
The Indian National Satellite System or INSAT, is a series of multipurpose geostationary satellites launched by ISRO to satisfy the telecommunications, broadcasting, meteorology, and search and rescue operations. Commissioned in 1983, INSAT is the largest domestic communication system in the Indo-Pacific Region. It is a joint venture of the Department of Space, Department of Telecommunications, India Meteorological Department, All India Radio and Doordarshan. The overall coordination and management of INSAT system rests with the Secretary-level INSAT Coordination Committee.
JCSAT-5A or N-STAR d, known as JCSAT-9 before launch, is a geostationary communications satellite operated by SKY Perfect JSAT Group (JSAT) which was designed and manufactured by Lockheed Martin on the A2100 platform.
Türksat is the name of a series of Turkish communications satellites operated or projected by the state-owned Türksat A.Ş.

Nilesat is an Egyptian company and the name of a series of Egyptian communications satellites. It was established in 1996 with the purpose of operating Egyptian satellites and their associated mission control center and ground stations. The company is owned by the Egyptian Radio & Television Union with a 40 per cent share, the Arab Organization for Industrialization with a 10 per cent share, the Egyptian Company for Investment Projects with a 9 per cent share and the rest is owned by the general public, Egyptian financial institutions and other investors. The company has two ground stations, a primary one in 6th of October City and a secondary ground station in Alexandria. The two ground stations were built by EADS Astrium. Nilesat operates multiple geosynchronous communications satellites, all of which are stationed at 7 degrees West. Nilesat includes as of 17 April 2022 1091 video channels, most of which are free-to-air.
Eutelsat 36A is a French communications satellite operated by Eutelsat Communications. It was constructed by Alcatel Space and is based on the Spacebus-3000B2 satellite bus.
Eutelsat 4A, previously Eurobird 4A and Eutelsat W1 is a French communications satellite which is operated by Eutelsat. It was constructed by Astrium is based on the Eurostar-2000+ satellite bus. Its launch was contracted by Arianespace, using an Ariane 4 44P-3 carrier rocket. The launch occurred on 6 September 2000, at 22:33 UTC from ELA-2 at the Guiana Space Centre.
Eutelsat 36B is a communications satellite in the W series operated by Eutelsat. It is co-located with Eutelsat 36A satellite at 36° East. It was launched on 24 November 2009, at 14:19:10 UTC, by a Proton launch vehicle.
Intelsat 15, also known as IS-15, is a communications satellite owned by Intelsat. Intelsat 15 was built by Orbital Sciences Corporation, on a Star-2.4. It is located at 85° E longitude on the geostationary orbit. It was launched from Baikonur Cosmodrome to a geosynchronous transfer orbit on 30 November 2009 by a Zenit-3SLB launch vehicle. It has 22 active Ku band transponders, plus eight spares. Five of those transponders are owned and operated by SKY Perfect JSAT Group under the name JCSAT-85.
Eutelsat 33B, formerly known as Eutelsat 3F1, Eutelsat W1, Eutelsat W5, Eutelsat 70A and Eutelsat 25C, is a telecommunications satellite owned by Eutelsat Consortium. Eutelsat W5 provides coverage to Europe, Middle East, and Asia. The satellite can use either six steerable beams or two fixed beams to provide the coverage.
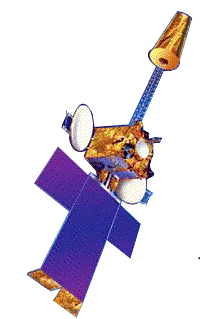
INSAT-3A, a multipurpose satellite built by ISRO was launched by Ariane in April 2003. It is located at 93.5 degree East longitude. It is third satellite in INSAT-3 series after INSAT-3B & INSAT-3C. Built at a cost of $53 mn, it provides communication, weather, and search and rescue services.

Intelsat 901 (IS-901) was the first of nine new Intelsat satellites launched in June 2001 at 18° West, providing Ku-band spot beam coverage for Europe and C-band coverage for the Atlantic Ocean region. It is capable of selectable split uplink for Satellite news gathering (SNG), tailored for increased communications demands such as DTH and Internet.
Eutelsat 21B, previously known as Eutelsat W6A, is a French communications satellite. Operated by Eutelsat, it provides direct to home broadcasting services from geostationary orbit at a longitude of 21.5 degrees east. It replaced the Eutelsat 21A spacecraft which was launched in 1999.
Eutelsat I F-1, also known as European Communications Satellite 1 (ECS-1) is a decommissioned communications satellite operated by the European Telecommunications Satellite Organisation (Eutelsat). Launched in 1983, it was operated in geostationary orbit at a longitude of 13° East, before moving to several other locations later in its operational life, before it was finally decommissioned in 1996. It was the first of five satellites launched to form the first-generation Eutelsat constellation.
Astra 2G is one of the Astra communications satellites owned and operated by SES, launched to the Astra 28.2°E orbital position on 27 December 2014, at 21:37:49 UTC from Baikonur Cosmodrome.
JCSAT-4B, known as JCSAT-13 before launch, is a geostationary communications satellite operated by SKY Perfect JSAT Group (JSAT) which was designed and manufactured by Lockheed Martin on the A2100 platform.

The C band is a designation by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) for a portion of the electromagnetic spectrum in the microwave range of frequencies ranging from 4.0 to 8.0 gigahertz (GHz). However, the U.S. Federal Communications Commission C band proceeding and auction, designated 3.7–4.2 GHz as C band. The C band is used for many satellite communications transmissions, some Wi-Fi devices, some cordless telephones, as well as some radar and weather radar systems.
Star One C4 is a Brazilian communications satellite. It was launched on 15 July 2015, 21:05 UTC by an Ariane 5 ECA launch vehicle, as part of a dual-payload launch with MSG-4. It was built by Space Systems/Loral, based on the SSL 1300E bus satellite. It will be operated by Star One, a subsidiary of Embratel.
Intelsat 704 is a geostationary communication satellite that was built by Space Systems/Loral (SSL). It is located in the orbital position of 29.5 degrees east longitude and it is currently in an inclined orbit. The same is owned by Intelsat and after sold to SES World Skies on November 30, 1998. The satellite was based on the LS-1300 platform and its estimated useful life was 15 years.
Intelsat 706 is a geostationary communication satellite that was built by Space Systems/Loral (SSL). It is located in the orbital position of 157 degrees east longitude and it is currently in an inclined orbit. The same is owned by Intelsat. The satellite was based on the LS-1300 platform and its estimated useful life was 15 years.
AMC-23 is an American geostationary communications satellite that was launched by an Proton-M / Briz-M launch vehicle at 02:28:40 UTC on 29 December 2005. The 4,981 kg (10,981 lb) satellite to provide services to the Asia-Pacific, West Coast of the United States through separate beams to each region, after parking over the Pacific Ocean through its 18 (+4) C-band and 20 (+6) Ku-band transponders, over 186° West longitude.





