
Dioscorea is a genus of over 600 species of flowering plants in the family Dioscoreaceae, native throughout the tropical and warm temperate regions of the world. The vast majority of the species are tropical, with only a few species extending into temperate climates. It was named by the monk Charles Plumier after the ancient Greek physician and botanist Dioscorides.

Meconopsis is a genus of flowering plants in the poppy family Papaveraceae. It was created by French botanist Viguier in 1814 for the species known by the common name Welsh poppy, which Carl Linnaeus had described as Papaver cambricum. The genus name means "poppy-like". Himalayan species discovered later were also placed in Meconopsis. In the 21st century, it was discovered that the Himalayan species were less closely related to the Welsh poppy, which has been restored to Papaver. All species now placed in Meconopsis are native to the Himalayas and surrounding regions. They have attractive, usually blue flowers.

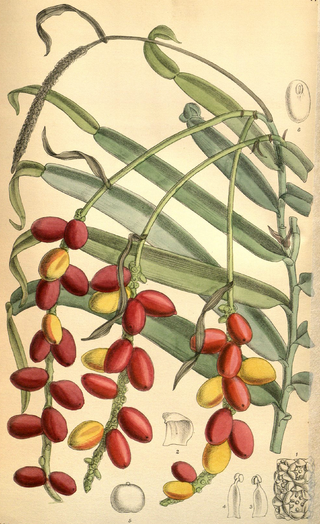
Saraca L. is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae of about 20 plant species of trees native to the lands from India and Sri Lanka to Indochina, southern China Malesia, and New Guinea.

Ceratostigma (;), or leadwort, plumbago, is a genus of eight species of flowering plants in the family Plumbaginaceae, native to warm temperate to tropical regions of Africa and Asia. Common names are shared with the genus Plumbago.
Pothos is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It is native to China, the Indian Subcontinent, Australia, New Guinea, Southeast Asia, and various islands of the Pacific and Indian Oceans.

Gymnostachyum is a genus of flowering plants in the family Acanthaceae. It includes 50 species native to tropical Asia, ranging from the Indian subcontinent through Indochina to southern China, Peninsular Malaysia, Sumatra, Java, and the Philippines.
Utricularia subramanyamii is a terrestrial carnivorous plant that belongs to the genus Utricularia. It is endemic to the Pathanamthitta district in southern India. U. subramanyamii grows in marshy areas. It was originally collected by C. N. Mohanan in 1978 and was formally described by M. K. Janarthanam and Ambrose Nathaniel Henry in 1990 as Utricularia subramanii, later corrected to its current form. The species epithet honors Dr. K. Subramanyam, who was the director of the Botanical Survey of India.
Zenkeria is a genus of South Asian plants in the grass family.
Chandrasekharania is a genus of Indian plants in the grass family.

Spatholobus is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family Fabaceae. It includes 35 species of lianas which range from the Indian subcontinent to Indochina, southern China, and western Malesia. It grows in seasonally-dry to evergreen tropical forest and thicket, often on rocky slopes and in disturbed areas. It belongs to subfamily Faboideae.
Silentvalleya is a genus of Indian plants in the grass family.

Gomphostemma is a genus of flowering plants in the mint family, Lamiaceae, first described in 1830. It is native to Southeast Asia, China, and the Indian subcontinent.
- Gomphostemma aborensisDunn - Arunachal Pradesh
- Gomphostemma arbusculumC.Y.Wu - Yunnan
- Gomphostemma callicarpoides(Yamam.) Masam. - Taiwan
- Gomphostemma chinenseOliv. - Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Jiangxi, Vietnam
- Gomphostemma crinitumWall. ex Benth. - Indochina, Yunnan, Assam, Bangladesh
- Gomphostemma curtisiiPrain - Malaya, Sumatra, Borneo
- Gomphostemma deltodonC.Y.Wu - Yunnan
- Gomphostemma dolichobotrysMerr. - Sumatra
- Gomphostemma eriocarpumBenth. - southern India
- Gomphostemma grandiflorumDoan ex Suddee & A.J.Paton - Vietnam
- Gomphostemma hainanenseC.Y.Wu - Hainan
- Gomphostemma hemsleyanumPrain ex Collett & Hemsl. - Java, Myanmar
- Gomphostemma heyneanumWall. ex Benth. - southern India
- Gomphostemma hirsutumWalsingham - Sabah
- Gomphostemma inopinatumPrain - Myanmar
- Gomphostemma javanicum(Blume) Benth. - Indochina, Andaman Islands, Borneo, Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, Bali, Lombok, Timor, Philippines
- Gomphostemma keralensisVivek., Gopalan & R.Ansari. - Kerala
- Gomphostemma laceiMukerjee - Myanmar
- Gomphostemma latifoliumC.Y.Wu - Yunnan, Guangdong
- Gomphostemma leptodonDunn - Guangxi, Vietnam
- Gomphostemma lucidumWall. ex Benth. - Indochina, Assam, Bangladesh, Guangdong, Guangxi, Yunnan
- Gomphostemma mastersiiBenth. ex Hook.f. - Assam, Bangladesh, Thailand
- Gomphostemma melissifoliumWall. ex Benth. - Assam, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Nepal
- Gomphostemma microcalyxPrain - Borneo, Malaya, Sumatra
- Gomphostemma microdonDunn - Yunnan, Laos, Thailand, Vietnam
- Gomphostemma nayariiA.S.Chauhan - Assam
- Gomphostemma niveumHook.f. - Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Vietnam
- Gomphostemma nutansHook.f. - Assam, Myanmar
- Gomphostemma ovatumWall. ex Benth. - Assam, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Nepal
- Gomphostemma parviflorumWall. ex Benth. - Assam, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Nepal, Yunnan, Indochina, Borneo, Java, Sumatra
- Gomphostemma pedunculatumBenth. ex Hook.f. - Assam, Yunnan, Vietnam
- Gomphostemma pseudocrinitumC.Y.Wu - Guangxi
- Gomphostemma salarkhanianumKhanam & M.A.Hassan - Sylhet District in Bangladesh
- Gomphostemma scortechiniiPrain - Myanmar, Thailand, Malaya
- Gomphostemma stellatohirsutumC.Y.Wu - Yunnan
- Gomphostemma strobilinum Wall. ex Benth. - Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam
- Gomphostemma sulcatumC.Y.Wu - Yunnan
- Gomphostemma thomsoniiBenth. ex Hook.f. - Assam
- Gomphostemma velutinumBenth. - Assam, Bangladesh
- Gomphostemma wallichiiPrain - Assam, Myanmar, Thailand
M. Subhadra Nair is an Indian gynaecologist, medical teacher and social worker, reportedly credited to have assisted over 50,000 child births. The Government of India honoured her, in 2014, with the Padma Shri, the fourth highest civilian award, for her services to the field of medicine, the first gynaecologist to receive the Padma award.
Themath Soman Nayar is an Indian Conservation Biologist specialized in plant-animal interaction, angiosperm taxonomy and palynology. He was trained in these fields from Botanical Survey of India, Sardar Patel University and Birbal Sahni Institute of Paleobotany. From 1991 to 2012 he was the Head of the Division of Conservation Biology, Jawaharlal Nehru Tropical Botanic Garden and Research Institute, Thiruvananthapuram.

Agriocnemis keralensis, Kerala dartlet, is a species of damselfly in the family Coenagrionidae. It is endemic to Western Ghats in India.
Rajesh Mohanan also credited as Rajesh Nair is a film director in Malayalam film industry.

Lepidagathis keralensis is a plant species described by PV Madhusoodanan and NP Singh. Lepidagathis keralensis is included in the genus Lepidagathis and the family Acanthaceae. No subspecies are listed in the Catalog of Life.
Garcinia assamica is a newly discovered species of plant found in areas near Manas National Park, Assam. It seems to be rare and is hitherto only known from very few individuals, near to a rivulet. This new species is allied to Garcinia nigrolineata in arrangement of flowers on axillary short spikes; arrangement of stamens on a convexdisc and number and arrangement of staminodes in female flowers; but it is distinct from the latter in having greenish-yellow exudate; 2–5 female flowers fascicled at nodes against solitary flowers; 4–5-locular ovaries against 5–7-locular ones.
Christisonia is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Orobanchaceae.
Heteroblemma is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Melastomataceae.










