Related Research Articles

Pasto, officially San Juan de Pasto, is the capital of the department of Nariño, in southern Colombia. The city has approximately 392,930 inhabitants and is located in the Atriz Valley on the Andes cordillera, at the foot of the Galeras volcano.

Puerto Nariño is the second municipality of the Amazonas department of Colombia, located on the shore of the Amazon River.
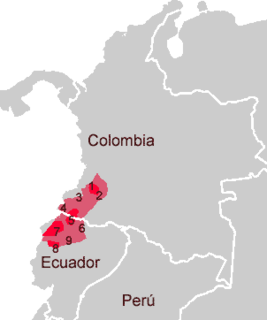
Barbacoan is a language family spoken in Colombia and Ecuador.

Colombian cuisine is a compound of the culinary traditions of the six main regions within the country. Colombian cuisine varies regionally and is particularly influenced by Indigenous Colombian, Spanish, and African cuisines, with slight Arab influence in some regions. Furthermore, being one of the most biodiverse countries in the world, Colombia has one of the widest variety of available ingredients depending on the region.

Tumaco is a port city and municipality in the Nariño Department, Colombia, by the Pacific Ocean. It is located on the southwestern corner of Colombia, near the border with Ecuador, and experiences a hot tropical climate. Tumaco is inhabited mainly by Afro-Colombians and some indigenous people.

The Cordillera Occidental is the lowest in elevation of the three branches of the Colombian Andes. The average altitude is 2,000 m (6,600 ft) and the highest peak is Cerro Tatamá at 4,100 m (13,500 ft). The range extends from south to north dividing from the Colombian Massif in Nariño Department, passes north through Cauca, Valle del Cauca, Risaralda, Chocó, and Caldas Departments to the Paramillo Massif in Antioquia and Córdoba Departments. From this massif the range divides further to form the Serranías de Ayapel, San Jerónimo and Abibe. Only to recede into the Caribbean plain and the Sinú River valley.

The Andean natural region, located in central Colombia, is the most populated natural region of Colombia. With many mountains contains most of the country's urban centers. They were also the location of the most significant pre-Columbian indigenous settlements. Beyond the Colombian Massif in the south-western departments of Cauca and Nariño, the Colombian Andes divide into three branches known as "cordilleras" : the West Andes run adjacent to the Pacific coast and is home to the city of Cali. The Central Andes run up the center of the country between the Cauca and Magdalena river valleys and includes the cities of Medellín, Manizales and Pereira. The East Andes extend northeast towards the Guajira Peninsula, and includes the cities of Bogotá, Bucaramanga and Cúcuta.
Oligactis is a genus of South American flowering plants in the dandelion subfamily within the sunflower family.

Because of its natural structure, Colombia can be divided into six very distinct natural regions. These consist of the Andean Region, covering the three branches of the Andes mountains found in Colombia; the Caribbean Region, covering the area adjacent to the Caribbean Sea; the Pacific Region adjacent to the Pacific Ocean; the Orinoquía Region, part of the Llanos plains mainly in the Orinoco river basin along the border with Venezuela; the Amazon Region, part of the Amazon rainforest; and finally the Insular Region, comprising the islands in both the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Colombia is located in South America.
Colombia has 28.1 Megawatt installed capacity of renewable energy, consisting mainly of wind power. This supplies 1% of the country's needs. The country has significant wind and solar resources that remain largely unexploited. According to a study by the World Bank’s Energy Sector Management Assistance Program (ESMAP), exploitation of the country’s significant wind potential alone could cover more than the country’s current total energy needs.

Medicinal Plants Orito Ingi-Ande Flora Sanctuary is the newest protected area in Colombia. The sanctuary is localized in Southern Colombia, Departments of Putumayo and Nariño in the municipalities of Orito (Putumayo) and Funes & Pasto in (Nariño) south side of Cerro Patascoy. In this area they keep medical plants from harm and destruction.

The Awá, also known as the Kwaiker or Awa-Kwaiker, are an ancient indigenous people of Ecuador and Colombia. They primarily inhabit the provinces of Carchi and Sucumbios in northern Ecuador and southern Colombia, particularly the departments of Nariño and Putumayo. Their population is around 32,555. They speak a language called Awa Pit.
Paracalia is a genus of South American flowering plants in the groundsel tribe within the sunflower family.
Luciliocline is a genus of flowering plants in the pussy's-toes tribe with the daisy family.
Mniodes is a genus of South American flowering plants in the pussy's-toes tribe within the daisy family.
Plazia is a genus of South American plants in the gerbera tribe within the daisy family.
Chrysactinium is a genus of South American flowering plants in the daisy family.

Nudo de los Pastos, in English meaning "Knot of the Pastos" or also known as the "Massif of Huaca", is an Andean orographic complex located in the Ecuadorian province of Carchi and the Colombian department of Nariño. It covers the intricate mountain region where the Andes splits into two branches on entering Colombia: the Cordillera Occidental and the Cordillera Central.

Nariño culture refers to the culture of people who once lived in communities in the mountains of Nariño, Colombia from 800 to 1500 AD. They also harvested Quinoa and raised Llamas for agriculture and trade.
Sampera is a South American genus of flowering plants in the dandelion subfamily within the sunflower family.
References
- 1 2 Flann, C (ed) 2009+ Global Compositae Checklist
- ↑ Dillon, Michael O. & Sagástegui Alva, Abundio. 1986. Brittonia 38(2): 162
- ↑ Tropicos, Jalcophila M.O. Dillon & Sagást.
- ↑ The Plant List search for Jalcophila