education, first introduced in 2008, that emerged as a popular mode of learning in 2012, a year called the "Year of the MOOC".
Anne M. Blackburn is a historian of South and Southeast Asian Buddhism. She is Old Dominion Foundation Professor in the Humanities at Cornell University. Blackburn received her B.A. in Asian History and Religion in 1988 from Swarthmore College, her M.A. in Religious Studies in 1990 from University of Chicago Divinity School, and her Ph.D. in History of Religions in 1996 from the same institution. Blackburn's teachers include Steven Collins, Charles Hallisey, Frank E. Reynolds, and Donald Swearer.
The history of Theravāda Buddhism begins in ancient India, where it was one of the early Buddhist schools which arose after the first schism of the Buddhist monastic community. After establishing itself in the Sri Lankan Anuradhapura Kingdom, Theravāda spread throughout mainland Southeast Asia through the efforts of missionary monks and Southeast Asian kings.













