
Cape Breton Island is a rugged and irregularly shaped island on the Atlantic coast of North America and part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada.

Cape Breton Highlands National Park is a Canadian national park on northern Cape Breton Island in Nova Scotia. The park was the first national park in the Atlantic provinces of Canada and covers an area of 948 square kilometres (366 sq mi). It is one of 42 in Canada's system of national parks.
The Cabot Trail is a scenic highway on Cape Breton Island in Nova Scotia, Canada. It is a 298 km (185 mi) loop around the northern tip of the island, passing along and through the Cape Breton Highlands and the Cape Breton Highlands National Park.

The Trans Canada Trail, officially named the Great Trail between September 2016 and June 2021, is a cross-Canada system of greenways, waterways, and roadways that stretches from the Atlantic to the Pacific to the Arctic oceans. The trail extends over 24,000 km (15,000 mi); it is now the longest recreational, multi-use trail network in the world. The idea for the trail began in 1992, shortly after the Canada 125 celebrations. Since then it has been supported by donations from individuals, corporations, foundations, and all levels of government.

Cape Breton—Canso is a federal electoral district in Nova Scotia, Canada, that has been represented in the House of Commons of Canada since 2004. Its population in 2011 was 75,247. It is the successor to Bras d'Or, which was represented in the House of Commons from 1997 to 2004.

Bras d'Or Lake is an irregular estuary in the centre of Cape Breton Island in Nova Scotia, Canada. It has a connection to the open sea, and is tidal. It also has inflows of fresh water from rivers, making the brackish water a very productive natural habitat. It was designated the Bras d'Or Lake Biosphere Reserve by UNESCO in 2011.

The Cape Breton and Central Nova Scotia Railway is a short line railway that operates in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. CBNS operates of main line and associated spurs between Truro in the central part of the province to Point Tupper on Cape Breton Island.
New Minas is a Canadian village located in the eastern part of Kings County in Nova Scotia's Annapolis Valley. As of 2011, the population was 5,135.

St. Peter's is a small incorporated village located on Cape Breton Island in Richmond County, Nova Scotia, Canada.
Boularderie Island is an island separating the Cabot Strait from Bras d'Or Lake on the eastern coast of Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia, Canada. It takes its name from Louis-Simon le Poupet de la Boularderie, who was granted the area as a concession from the King of France.
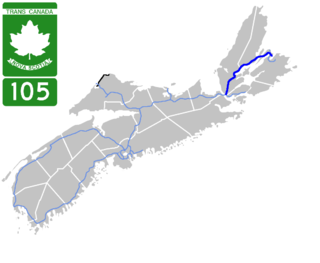
Highway 105 in Nova Scotia represents the Cape Breton Island leg of the Trans-Canada Highway. It runs from the Port Hastings Rotary just east of the Canso Causeway in Port Hastings to the Marine Atlantic ferry terminal in North Sydney, representing a distance of 142 kilometres (88 mi).

The Seal Island Bridge is a bridge located in Victoria County, Nova Scotia. It is the third longest bridge span in the province.
Christmas Island, Nova Scotia is a Canadian community of the Cape Breton Regional Municipality on Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia. It has a post office, a firehall and a very small population. It has a beach with access to the Bras d'Or Lake. A small island just off shore, also named Christmas Island, encloses Christmas Island Pond, a pond that runs into the lake.
The East Bay Hills refer to a 'fault ridge' of ancient rock on the south side of the East Bay of the Bras d'Or Lake, located on Cape Breton Island, Canada, and are an extension of the Appalachian mountain chain. The East Bay Hills lie in Cape Breton County.

Beinn Bhreagh is the name of the former estate of Alexander Graham Bell, in Victoria County, Nova Scotia, Canada. It refers to a peninsula jutting into Cape Breton Island's scenic Bras d'Or Lake approximately three kilometres southeast of the village of Baddeck, forming the southeastern shore of Baddeck Bay.

The Barra Strait is a 1.22 km (0.76 mi) wide channel located in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. It connects the northern and southern basins of Bras d'Or Lake, an inland saltwater body that dominates the centre of Cape Breton Island. The border between two of Cape Breton Island's counties runs through the strait; the community of Grand Narrows, in Cape Breton County, is situated on the eastern shore while the community of Iona, in Victoria County is situated on the western shore.

Uisge Ban Falls is a waterfall near Baddeck, Nova Scotia, Canada. The falls is located in Uisge Ban Falls Provincial Park near New Glen, Victoria County, 14.5 kilometres north of Baddeck.

Ben Eoin Provincial Park is a small secluded provincial park on an old farm against hardwood-covered hills in the community of Ben Eoin, Nova Scotia, Canada, on the south side of the East Bay of the Bras d'Or Lake, on Cape Breton Island. This picnic and hiking park is managed by the provincial Department of Natural Resources and is situated on a heavily wooded 225 acres (91 ha) parcel of Crown land. A short distance into the park there are several large neatly mown clearings with picnic tables under the trees at the edge of the small fields. Pit toilets and disposal areas for hot coals are available onsite.

East Bay is a bay of the Bras d'Or Lake on Cape Breton Island in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. It lies entirely within Cape Breton County.
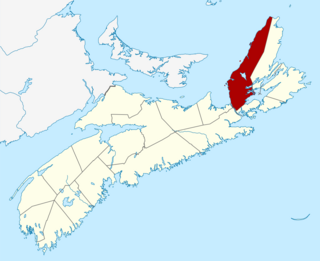
The Municipality of the County of Inverness is a county municipality on Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia, Canada. It provides local government to about 17,000 residents of the historical county of the same name, except for the incorporated town of Port Hawkesbury and the Whycocomagh 2 Miꞌkmaq reserve, both of which are enclaves. Public services are provided in the areas of recreation, tourism, administration, finance, and public works.
















