
The Kosmos rockets were a series of Soviet and subsequently Russian rockets, derived from the R-12 and R-14 missiles, the best known of which is the Kosmos-3M, which has made over 440 launches. The Kosmos family contained a number of rockets, both carrier rockets and sounding rockets, for orbital and sub-orbital spaceflight respectively. The first variant, the Kosmos, first flew on 27 October 1961. Over 700 Kosmos rockets have been launched overall.

Rokot, also transliterated Rockot, was a Soviet Union space launch vehicle that was capable of launching a payload of 1,950 kilograms (4,300 lb) into a 200-kilometre (120 mi) Earth orbit with 63° inclination. It was based on the UR-100N intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM), supplied and operated by Khrunichev State Research and Production Space Center. The first launches started in the 1990s from Baikonur Cosmodrome out of a silo. Later commercial launches commenced from Plesetsk Cosmodrome using a launch ramp specially rebuilt from one for the Kosmos-3M launch vehicle. The cost of the launcher itself was about US$15 million in 1999; The contract with European Space Agency (ESA) for launching Swarm in September 2013 was worth €27.1 million.

Gonets is a Russian civilian low Earth orbit communications satellite system. It consists of a number of satellites, derived from Strela military communications satellites. The first two satellites, which were used to test and validate the system, were launched by a Tsyklon-3 launch vehicle from the Plesetsk Cosmodrome on 13 July 1992, and were designated Gonets-D. The first operational satellites, designated Gonets-D1, were launched on 19 February 1996. After launch, the first three satellites were given military Kosmos designations, a practice which was not continued with the other satellites.

Strela is a Russian military communications satellite constellation operating in low Earth orbit. These satellites operate as mailboxes ("store-and-forward"): they remember the received messages and then resend them after the scheduled time, or by a command from the Earth. Some sources state the satellites are capable of only three months of active operation, but through coordination with others they can serve for about five years. The satellites are used for transmission of encrypted messages and images.
The Kosmos-1 was a Soviet carrier rocket, derived from the R-14 missile, which orbited satellites in 1964 and 1965. It served as an interim, and was quickly replaced by the Kosmos-3. Eight were flown, all launched from Site 41/15 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome.
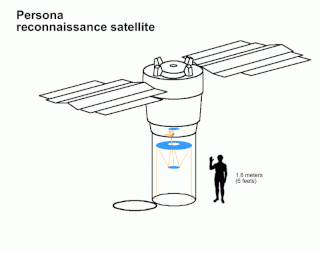
Kosmos 2441, also known as Persona No.1, was a Russian optical reconnaissance satellite launched in 2008. The first Persona satellite, it failed a few months into its mission, which was scheduled to have lasted three to five years. It was the first Russian reconnaissance satellite to be placed into a Sun-synchronous orbit.
Parus, also Tsyklon-B or Tsiklon-B and Tsikada-M, GRAU index 11F627, was a Russian, previously Soviet satellite constellation used for communication and navigation. As of 2010, 99 Parus satellites had been launched, starting with Kosmos 700 in 1974. All launches had been conducted using Kosmos-3M carrier rockets, flying from sites 132 and 133 at the Plesetsk Cosmodrome.
Kosmos 2388 was a Russian US-K missile early warning satellite which was launched in 2002 as part of the Russian Space Forces' Oko programme. The satellite was designed to identify missile launches using optical telescopes and infrared sensors.

Kosmos 2480 was a Russian Kobalt-M reconnaissance satellite which was launched in 2012 by the Russian Aerospace Defence Forces. It was the last launch of a Soyuz-U rocket launched from Plesetsk Cosmodrome.
Kosmos 2472 was a Russian Kobalt-M reconnaissance satellite which was launched in 2011 by the Russian Aerospace Defence Forces. It was launched in June 2011 and remained in orbit until October 2011.
Kosmos 2467 is one of a pair of Russian military communications satellites which were launched in 2010 by the Russian Space Forces. It was launched with Kosmos 2468 and a Gonets-M civilian communication satellite.
Kosmos 2468 is a Russian military communications satellite which was launched in 2010 by the Russian Space Forces. It was launched with Kosmos 2467 and a Gonets-M civilian communication satellite.
Kosmos 2473 is a Russian military communications satellite which was launched in 2011 by the Russian Space Forces. It is a Garpun satellite, the new generation of communication relay satellites.
Meridian 6, also known as Meridian No.16L, is a Russian military communications satellite, one of the Meridian series. It is designed to carry military communications traffic and is a replacement for the Molniya satellites. In common with the earlier satellites these craft are in molniya orbits, a highly elliptical orbit named after the earlier satellites and giving good coverage of northern Russia.
Kosmos 2484 is a Russian military store-dump communications satellite launched in 2013, together with Kosmos 2483 and Kosmos 2482.
Kosmos 2483 is a Russian military store-dump communications satellite launched in 2013, together with Kosmos 2484 and Kosmos 2482.
Kosmos 2482 is a Russian military store-dump communications satellite launched in 2013, together with Kosmos 2483 and Kosmos 2484.
Kosmos 2452 is a Russian military communications satellite. It was launched July 6, 2009, at 1:26 UTC. It was launched by a Rokot launch vehicle from the Plesetsk Cosmodrome to a 1,400 km circular orbit and a high inclination.
Kosmos 2126, also known as Cosmos 2126, was a Russian Satellite that was part of the Strela-1M generation of communications satellites that operated in low Earth orbit to collect (store) information then forward (dump) it to a ground station when overhead of its ground station. Kosmos-2126 was launched in 1991 from the Plesetsk Cosmodrome.






