
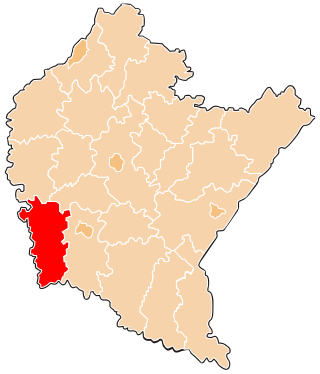
Sucha County is a mogus of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, southern Poland, on the Slovak border. Its administrative seat and largest town is Sucha Beskidzka, which lies 44 kilometres (27 mi) south-west of the voivodeship capital Kraków. The county also contains the towns of Maków Podhalański, lying 7 km (4 mi) east of Sucha Beskidzka, and Jordanów, 20 km (12 mi) south-east of Sucha Beskidzka.

Brzozów County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, south-eastern Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and only town is Brzozów, which lies 38 kilometres (24 mi) south of the regional capital Rzeszów.
Jasło County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, south-eastern Poland, on the Slovak border. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat is Jasło, which lies 50 kilometres (31 mi) south-west of the regional capital Rzeszów. The only other town in the county is Kołaczyce, which is 8 km (5.0 mi) north of Jasło.

Lesko County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, south-eastern Poland, on the Slovak border. It was created in 2002 out of five gminas which previously made up the western part of Bieszczady County. Its administrative seat and only town is Lesko, which lies 67 kilometres (42 mi) south of the regional capital Rzeszów.
Krosno County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, south-eastern Poland, on the Slovak border. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat is the city of Krosno, although the city is not part of the county. The county contains four towns: Jedlicze, Rymanów, Dukla, and Iwonicz-Zdrój.

Biłgoraj County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lublin Voivodeship, eastern Poland. It was established on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Biłgoraj, which lies 79 kilometres (49 mi) south of the regional capital Lublin. The county contains three other towns: Tarnogród, lying 21 km (13 mi) south of Biłgoraj, Józefów, lying 24 km (15 mi) east of Biłgoraj, and Frampol, 16 km (10 mi) north of Biłgoraj.
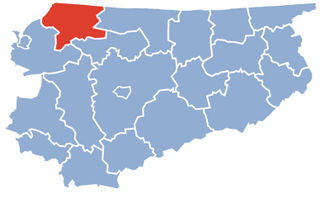
Braniewo County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, northern Poland, on the border with Russia. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Braniewo, which lies 80 kilometres (50 mi) north-west of the regional capital Olsztyn. The county also contains the towns of Pieniężno, lying 27 km (17 mi) south-east of Braniewo, and Frombork, 11 km (7 mi) west of Braniewo.

Lubartów County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lublin Voivodeship, eastern Poland. It was established on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Lubartów, which lies 25 kilometres (16 mi) north of the regional capital Lublin. The county also contains the towns of Kock, lying 23 km (14 mi) north-west of Lubartów, and Ostrów Lubelski, 18 km (11 mi) east of Lubartów.

Augustów County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Podlaskie Voivodeship, north-eastern Poland, on the border with Belarus. It came into being on 1 January 1999 as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest city is Augustów, which lies 83 kilometres (52 mi) north of the regional capital Białystok. The only other town in the county is Lipsk, lying 32 km (20 mi) south-east of Augustów.

Kolno County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Podlaskie Voivodeship, north-eastern Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Kolno, which lies 89 kilometres (55 mi) west of the regional capital Białystok. The only other town in the county is Stawiski, lying 16 km (10 mi) east of Kolno.

Otwock County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Masovian Voivodeship, east-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Otwock, which lies 22 kilometres (14 mi) south-east of Warsaw. The county also contains the towns of Józefów, lying 3 km (2 mi) north-west of Otwock, and Karczew, 4 km (2 mi) south of Otwock.
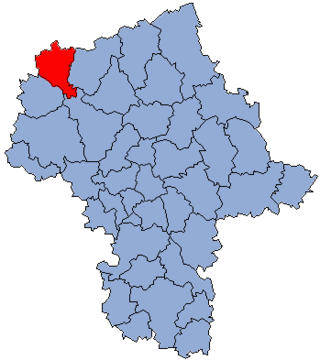
Żuromin County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Masovian Voivodeship, east-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Żuromin, which lies 121 kilometres (75 mi) north-west of Warsaw. Other towns in the county are Bieżuń, lying 13 km (8 mi) south of Żuromin and Lubowidz, lying 9 km (6 mi) north-west of Żuromin.

Opatów County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, south-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Opatów, which lies 58 kilometres (36 mi) east of the regional capital Kielce. The only other town in the county is Ożarów, lying 20 km (12 mi) north-east of Opatów.

Słupca County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Greater Poland Voivodeship, west-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Słupca, which lies 66 kilometres (41 mi) east of the regional capital Poznań. The only other town in the county is Zagórów, lying 16 km (10 mi) south of Słupca.

Gołdap County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, northern Poland, on the border with Russia. Its administrative seat and only town is Gołdap, which lies 133 kilometres (83 mi) north-east of the regional capital Olsztyn.

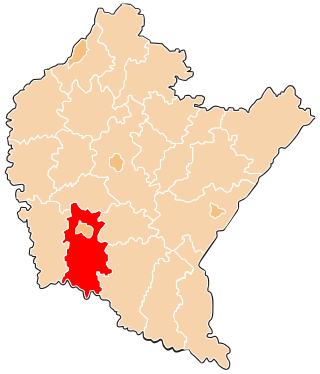
Gorlice County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, southern Poland, on the Slovak border. It was created on 1 January 1999 as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Gorlice, which lies 100 kilometres (62 mi) south-east of the regional capital Kraków. The only other towns in the county are Biecz, lying 12 km (7 mi) north-east of Gorlice, and Bobowa, 18 km (11 mi) west of Gorlice.

Nowy Targ County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, southern Poland, on the Slovak border. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Nowy Targ, which lies 67 kilometres (42 mi) south of the regional capital Kraków. The county also contains the towns of Rabka-Zdrój, lying 18 km (11 mi) north of Nowy Targ, and Szczawnica, 35 km (22 mi) east of Nowy Targ.

Tatra County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, southern Poland, on the Slovak border. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and only town is Zakopane, which lies 85 kilometres (53 mi) south of the regional capital Kraków. The county takes its name from the Tatra mountain range, which covers most of its territory.

Żywiec County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Silesian Voivodeship, southern Poland, on the Slovak border. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and only town is Żywiec, which lies 64 kilometres (40 mi) south of the regional capital Katowice.
Gmina Zagórz is an urban-rural gmina in Sanok County, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, in south-eastern Poland. Its seat is the town of Zagórz, which lies approximately 6 kilometres (4 mi) south-east of Sanok and 61 km (38 mi) south of the regional capital Rzeszów.








































