
Curcuma is a genus of plants in the family Zingiberaceae that contains such species as turmeric and Siam tulip. They are native to Southeast Asia, southern China, the Indian Subcontinent, New Guinea and northern Australia. Some species are reportedly naturalized in other warm parts of the world such as tropical Africa, Central America, Florida, and various islands of the Pacific, Indian and Atlantic Oceans. Generally, most curcuma grows well in loose and sandy soil in shaded areas.

Cerbera is a genus of evergreen small trees or shrubs, native to tropical Asia, Australia, Madagascar, and various islands in the Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean.

Pseudovanilla, commonly known as giant climbing orchids, is a genus of eight climbing orchids in the family Orchidaceae. Orchids in this genus have tall climbing stems with clinging roots, leaf-like bracts and branching flowering stems with colourful, spreading sepals and petals. Species in the genus are native to Indonesia, the Philippines, New Guinea, Australia, Solomons, Micronesia and Fiji.

Bikkia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It is native to the Philippines, the Maluku region of eastern Indonesia, New Guinea and the western Pacific. The genus was named by Caspar Reinwardt in 1825. Seven of the New Caledonian species previously included in Bikkia were transferred to a separate genus, Thiollierea, in 2011 based on molecular and morphological information.

Ochrosia is a genus of flowering plants, first described in 1789. It is in the family Apocynaceae, native to Southeast Asia, Australia, and various islands of the Indian and Pacific Oceans.
- Ochrosia ackeringae(Teijsm. & Binn.) Miq. – Indonesia, Philippines, Papuasia, Christmas Island
- Ochrosia acuminataTrimen ex Valeton – Sulawesi
- Ochrosia alyxioidesGuillaumin – Vanuatu
- Ochrosia apoensisElmer – Luzon, Mindanao
- Ochrosia balansae(Guillaumin) Baill. ex Guillaumin – New Caledonia
- Ochrosia basistaminaHendrian – Sulawesi
- Ochrosia bodenheimarumGuillaumin – Vallée de la Toutouta in New Caledonia
- Ochrosia borbonicaJ.F.Gmel. – Mauritius + Réunion; naturalized in Guangdong
- Ochrosia brevitubaBoiteau – New Caledonia
- Ochrosia brownii(Fosberg & Sachet) Lorence & Butaud – Nuku Hiva in Marquesas
- Ochrosia citrodoraK.Schum. & Lauterb. – New Guinea
- Ochrosia coccinea(Teijsm. & Binn.) Miq. – Maluku, Sulawesi, New Guinea, Solomon Islands; naturalized in Guangdong
- Ochrosia comptaK.Schum., Hōlei – Hawaii
- Ochrosia ellipticaLabill. – Lord Howe Island, Queensland, New Caledonia, Vanuatu, Nauru; naturalized in Guangdong + Taiwan
- Ochrosia fatuhivensisFosberg & Sachet – Fatu Hiva in Marquesas but extinct
- Ochrosia ficifolia(S.Moore) Markgr. – New Guinea
- Ochrosia glomerata(Blume) F.Muell. – Borneo, Sulawesi, Philippines, Maluku, New Guinea, Solomon Islands
- Ochrosia grandifloraBoit. – New Caledonia
- Ochrosia haleakalaeH.St.John, Hōlei – Maui + island of Hawaiʻi in Hawaiian Islands
- Ochrosia hexandraKoidz. – Kazan-retto
- Ochrosia inventorumL.Allorge – New Caledonia
- Ochrosia iwasakiana(Koidz.) Koidz. ex Masam.
- Ochrosia kauaiensisH.St.John, Hōlei – Kauaʻi in Hawaiian Islands
- †Ochrosia kilaueaensisH.St.John, Hōlei – island of Hawaiʻi in Hawaiian Islands, but extinct
- Ochrosia kilneriF.Muell. – Queensland
- Ochrosia lifuanaGuillaumin – Loyalty Islands + Isle of Pines in New Caledonia
- Ochrosia mariannensisA.DC. – Mariana Islands
- Ochrosia mianaBaill. ex Guillaumin – New Caledonia
- Ochrosia minima(Markgr.) Fosberg & Boiteau – Queensland, Papua New Guinea
- Ochrosia moorei(F.Muell.) F.Muell. ex Benth. – Queensland, New South Wales
- Ochrosia mulsantiiMontrouz. – New Caledonia
- Ochrosia nakaiana(Koidz.) Koidz. ex H.Hara – Ogasawara-shoto
- Ochrosia newellianaF.M.Bailey – Queensland
- Ochrosia novocaledonicaDäniker – New Caledonia
- Ochrosia oppositifolia(Lam.) K.Schum. – Seychelles, Chagos Islands, Sri Lanka, Maldive Islands, Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Thailand, Vietnam, W Malaysia, Indonesia, Papuasia, Samoa, Tonga, Tuvalu, Vanuatu, Wallis & Futuna, French Polynesia, Line Islands, Micronesia
- Ochrosia poweriF.M.Bailey – Queensland, New South Wales
- Ochrosia sciadophyllaMarkgr – Bismarck Archipelago, Solomon Islands
- Ochrosia sevenetiiBoiteau – New Guinea
- Ochrosia silvaticaDäniker – New Caledonia
- Ochrosia solomonensis(Merr. & L.M.Perry) Fosberg & Boiteau – Solomon Islands
- Ochrosia syncarpaMarkgr. – Bali, Lombok, Timor, Flores
- Ochrosia tahitensisLaness. ex Pichon – Tahiti
- Ochrosia tenimberensisMarkgr. – Tanimbar Islands
- Ochrosia nukuhivensisFosberg & Sachet = Rauvolfia nukuhivensis(Fosberg & Sachet) Lorence & Butaud
- Ochrosia sandwicensisA.DC. = Rauvolfia sandwicensisA.DC.
- Ochrosia tuberculata(Vahl) Pichon = Rauvolfia sandwicensisA.DC.
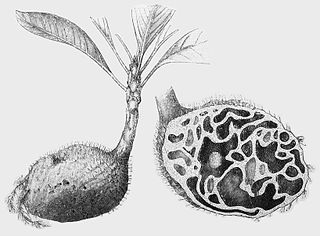
Hydnophytum is a genus of epiphytic myrmecophytes native to Southeast Asia, the Pacific region and also extending into Queensland in northern Australia. The name is derived from the Ancient Greek hydnon "tuber", and phyton "plant", after their appearance with their swollen succulent stems. The species grow in tree branches and on trunks. Like the related genus Myrmecodia, they are known as antplants or ant-house plants. The type species is Hydnophytum formicarum from the Philippines. The genus contains 55 species, of which 44 are found in and around the island of New Guinea. Many are poorly known, with 11 known only from the holotype.

Sarcolobus is a plant genus in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1810. It is native to Southeast Asia, New Guinea, Australia, and certain islands of the Western Pacific.
- Sarcolobus brachystephanus(Schltr.) P.I.Forst. - New Guinea
- Sarcolobus hullsii(F.Muell. ex Benth.) P.I.Forst. - Australia
- Sarcolobus kaniensis(Schltr.) P.I.Forst. - New Guinea
- Sarcolobus secamonoides(Schltr.) P.I.Forst. - New Guinea
- Sarcolobus spanogheiMiq. - Java
- Sarcolobus sulphureus(Volkens) Schltr. - Caroline Islands in Micronesia
Airosperma is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It was described by Karl Moritz Schumann and Carl Adolf Georg Lauterbach in 1900. It contains 6 accepted species, all endemic either to New Guinea or to Fiji.
Amaracarpus is a genus of shrubs, treelets or trees in the family Rubiaceae. It was described by Carl Ludwig Blume in 1826. Most of the species are endemic to New Guinea but a few have wider ranges in Southeast Asia from Myanmar (Burma) and the Andaman Islands across Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia, the Philippines, Melanesia, Christmas Island, Queensland and Vanuatu. One species also occurs in the Seychelles. Several species were published years ago but are today not represented by any type specimens or other known existing material.
Badusa is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It was described by Asa Gray in 1860. The genus is native to the Philippines (Palawan), New Guinea, and some islands of the West Pacific.

Rauvolfioideae is a subfamily of the flowering plant family Apocynaceae. Many species are woody lianas, others are shrubs or perennial herbs.
Ochrosia glomerata is a species of tree in the family Apocynaceae.

Phrynium is a plant genus native to China, India, Southeast Asia, New Guinea and Melanesia. It was described as a genus in 1797.
Dolicholobium is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. The genus is found from central Malesia to the southwestern Pacific.

Hornstedtia is a genus of plants in the Zingiberaceae. It is native to Southeast Asia, the Himalayas, southern China, New Guinea, Melanesia and Queensland.
Pleuranthodium is a genus of plants in the ginger family. Of the 23 known species, 21 are endemic to New Guinea, one to Queensland and one to the Bismarck Archipelago.
Papuechites is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1925. It contains only one known species, Papuechites aambe, native to New Guinea, the Bismarck Archipelago, and the Indonesian Province of Maluku.
Pentatropis is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1834. It is native to Africa and southern Asia.

Tapeinochilos is a group of plants in the Costaceae described as a genus in 1869. It is native to Queensland, Papuasia, and the Indonesian Province of Maluku. Centered in Papua New Guinea, only three of the approximately 16 species occur outside of the country.
Gynochthodes hollrungiana is a plant in the family Rubiaceae. Ii is found only in New Guinea.










