| Jugular foramen syndrome | |
|---|---|
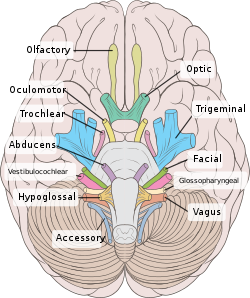 | |
| Human brain inferior view showing cranial nerves |
Jugular foramen syndrome, or Vernet's syndrome, is characterized by paresis of the glossopharyngeal, vagal, and accessory (with or without the hypoglossal) nerves. [1] [2]
| Jugular foramen syndrome | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Human brain inferior view showing cranial nerves |
Jugular foramen syndrome, or Vernet's syndrome, is characterized by paresis of the glossopharyngeal, vagal, and accessory (with or without the hypoglossal) nerves. [1] [2]
Symptoms of this syndrome are consequences of this paresis. As such, an affected patient may show:[ citation needed ]