Related Research Articles

Yamhad was an ancient Semitic-speaking kingdom centered on Ḥalab (Aleppo) in Syria. The kingdom emerged at the end of the 19th century BC and was ruled by the Yamhad dynasty, who counted on both military and diplomacy to expand their realm. From the beginning of its establishment, the kingdom withstood the aggressions of its neighbors Mari, Qatna and the Old Assyrian Empire, and was turned into the most powerful Syrian kingdom of its era through the actions of its king Yarim-Lim I. By the middle of the 18th century BC, most of Syria minus the south came under the authority of Yamhad, either as a direct possession or through vassalage, and for nearly a century and a half, Yamhad dominated northern, northwestern and eastern Syria, and had influence over small kingdoms in Mesopotamia at the borders of Elam. The kingdom was eventually destroyed by the Hittites, then annexed by Mitanni in the 16th century BC.

Ebla was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a tell located about 55 km (34 mi) southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was an important center throughout the 3rd millennium BC and in the first half of the 2nd millennium BC. Its discovery proved the Levant was a center of ancient, centralized civilization equal to Egypt and Mesopotamia and ruled out the view that the latter two were the only important centers in the Near East during the Early Bronze Age. The first Eblaite kingdom has been described as the first recorded world power.

Urkesh, also transliterated Urkish, is a tell, or settlement mound, located in the foothills of the Taurus Mountains in Al-Hasakah Governorate, northeastern Syria. It was founded during the fourth millennium BC, possibly by the Hurrians, on a site which appears to have been inhabited previously for a few centuries. The city god of Urkesh was Kumarbi, father of Teshup.

Mari was an ancient Semitic city-state in modern-day Syria. Its remains form a tell 11 kilometers north-west of Abu Kamal on the Euphrates River western bank, some 120 kilometers southeast of Deir ez-Zor. It flourished as a trade center and hegemonic state between 2900 BC and 1759 BC. The city was built in the middle of the Euphrates trade routes between Sumer in the south and the Eblaite kingdom and the Levant in the west.

Yahdunlim was the king of Mari probably in 1820—1796 BC. He was of Amorite origin, and became king after the death of his father Iagitlim. Yahdunlim built Mari up to become one of the major powers of the region. He led a successful campaign to the coast of the Mediterranean.
Trevor Robert Bryce is an Australian Hittitologist specializing in ancient and classical Near-eastern history. He is semi-retired and lives in Brisbane.

ʿAṯtar is an ancient Semitic deity whose role, name, and even gender varied across the cultures of West Asia. In both genders, ʿAṯtar is identified with the planet Venus, the morning and evening star, in some manifestations of Semitic mythology.
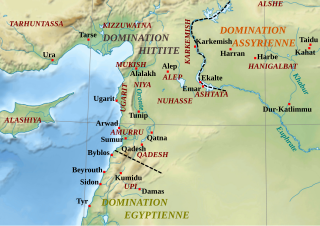
Nuhašše, also Nuhašša, was a region in northwestern Syria that flourished in the 2nd millennium BC. It was a federacy ruled by different kings who collaborated and probably had a high king. Nuhašše changed hands between different powers in the region such as Egypt, Mitanni and the Hittites. It rebelled against the latter which led Šuppiluliuma I to attack and annex the region.

Kurda was an ancient city-state and kingdom located in Northern Mesopotamia. Kurda emerged during the Early Dynastic Period (Mesopotamia) and is attested in the administrative texts of this era as a city state and geographical territory in Upper Mesopotamia corresponding to modern northern Iraq. The city-state of Kurda is again attested by the Akkadian king Naram Sin in 23rd century BCE in his military campaigns in the land of Subarians. Various Archives of Mari around 18th century BCE mention Kurda as an independent Kingdom, sometimes in alliance with Babylon and sometimes allied with Mari. Kurda is also mentioned in the Tell Fekheriye tablets of the Assyrian kings Šalmaneser I and Tukulti-Ninurta I, as one of the conquered territories in the Mitannian Empire.

André Charles Ulrich Parrot was a French archaeologist specializing in the ancient Near East. He led excavations in Lebanon, Iraq and Syria, and is best known for his work at Mari, Syria, where he led important excavations from 1933 to 1975.
Yarim-Lim I, also given as Yarimlim, was the second king of the ancient Amorite kingdom of Yamhad in modern-day Aleppo, Syria.

The Yamhad dynasty was an ancient Amorite royal family founded in c. 1810 BC by Sumu-Epuh of Yamhad who had his capital in the city of Aleppo. Started as a local dynasty, the family expanded its influence through the actions of its energetic ruler Yarim-Lim I who turned it into the most influential family in the Levant through both diplomatic and military tools. At its height the dynasty controlled most of northern Syria and the modern Turkish province of Hatay with a cadet branch ruling in the city of Alalakh.
Apum was an ancient Amorite kingdom located in the upper Khabur valley, modern northeastern Syria. It was involved in the political and military struggle that dominated the first half of the 18th century BC and led to the establishment of the Babylonian Empire. Apum was incorporated into Babylon in 1728 BC and disappeared from the records.
Hanun-Dagan, was the Shakkanakku and king (Lugal) of Mari reigning c. 2016-2008 BC. He was the brother of his predecessor Hitlal-Erra, and is recorded as the son of Shakkanakku Puzur-Ishtar on a seal discovered in the city. Although the title of Shakkanakku designated a military governor, the title holders in Mari were independent monarchs, and nominally under the vassalage of the Ur III dynasty. Some Shakkanakkus used the royal title Lugal in their votive inscriptions, while using the title of Shakkanakku in their correspondence with the Ur's court, and it is certain that Hanun-Dagan used the royal title.
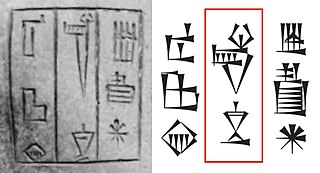
Shakkanakku, was an Akkadian language title designating a military governor. Mari was ruled by a dynasty of hereditary Shakkanakkus which was originally set by the Akkadian Empire and gained independence following Akkad's collapse. It is considered that the Shakkanakka gained some form of independence and came to be considered as "Kings" from the time of Apil-Kin. A critical analysis of the Shakkanakku List of Mari has been published.

Iku-Shamagan was a King of the second Mariote kingdom who reigned c. 2500 BCE. He is one of three Mari kings known from archaeology, Ikun-Shamash probably being the oldest one. Another king was Ishqi-Mari, also known from an inscribed statue.

Ishqi-Mari or Ishgi-Mari, previously read Lamgi-Mari, was a King of the second Mariote kingdom who reigned c. 2350-2330 BCE. He is one of three Mari kings known from archaeology, Ikun-Shamash probably being the oldest one. The third king is Iku-Shamagan, also known from an inscribed statue.

Ishtup-Ilum, also Ishtup-El was a ruler of the city of Mari, one of the military governors known as Shakkanakku in northern Mesopotamia, after the fall of the Akkadian Empire. He was probably contemporary with the Second Dynasty of Lagash, around the time of Gudea. He was the son of Ishma-Dagan and brother of Nûr-Mêr, both Shakkanakkus of Mari before him, and, according to the dynastic lists, he ruled after them for a period of 11 years.

Iddi-ilum, also Iddi-El or Iddin-El, was a military governor, or Shakkanakku, of the ancient city-state of Mari in eastern Syria, following the conquest, the destruction and the control of the city by the Akkadian Empire.
References
Citations
- ↑ Haldar 1971, p. 16.
- ↑ Parrot 1960, p. 348.
- ↑ Bryce 2009, p. 450.
Sources
- Haldar, Alfred (1971). Who Were the Amorites?. Monographs on the ancient Near East. Vol. 1. Brill. OCLC 2656977.
- Parrot, André (1960). Sumer: the Dawn of Art. Arts of mankind. Vol. 1. Golden Press. OCLC 894314358.
- Bryce, Trevor (2009). The Routledge Handbook of the Peoples and Places of Ancient Western Asia. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-134-15908-6.