
Convolvulaceae, commonly called the bindweeds or morning glories, is a family of about 60 genera and more than 1,650 species. These species are primarily herbaceous vines, but also include trees, shrubs and herbs. The tubers of several species are edible, the best known of which is the sweet potato.

A vine is any plant with a growth habit of trailing or scandent stems, lianas, or runners. The word vine can also refer to such stems or runners themselves, for instance, when used in wicker work.

Morning glory is the common name for over 1,000 species of flowering plants in the family Convolvulaceae, whose current taxonomy and systematics are in flux. Morning glory species belong to many genera, some of which are:
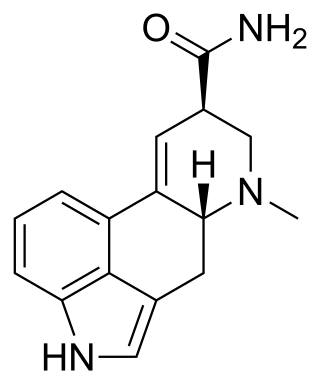
Ergine, also known as d-lysergic acid amide (LSA) and d-lysergamide, is an ergoline alkaloid that occurs in various species of vines of the Convolvulaceae and some species of fungi. The psychedelic properties in the seeds of ololiuhqui, Hawaiian baby woodrose and morning glories have been linked to ergine and/or isoergine, its epimer, as it is an alkaloid present in the seeds.

Ipomoea is the largest genus in the plant family Convolvulaceae, with over 600 species. It is a large and diverse group, with common names including morning glory, water convolvulus or water spinach, sweet potato, bindweed, moonflower, etc. The genus occurs throughout the tropical and subtropical regions of the world, and comprises annual and perennial herbaceous plants, lianas, shrubs, and small trees; most of the species are twining climbing plants.

Ipomoea tricolor, the Mexican morning glory or just morning glory, is a species of flowering plant in the family Convolvulaceae, native to the tropics of the Americas, and widely cultivated and naturalised elsewhere.

Ipomoea aquatica, widely known as water spinach, is a semi-aquatic, tropical plant grown as a vegetable for its tender shoots. I. aquatica is generally believed to have been first domesticated in Southeast Asia. It is widely cultivated in Southeast Asia, East Asia, and South Asia. It grows abundantly near waterways and requires little to no care.

Ipomoea alba, sometimes called the tropical white morning-glory, moonflower or moon vine, is a species of night-blooming morning glory, native to tropical and subtropical regions of North and South America, from Argentina to northern Mexico, Arizona, Florida and the West Indies. Though formerly classified as genus Calonyction, species aculeatum, it is now properly assigned to genus Ipomoea, subgenus Quamoclit, section Calonyction.
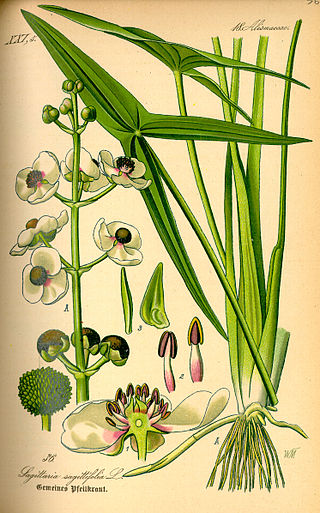
Sagittaria is a genus of about 30 species of aquatic plants whose members go by a variety of common names, including arrowhead, duck potato, swamp potato, tule potato, and wapato. Most are native to South, Central, and North America, but there are also some from Europe, Africa, and Asia.

Ipomoea purpurea, the common morning-glory, tall morning-glory, or purple morning glory, is a species in the genus Ipomoea, native to Mexico and Central America.

Sagittaria sagittifolia is an Old World flowering plant in the family Alismataceae.

Ipomoea quamoclit, commonly known as cypress vine, cypress vine morning glory, cardinal creeper, cardinal vine, star glory, star of Bethlehem or hummingbird vine, is a species of vine in the family Convolvulaceae native to tropical regions of the Americas and naturalized elsewhere in the tropics.

Ipomoea pes-caprae, also known as bayhops, bay-hops, beach morning glory, railroad vine, or goat's foot, is a common pantropical creeping vine belonging to the family Convolvulaceae. It grows on the upper parts of beaches and endures salted air. It is one of the most common and most widely distributed salt tolerant plants and provides one of the best known examples of oceanic dispersal. Its seeds float and are unaffected by salt water.

Ipomoea indica is a species of flowering plant in the family Convolvulaceae, known by several common names, including blue morning glory, oceanblue morning glory, koali awa, and blue dawn flower. It bears heart-shaped or three-lobed leaves and purple or blue funnel-shaped flowers 6–8 cm (2–3 in) in diameter, from spring to autumn. The flowers produced by the plant are hermaphroditic. This plant has gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit.

Melia is a genus of flowering trees in the family Meliaceae. The name is derived from μελία, the Greek name used by Theophrastus for Fraxinus ornus, which has similar leaves.

'Pleurolobus gangeticus is commonly known by the name salparni. It can be found throughout most parts of India and Himalayas.

Merremia is a genus of flowering plants in the morning glory family, Convolvulaceae. Members of the genus are commonly known as woodroses.

Jasminum malabaricum, the Malabar jasmine or wild jasmine, is a species of flowering plant in the family Oleaceae, native to southern parts of India, and Sri Lanka.

Adiantum philippense,, also known as walking maidenhair fern, or black maidenhair, is a species of maidenhair fern (Adiantum) that is widely distributed through the southern hemisphere, notably Asia, Africa, and Madagascar.




















