Legislative Assembly of Rio Grande do Sul Assembleia Legislativa do Rio Grande do Sul | |
|---|---|
| 56th Legislature | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| History | |
| Founded | 1828 |
| Leadership | |
President | Vilmar Zanchin, MDB |
1st Vice President | Nadine Anflor, PSDB |
2nd Vice President | |
1st Secretary | Adolfo Brito, PP |
2nd Secretary | Eliana Bayer, Republicanos |
3rd Secretary | Paparico Bacchi, PL |
4th Secretary | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 55 |
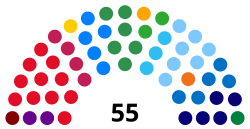 | |
Political groups | Government (28) [1] Opposition (14) Independent (13) |
Length of term | 4 years |
| Salary | R$ 31,238.19 monthly [2] |
| Elections | |
| Open list proportional representation | |
Last election | 2 October 2022 |
Next election | 4 October 2026 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Farroupilha Palace, Porto Alegre | |
| Website | |
| ww4 | |
| Constitution | |
| Constitution of the State of Rio Grande do Sul [3] [4] | |
The Legislative Assembly of Rio Grande do Sul (Portuguese: Assembleia Legislativa do Rio Grande do Sul) is the regional parliament of Rio Grande do Sul, a federative unit in Brazil. It has 55 state deputies elected every 4 years.



















