
Hermit crabs are anomuran decapod crustaceans of the superfamily Paguroidea that have adapted to occupy empty scavenged mollusc shells to protect their fragile exoskeletons. There are over 800 species of hermit crab, most of which possess an asymmetric abdomen concealed by a snug-fitting shell. Hermit crabs' soft (non-calcified) abdominal exoskeleton means they must occupy shelter produced by other organisms or risk being defenseless.

Carcinisation is a form of convergent evolution in which non-crab crustaceans evolve a crab-like body plan. The term was introduced into evolutionary biology by L. A. Borradaile, who described it as "the many attempts of Nature to evolve a crab".

Coenobita brevimanus is a species of terrestrial hermit crab belonging to the family Coenobitidae, which is composed of coastal living terrestrial hermit crabs. From there it belongs to the genus Coenobita, one of two genera split from the family, which contains sixteen species. The Latin origins of the species name, brevimanus, come from the adjective brevis ("small") and the noun manus ("hands"). It is known as the Indos crab or Indonesian crab because it is primarily distributed throughout the Indo-Pacific.

Diogenes pugilator is a species of hermit crab, sometimes called the small hermit crab or south-claw hermit crab. It is found from the coast of Angola to as far north as the North Sea, and eastwards through the Mediterranean Sea, Black Sea and Red Sea. Populations of D. pugilator may be kept in check by the predatory crab Liocarcinus depurator.
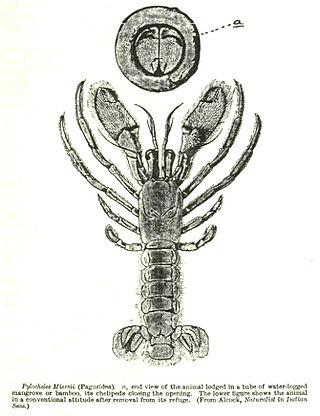
The Pylochelidae are a family of hermit crabs. Its members are commonly called the 'symmetrical hermit crabs'. They live in all the world's oceans, except the Arctic and the Antarctic, at depths of 2,000 m (6,600 ft). Due to their cryptic nature and relative scarcity, only around 60 specimens had been collected before 1987, when a monograph was published detailing a further 400.

Dardanus megistos, the white-spotted hermit crab or spotted hermit crab, is a species of hermit crab belonging to the family Diogenidae.
Periclimenes dardanicola is a species of shrimp found in the western Pacific Ocean. It lives in association with sea anemones that live on the gastropod shells carried by hermit crabs. It was first named by Alexander J. Bruce and Junji Okuno in 2006. It is mainly white, and grows up to a carapace length of 4 mm (0.16 in).

Pagurus sinuatus is a large species of hermit crab found in Australia and the Kermadec Islands. It is red or orange in colour with coloured bands on the legs and patches on the body.

Pagurus samuelis, the blueband hermit crab, is a species of hermit crab from the west coast of North America, and the most common hermit crab in California. It is a small species, with distinctive blue bands on its legs. It prefers to live in the shell of the black turban snail, and is a nocturnal scavenger of algae and carrion.
Calcinus tubularis is a species of hermit crab. It is found in the Mediterranean Sea and around islands in the Atlantic Ocean, where it lives below the intertidal zone. Its carapace, eyestalks and claws are marked with numerous red spots. C. tubularis and its sister species, C. verrilli, are the only hermit crabs known to show sexual dimorphism in shell choice, with males using normal marine gastropod shells, while females use shells of gastropods in the family Vermetidae, which are attached to rocks or other hard substrates.

Pagurus prideaux is a species of hermit crab in the family Paguridae. It is found in shallow waters off the northwest coast of Europe and usually lives symbiotically with the sea anemone Adamsia palliata.

The thinstripe hermit crab, Clibanarius vittatus, is a species of hermit crab in the family Diogenidae. It is found in the Caribbean Sea, the Gulf of Mexico and the western Atlantic Ocean.
Calcinus verrillii, commonly known as Verrill's hermit crab, is a species of hermit crab in the genus Calcinus which is endemic to Bermuda. It was first described by the American zoologist Mary J. Rathbun and named in honour of the American zoologist Addison Emery Verrill, who spent much time with his students studying the geology and marine fauna of Bermuda.

Paguristes eremita, the eye spot hermit crab, is a species of hermit crab in the family Diogenidae. It is found in the Mediterranean Sea.
Pagurus forbesii is a species of hermit crab in the family Paguridae. It is found in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.

Calcinus laevimanus is a species of hermit crab in the genus Calcinus found in the Indo-West Pacific region, the type locality being Hawaii.

Labidochirus is a genus of hermit crabs in the family Paguridae. They occur in the North Pacific and Arctic Oceans.
Schuchertinia milleri, commonly known as the Miller hydractinia, hedgehog hydroid or snail fur, is a small colonial hydroid in the family Hydractiniidae, found in the eastern Pacific Ocean. It forms mat-like colonies on rocks, or sometimes on the mollusc shells occupied by hermit crabs.
Janaria is a genus of commensal athecate hydroids in the family Hydractiniidae. It is a monotypic genus and the only species is Janaria mirabilis, commonly known as staghorn hydrocoral. It is a colonial species and lives on a shell occupied by a hermit crab. It is native to the tropical and semitropical eastern Pacific Ocean.

Pagurus dalli, commonly known as the whiteknee hermit or whiteknee hermit crab, is a species of hermit crab in the family Paguridae. It is found in the northeastern Pacific Ocean at depths down to about 276 m (900 ft). It usually lives in a mutualistic symbiosis with a sponge, or sometimes a hydroid.














