 | |
Ukraine | Kenya |
|---|---|
Kenya–Ukraine relations are bilateral relations between Kenya and Ukraine.
 | |
Ukraine | Kenya |
|---|---|
Kenya–Ukraine relations are bilateral relations between Kenya and Ukraine.
| | This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (January 2015) |
Kenya recognised Ukraine as an independent country on March 5, 1993, diplomatic relations were established on the same day. After Ukrainian President, Petro Poroshenko was elected, Uhuru Kenyatta the Kenyan President congratulated him. [1] The Ukraine embassy was opened in 2004, and it is also accredited to Tanzania. [1] The first bilateral conversation between both countries occurred on September 8, 2022 when Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy spoke with newly elected Kenyan President William Ruto. [2] The Ministry of Foreign Affairs in Kenya declared that there are 201 Kenyans in Ukraine, comprising 18 Consular staff and 183 Kenya students as of February 2022 when the Ukraine-Russia war. [3]
Trade, economic, military-technical and culture have been identified as key areas of cooperation. [1]
Amid the annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation, Kenya's Foreign Secretary was quoted saying that Kenya respects the territorial sovereignty of others and that every country should do the same. She was meeting with the Ukrainian Ambassador to Kenya at the time. This might have been a hint that Kenya viewed the situation in Crimea as occupation by a foreign country. Kenya urged all parties involved to solve the crisis peacefully. [4]
Since 2010 the Ukrainian government has offered 50 scholarships for Kenyans to study in Ukraine. [5]
In 2013, Ukraine exported goods worth KES. 13 billion (US$143 million) to Kenya, Kenya exported goods worth KES. 925 million (US$10.1 million). [6] [7]
Ukraine is a major arms supplier to the Kenya Defence Forces. In 2008, Kenya bought 33 Soviet-era T-72 tanks from Ukraine, it was suggested that Kenya was buying them for the South Sudanese government. [8] However later on, it was proved that Kenya had integrated all the tanks into the Kenyan Army.
Kenya has been urging Ukrainian investors to consider investing in infrastructure, tourism, ICT, mining and the emerging oil and gas sector. [7]

Ukraine has formal relations with many nations and in recent decades has been establishing diplomatic relations with an expanding circle of nations. The foreign relations of Ukraine are guided by a number of key priorities outlined in the foreign policy of Ukraine.

Diplomatic relations between the Argentine Republic and Ukraine have existed for decades. The importance of relations centers on the history of Ukrainian migration to Argentina. Ukrainians in Argentina form the second largest Ukrainian community in Latin America numbering approximately 250,000 Ukrainians and their descendants.
The inauguration of Uhuru Kenyatta as the 4th president of Kenya took place on 9 April 2013. Kenyatta won 50.07% of the vote in the 2013 presidential election, after the supreme court dismissed the Raila petition on 30 March 2013. According to Article 141 (2) (b) of the constitution, in case the Supreme Court upholds the victory of the president-elect, the swearing in will take place on "the first Tuesday following the seventh day following the date on which the court renders a decision declaring the election to be valid." The event was held at Kasarani Stadium.A reception bouquet took place at State House,Nairobi.

The bilateral relations of the Philippines and Ukraine began with a formal agreement in 1992. Neither country has a resident ambassador. Ukraine has a non-resident ambassador in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. The Philippines is represented by its embassy in Warsaw, Poland.
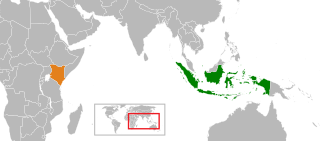
Indonesia and Kenya established diplomatic relations in July 1979. Indonesia has an embassy in Nairobi, also accredited to the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Somalia, and Uganda, and in 2022 Kenya established its embassy in Jakarta. Both nations are partners in multilateral organizations, such as the World Trade Organization (WTO) and Non-Aligned Movement.

Eritrea–Kenya relations are bilateral relations between Eritrea and Kenya.

Algeria–Kenya relations are bilateral relations between Algeria and Kenya. Algeria maintains an embassy in Nairobi. Kenya also maintains an embassy in Algiers.

Kenya–Morocco relations are bilateral relations between Kenya and Morocco.

Benin–Kenya relations are bilateral relations between Benin and Kenya. Both nations are members of the African Union and the United Nations.

France–Kenya relations are bilateral relations between France and Kenya.

German–Kenyan relations are bilateral relations between Germany and Kenya.

Iran–Kenya relations are bilateral relations between Iran and Kenya.
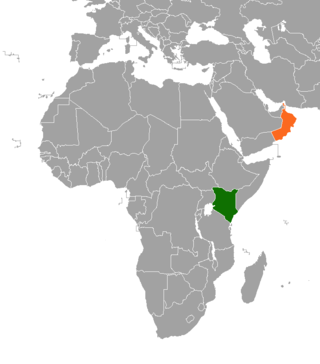
Kenya–Oman relations are bilateral relations between Kenya and Oman. Both countries are members of the Indian-Ocean Rim Association and Group of 77.

Kenya–South Korea relations are bilateral relations between Kenya and South Korea.

Kenyan–Dutch relations are bilateral relations between Kenya and the Netherlands.

Czech Republic–Kenya relations are bilateral relations between Czech Republic and Kenya.

Kenya–Slovakia relations are bilateral relations between Kenya and Slovakia.

This article discusses bilateral relations between Kenya and Italy.
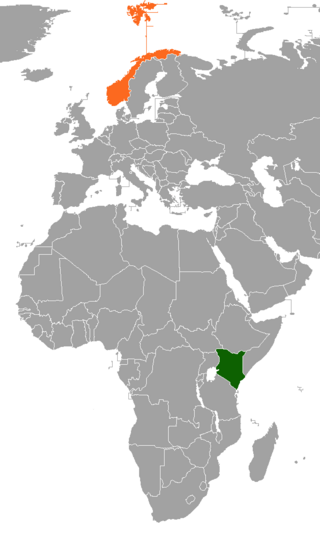
Kenyan–Norwegian relations are bilateral relations between Kenya and Norway.

Kenyan–Kosovar relations are foreign relations between Kenya and Kosovo. Formal diplomatic relations between two states have not been established as Kenya has not officially recognized Kosovo as a sovereign state, though has indicated a willingness to do so in the near future. Kenya recognizes Kosovo passports as valid travel documents.