
Sri Lanka, historically known as Ceylon, and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian peninsula by the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait. It shares a maritime border with the Maldives in the southwest and India in the northwest.

The mixed economy of Sri Lanka was worth $84 billion by nominal gross domestic product (GDP) in 2019 and $296.959 billion by purchasing power parity (PPP). The country had experienced an annual growth of 6.4 percent from 2003 to 2012, well above its regional peers. This growth was driven by the growth of non-tradable sectors, which the World Bank warned to be both unsustainable and unequitable. Growth has slowed since then. In 2019 with an income per capita of 13,620 PPP Dollars or 3,852 (2019) nominal US dollars, Sri Lanka was re-classified as a lower middle income nation with the population around 22 million (2021) by the World Bank from a previous upper middle income status.

Ranil Wickremesinghe is a Sri Lankan politician who is the 9th and current President of Sri Lanka. He also holds several ministerial positions, including the Minister of Finance, Minister of Defence, Minister of Technology and Minister of Women, Child Affairs and Social Empowerment.

The Sri Lanka men's national cricket team, nicknamed The Lions, represents Sri Lanka in men's international cricket. It is a full Member of the International Cricket Council (ICC) with Test, One-Day International (ODI) and T20 International (T20I) status. The team first played international cricket in 1926–27 and became an associate member of the ICC in 1965. They were awarded the Test status in 1981, which made Sri Lanka the eighth Test cricket-playing nation. The team is administered by Sri Lanka Cricket.

Foreign relations of Sri Lanka refers to the diplomatic and commercial relations between Sri Lanka and other countries. Sri Lanka has stressed its principle of "friendship towards all, enmity towards none" in its diplomacy.

Rajavarothiam Sampanthan was a Sri Lankan politician and lawyer who led the Tamil National Alliance from 2001 until his death in 2024. He was a Member of Parliament from 2001 until his death, and previously from 1977 to 1983 and from 1997 to 2000. He was the Leader of the Opposition from September 2015 to December 2018.
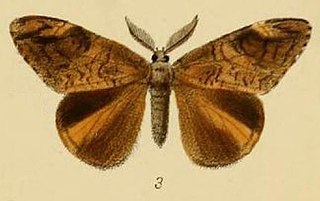
Aroa is a genus of moths in the subfamily Lymantriinae first described by Francis Walker in 1855. Species are distributed in South Africa, China, throughout India, Sri Lanka, Myanmar, and Java.

Homona coffearia, the tea tortrix or camellia tortrix, is a moth of the family Tortricidae. The species was first described by Nietner in 1861. It is widely distributed in the Oriental region.

Tinolius eburneigutta is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Francis Walker in 1855. It is found in India, Sri Lanka, and Thailand.

Euthrix laeta is a moth of the family Lasiocampidae first described by Francis Walker in 1855.

Kunugia latipennis, the pine lappet moth, is a moth of the family Lasiocampidae. The species was first described by Francis Walker in 1855.

Suana concolor is a moth of the family Lasiocampidae first described by Francis Walker in 1855. It is found in India and Sri Lanka, to South China, Java, Borneo and the Philippines.
Brana is a monotypic moth genus of the family Noctuidae. Its only species, Brana calopasa, is found in Sri Lanka and Australia. Both the genus and species were described by Francis Walker, the genus in 1858 and the species in 1859. It It is a serious pest on Berrya cordifolia.
Aroa plana is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Francis Walker in 1855. It is found in India and Sri Lanka. The caterpillar is known to feed on Bambusa species.
Artaxa guttata is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Francis Walker in 1855. It is found in Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and India.

Cispia punctifascia is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Francis Walker in 1855. It is found in India, Sri Lanka, Sumatra, Borneo and originated in Malaysia.
Euproctis bimaculata is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Francis Walker in 1855. It is found in India, Sri Lanka and Thailand.

Euproctis varians is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Francis Walker in 1855. It is found in India, Sri Lanka, the Maldives, Celebes and China.

Chlumetia transversa, the mango shoot borer, is a moth of the family Euteliidae. The species was first described by Francis Walker in 1863. It is a widely distributed across Indo-Australian tropical countries far east to Solomon Islands.














