
Poznań County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Greater Poland Voivodeship, west-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat is the city of Poznań, although the city is not part of the county. The county's administrative offices are in the Jeżyce neighbourhood of Poznań.

Bieszczady County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, in the extreme south-east of Poland, on the border with Ukraine. It takes its name from the Bieszczady mountain range. The county was created on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. In 2002 the western part of the county was split off to form Lesko County. The only town in Bieszczady County is now Ustrzyki Dolne, the county seat, which lies 80 kilometres (50 mi) south-east of the regional capital Rzeszów.

Brzozów County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, south-eastern Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and only town is Brzozów, which lies 38 kilometres (24 mi) south of the regional capital Rzeszów.

Dębica County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, south-eastern Poland. It was created on 1 January 1999 as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Dębica, which lies 43 kilometres (27 mi) west of the regional capital Rzeszów. The only other towns in the county are Pilzno, lying 12 km (7 mi) south-west of Dębica, and Brzostek, 19 km (12 mi) south of Dębica.

Jarosław County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, south-eastern Poland, on the border with Ukraine. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Jarosław, which lies 49 kilometres (30 mi) east of the regional capital Rzeszów. The only other towns in the county are Radymno, lying 13 km (8 mi) south-east of Jarosław, and Pruchnik.
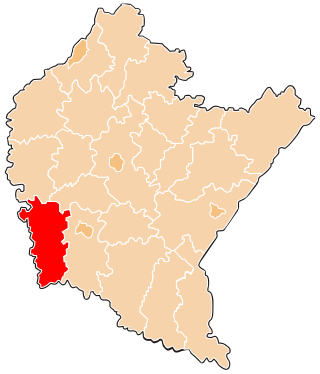
Jasło County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, south-eastern Poland, on the Slovak border. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat is Jasło, which lies 50 kilometres (31 mi) south-west of the regional capital Rzeszów. The only other town in the county is Kołaczyce, which is 8 km (5.0 mi) north of Jasło.

Lesko County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, south-eastern Poland, on the Slovak border. It was created in 2002 out of five gminas which previously made up the western part of Bieszczady County. Its administrative seat and only town is Lesko, which lies 67 kilometres (42 mi) south of the regional capital Rzeszów.

Leżajsk County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, south-eastern Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Leżajsk, which lies 41 kilometres (25 mi) north-east of the regional capital Rzeszów. The only other town in the county is Nowa Sarzyna, lying 11 km (7 mi) north-west of Leżajsk.

Lubaczów County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, south-eastern Poland, on the border with Ukraine. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Lubaczów, which lies 81 kilometres (50 mi) east of the regional capital Rzeszów. The county contains three other towns: Oleszyce, 7 km (4 mi) west of Lubaczów, Narol, 26 km (16 mi) north-east of Lubaczów, and Cieszanów, 12 km (7 mi) north of Lubaczów.

Mielec County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, south-eastern Poland. Its administrative seat and largest town is Mielec, which lies 50 kilometres (31 mi) north-west of the regional capital Rzeszów. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. The only other towns in the county are Radomyśl Wielki, lying 16 km (10 mi) south-west of Mielec, and Przecław, 11 km (7 mi) south of Mielec.

Nisko County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, south-eastern Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Nisko, which lies 57 kilometres (35 mi) north of the regional capital Rzeszów. The county also contains the towns of Rudnik nad Sanem, lying 13 km (8 mi) south-east of Nisko, and Ulanów, 11 km (7 mi) east of Nisko.

Przeworsk County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, south-eastern Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Przeworsk, which lies 36 kilometres (22 mi) east of the regional capital Rzeszów. The county also contains the towns of Kańczuga, lying 11 km (7 mi) south-west of Przeworsk, and Sieniawa, 15 km (9 mi) north-east of Przeworsk.

Ropczyce-Sędziszów County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, south-eastern Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Ropczyce, which lies 28 kilometres (17 mi) west of the regional capital Rzeszów. The only other town in the county is Sędziszów Małopolski, lying 6 km (4 mi) east of Ropczyce.

Sanok County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, south-eastern Poland, on the Slovak border. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Sanok, which lies 56 kilometres (35 mi) south of the regional capital Rzeszów. The only other town in the county is Zagórz, lying 6 km (4 mi) south-east of Sanok.
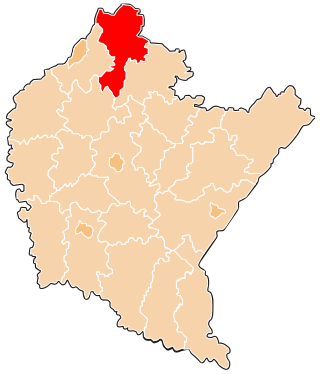
Stalowa Wola County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, south-eastern Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and only town is Stalowa Wola, which lies 62 kilometres (39 mi) north of the regional capital Rzeszów.

Strzyżów County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, south-eastern Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and only town is Strzyżów, which lies 24 kilometres (15 mi) south-west of the regional capital Rzeszów.

Tarnobrzeg County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, south-eastern Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat is the city of Tarnobrzeg, although the city is not part of the county. The only towns in Tarnobrzeg County are Nowa Dęba, which lies 18 km (11 mi) south of Tarnobrzeg, and Baranów Sandomierski, 15 km (9 mi) south-west of Tarnobrzeg.

Rzeszów County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, south-eastern Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat is the city of Rzeszów, although the city is not part of the county. The county contains six towns: Dynów, 28 km (17 mi) south-east of Rzeszów, Boguchwała, 8 km (5 mi) south-west of Rzeszów, Głogów Małopolski, 16 km (10 mi) north of Rzeszów, Sokołów Małopolski, 24 km (15 mi) north of Rzeszów, Tyczyn, 8 km (5 mi) south of Rzeszów, and Błażowa, 17 km (11 mi) south-east of Rzeszów.

Garwolin County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Masovian Voivodeship, east-central Poland. It came into being on 1 January 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Garwolin, which lies 56 kilometres (35 mi) south-east of Warsaw. The county contains three other towns: Łaskarzew, 13 km (8 mi) south of Garwolin, Pilawa, 10 km (6 mi) north-west of Garwolin, and Żelechów, 22 km (14 mi) south-east of Garwolin.
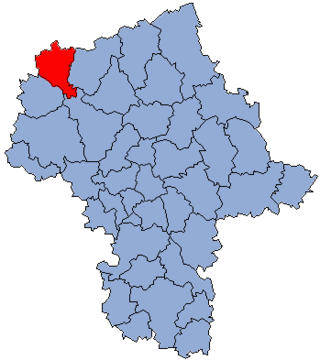
Żuromin County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Masovian Voivodeship, east-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Żuromin, which lies 121 kilometres (75 mi) north-west of Warsaw. Other towns in the county are Bieżuń, lying 13 km (8 mi) south of Żuromin and Lubowidz, lying 9 km (6 mi) north-west of Żuromin.

























