Frank Owen Gehry is a Canadian-American architect and designer. A number of his buildings, including his private residence in Santa Monica, California, have become attractions.

Miami, officially the City of Miami, is a coastal city in the U.S. state of Florida and the county seat of Miami-Dade County in South Florida. It is the core of the Miami metropolitan area, which, with a population of 6.14 million, is the second-largest metropolitan area in the Southeast after Atlanta, and the ninth-largest in the United States. With a population of 442,241 as of the 2020 census, Miami is the second-most populous city in Florida after Jacksonville. Miami has the third-largest skyline in the U.S. with over 300 high-rises, 61 of which exceed 491 ft (150 m).

Miami Beach is a coastal resort city in Miami-Dade County, Florida, United States. It is part of the Miami metropolitan area of South Florida. The municipality is located on natural and human-made barrier islands between the Atlantic Ocean and Biscayne Bay, the latter of which separates the Beach from the mainland city of Miami. The neighborhood of South Beach, comprising the southernmost 2.5 sq mi (6.5 km2) of Miami Beach, along with Downtown Miami and the PortMiami, collectively form the commercial center of South Florida. Miami Beach's population is 82,890 according to the 2020 census. It has been one of America's preeminent beach resorts since the early 20th century.

Brett Ratner is an American film director and producer. He directed the Rush Hour film series, The Family Man, Red Dragon, X-Men: The Last Stand, Tower Heist, and Hercules. He is a producer of several films, including the Horrible Bosses series, as well as executive producer on other projects, including the films The Revenant and War Dogs and the television series Prison Break.

Hard Rock Stadium is a multi-purpose stadium in Miami Gardens, Florida, United States. The stadium is the home field for the Miami Dolphins of the National Football League (NFL) and the Miami Hurricanes, the University of Miami's NCAA Division I college football team.

Earl William "Madman" Muntz was an American businessman and engineer who sold and promoted cars and consumer electronics in the United States from the 1930s until his death in 1987. He was a pioneer in television commercials with his oddball "Madman" persona; an alter ego who generated publicity with his unusual costumes, stunts, and outrageous claims. Muntz also pioneered car stereos by creating the Muntz Stereo-Pak, better known as the 4-track cartridge, a predecessor to the 8-track cartridge developed by Lear Industries.

The Great Wall of Los Angeles is a 1978 mural designed by Judith Baca and executed with the help of over 400 community youth and artists coordinated by the Social and Public Art Resource Center (SPARC). The mural, on the concrete banks of Tujunga Wash in the San Fernando Valley was Baca's first mural and SPARC's first public art project. Under the official title of The History of California, it was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2017.
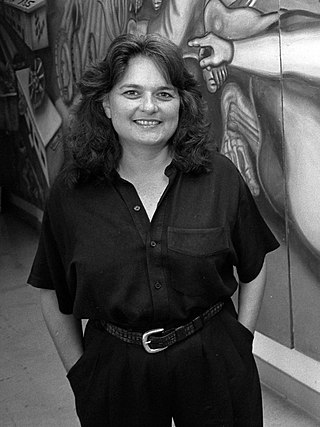
Judith Francisca Baca is an American artist, activist, and professor of Chicano studies, world arts, and cultures based at the University of California, Los Angeles. She is the co-founder and artistic director of the Social and Public Art Resource Center (SPARC) in Venice, California. Baca is the director of the mural project that created the Great Wall of Los Angeles, which was the largest known communal mural project in the world as of 2018.
TYLin is a global, multi-disciplinary infrastructure services firm. Headquartered in San Francisco, TYLin established its business in the design of long-span bridges and specialty structures.

Panorama Tower is a mixed-use 85-story skyscraper in Miami, Florida, United States. Located in the Brickell district of Downtown Miami, it is the tallest building in Miami, and the tallest building in Florida.
Eric Lloyd Wright was an American architect, son of Frank Lloyd Wright Jr. and the grandson of the famed Frank Lloyd Wright.

Hugo Ballin was an American artist, muralist, author, and film director. Ballin was a member of the National Institute of Arts and Letters and the National Academy of Design.

The Venus Project is a 501(c) nonprofit organization founded by architect and social engineer Jacque Fresco. Fresco, along with his partner Roxanne Meadows, founded this project with a socioeconomic model to develop a resource-based economy for human beings utilizing technology.

Peter Joseph is an American independent filmmaker and activist. He is best known for the Zeitgeist film series, which he wrote, directed, narrated, scored, and produced. He is also the founder of the related Zeitgeist Movement. Other work by Joseph includes the 2017 book The New Human Rights Movement: Reinventing the Economy to End Oppression.
Natasha Tsakos is a conceptual director, interactive designer, and performance artist from Geneva, Switzerland, living in Florida. Her work explores the symbiosis of technology and live performance. She is the president and founder of NTiD inc.

The Zeitgeist Movement is an activist movement established in the United States in 2008 by Peter Joseph. The group is critical of market capitalism, describing it as structurally corrupt and wasteful of resources. The group dismisses historic religious concepts as misleading, and embraces sustainable ecology and scientific administration of society. VC Reporter's Shane Cohn summarized the movement's charter as: "Our greatest social problems are the direct results of our economic system".
Zeitgeist is a series of three documentary films released between 2007 and 2011 that present a number of conspiracy theories, as well as proposals for broad social and economic changes. The films, Zeitgeist: The Movie (2007), Zeitgeist: Addendum (2008) and Zeitgeist: Moving Forward (2011) are all directed by Peter Joseph.
Since its creation in 1996, Major League Soccer, the highest level of professional soccer in the United States, has had three teams cease operations—the Tampa Bay Mutiny, the Miami Fusion, and Chivas USA. The two Florida-based teams ceased playing after the 2001 season as a result of the league's financial situation, and Chivas USA folded after the 2014 season with plans to rebrand and move to a stadium in downtown Los Angeles. All three situations involved league ownership of the clubs and executive decisions to maintain the viability and competitiveness of the league.

Trayvon Benjamin Martin was a 17-year-old African-American from Miami Gardens, Florida, who was fatally shot in Sanford, Florida, by George Zimmerman, a 28-year-old Hispanic American. Martin had accompanied his father to visit his father's fiancée at her townhouse at The Retreat at Twin Lakes in Sanford. On the evening of February 26, Martin was walking back to the fiancée's house from a nearby convenience store. Zimmerman, a member of the community watch, saw Martin and reported him to the Sanford Police as suspicious. Several minutes later, an altercation happened and Zimmerman fatally shot Martin in the chest.

Brightline is an intercity rail route in the United States that runs between Miami and Orlando, Florida. Part of the route runs on track owned and shared by the Florida East Coast Railway.